Abstract
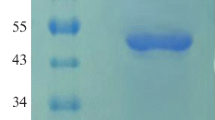
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is an oxidoreductase enzyme and oxidizes various inorganic and organic compounds. It has wide application areas such as immunological tests, probe-based test techniques, removal of phenolic pollutants from wastewater and organic synthesis. HRP is found in the root of the horseradish plant as a mixture of different isoenzymes, and it is very difficult to separate these enzymes from each other. In this regard, recombinant production is a very advantageous method in terms of producing the desired isoenzyme. This study was performed to produce HRP A2A isoenzyme extracellularly in Pichia pastoris and to purify this enzyme in a single step using a 3-amino-4-chloro benzohydrazide affinity column. First, codon-optimized HRP A2A gene was amplified and inserted into pPICZαC. So, obtained pPICZαC-HRPA2A was cloned in E. coli cells