Abstract
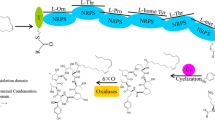
Echinocandin B (ECB) is the key precursor compound of the antifungal drug Anidulafungin. The effects of the five precursor amino acids on ECB biosynthesis were firstly investigated. It showed that although L-threonine was a main compound of the hexapeptide scaffold of ECB, exogenous addition of L-threonine had no significant effect on the increase of ECB fermentation titer. Meanwhile, the ECB fermentation titer with methyl oleate showed two times higher than that of the other carbon sources. Transcription level analysis of the key genes for ECB biosynthesis indicated that the gene an655543 related to L-threonine biosynthesis showed higher value during the fermentation process, therefore, the exogenous addition of L-threonine had no obvious affection. Furthermore, it indicated that the transcription level of gene ecdA might be the main restriction factor for the ECB biosynthesis. The study provided the research foundation for the modification of the ECB producing strains in the following work.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Capoor MR, Bal AM (2022) Echinocandins. In: Kenakin T (ed) Comprehensive pharmacology. Elsevier, Oxford
Perlin DS, Hope WW (2010) Echinocandins. In: Comarú Pasqualotto A (ed) Aspergillosis: from diagnosis to prevention. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht
Emri T, Majoros L, Toth V, Pocsi I (2013) Echinocandins: production and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(8):3267–3284
Bofinger P (2019) ECB: time is ripe for a real strategy. Intereconomics 54(6):322–323
Abel J, Rich R, Song J, Tracy J (2016) The measurement and behavior of uncertainty: evidence from the ECB survey of professional forecasters. J Appl Economet 31(3):533–550
Lan N, Yue Q, An ZQ, Bills GF (2020) Apc.LaeA and Apc.VeA of the velvet complex govern secondary metabolism and morphological development in the Echinocandin-producing fungus Aspergillus pachycristatus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 47(1):155–168
Huttel W (2021) Echinocandins: structural diversity, biosynthesis, and development of antimycotics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(1):55–66
Min T, Xiong L, Liang Y, Xu R, Fa C, Yang S, Hu H (2019) Disruption of stcA blocks sterigmatocystin biosynthesis and improves Echinocandin B production in Aspergillus delacroxii. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35(7):109
Birch M, Sibley G (2017) Antifungal chemistry review. In: Chackalamannil S, Rotella D, Ward SE (eds) Comprehensive medicinal chemistry III. Elsevier, Oxford
Mattay J, Houwaart S, Huttel W (2018) Cryptic production of trans-3-hydroxyproline in Echinocandin B biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(7):10
Kumar A, Jaiswal V, Kumar V, Dey A, Kumar A (2018) functional redundancy in Echinocandin B in-cluster transcription factor ecdB of Emericella rugulosa NRRL 11440. Biotechnol Rep 19:e00264
Taj-Aldeen SJ, Salah H, Perez WB, Almaslamani M, Motyl M, AbdulWahab A, Healey KR, Perlin DS (2018) Molecular analysis of resistance and detection of non-wild-type strains using etest epidemiological cutoff values for Amphotericin B and echinocandins for bloodstream candida infections from a tertiary hospital in qatar. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62(9):9
Toth V, Nagy CT, Pocsi I, Emri T (2012) The Echinocandin B producer fungus Aspergillus nidulans var. roseus ATCC 58397 does not possess innate resistance against its lipopeptide antimycotic. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(1):113–122
Liu ZB, Wang ZY, Sun JY, Ni L (2020) The dynamics of volatile compounds and their correlation with the microbial succession during the traditional solid-state fermentation of gutian hong qu glutinous rice wine. Food Microbiol 86:10
Zou SP, Zhong W, Xia CJ, Gu YN, Niu K, Zheng YG, Shen YC (2015) Mutagenesis breeding of high Echinocandin B producing strain and further titer improvement with culture medium optimization. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38(10):1845–1854
Hu ZC, Peng LY, Zheng YG (2016) Enhancement of Echinocandin B production by a UV- and microwave-induced mutant of Aspergillus nidulans with precursor- and biotin-supplying strategy. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179(7):1213–1226
Zou SP, Xiong Y, Niu K, Hu ZC, Zheng YG (2019) integrated strategy of temperature shift and mannitol feeding for enhanced production of Echinocandin B by Aspergillus nidulans CCTCC M2012300. 3 Biotech 9(4):8
Hu ZC, Li WJ, Zou SP, Niu K, Zheng YG (2020) Mutagenesis of Echinocandin B overproducing Aspergillus nidulans capable of using starch as main carbon source. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 50(8):745–752
Niu K, Wu XP, Hu XL, Zou SP, Hu ZC, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2020) Effects of methyl oleate and microparticle-enhanced cultivation on Echinocandin B fermentation titer. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43(11):2009–2015
Zou SP, Han X, Zhu HY, Sheng Q, Tang H, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2021) Functional expression of an Echinocandin B deacylase from actinoplanes utahensis in Escherichia coli. Int J Biol Macromol 187:850–857
Niu K, Wu XP, Fu Q, Lang KP, Zou SP, Hu ZC, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2021) Effects of lipids and surfactants on the fermentation production of Echinocandin B by Aspergillus nidulans. J Appl Microbiol 131(6):2849–2860
Yang J, Jiao RH, Yao LY, Han WB, Lu YH, Tan RX (2016) Control of fungal morphology for improved production of a novel antimicrobial alkaloid by marine-derived fungus Curvularia sp IFB-Z10 under submerged fermentation. Process Biochem 51(2):185–194
Zou SP, Liu M, Wang QL, Xiong Y, Niu K, Zheng YG, Shen YC (2015) Preparative separation of Echinocandin B from Aspergillus nidulans broth using macroporous resin adsorption chromatography. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 978:111–117
Son SH, Lee MK, Son YE, Park HS (2021) HbxB is a key regulator for stress response and beta-glucan biogenesis in Aspergillus nidulans. Microorganisms 9(1):144
Leal NA, Kim HJ, Hoshika S, Kim MJ, Carrigan MA, Benner SA (2015) Transcription, reverse transcription, and analysis of RNA containing artificial genetic components. ACS Synth Biol 4(4):407–413
Quan C, Wei F, Huang S, Wei K, Chen S, Miao J, Tang D (2022) RNA editing analysis of some chloroplast transcripts and its response to light and salt stress in mesona chinensis benth. J Plant Interact 17(1):779–788
Shivakumar MC, Manohar S, Ishwar B, Raghu P, Savitha J (2019) Deacylation of Echinocandin B by streptomyces species: a novel method for the production of Echinocandin B nucleus. 3 Biotech 9(11):6
Semighini CP, Marins M, Goldman MH, Goldman GH (2002) Quantitative analysis of the relative transcript levels of ABC transporter atr genes in Aspergillus nidulans by real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(3):1351–1357
Khanthapok P, Sang-Awut N, Chakhonkaen S, Pitngam K, Osadcenco A, Sukrong S, Muangprom A (2017) Identification of ethanol-inducible genes and isolation of the Myb-related protein-like promoter in Oryza Sativa L. J Plant Growth Regul 37(2):452–470
Mouslim J, David L, Petel G, Gendraud M (1993) Effect of exogeneous methyl oleate on the time-course of some parameters of Streptomyces-Hygroscopicus NRRL B-1865 culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39(4–5):585–588
Huttel W, Youssar L, Gruning BA, Gunther S, Hugentobler KG (2016) Echinocandin B biosynthesis: a biosynthetic cluster from Aspergillus nidulans NRRL 8112 and reassembly of the Subclusters Ecd and Hty from Aspergillus pachycristatus NRRL 11440 reveals a single coherent gene cluster. BMC Genom 17:8
Cacho RA, Jiang W, Chooi YH, Walsh CT, Tang Y (2012) Identification and characterization of the Echinocandin B biosynthetic gene cluster from Emericella rugulosa NRRL 11440. J Am Chem Soc 134(40):16781–16790
Panagiotou G, Kouskoumvekaki I, Jonsdottir SO, Olsson L (2007) Monitoring novel metabolic pathways using metabolomics and machine learning: induction of the phosphoketolase pathway in Aspergillus nidulans cultivations. Metabolomics 3(4):503–516
Lautru S, Challis GL (2004) Substrate recognition by nonribosomal peptide synthetase multi-enzymes. Microbiology-(UK) 150:1629–1636
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports of the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2022YFC2105400), Science and technology Project of Zhejiang Province (LGF22B060006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z-QL and Y-GZ initiated and supervised the project; KN contributed to manuscript editing; Y-XQ conducted the experiments and data analysis; H-WC, Y-XY and X-TL participated in some of the experiments; H-YZ participated in the revision of the text. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, K., Qi, YX., Cai, HW. et al. Investigation of the enhancement for Echinocandin B fermentation with methyl oleate from transcription level. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 46, 1045–1052 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02883-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02883-4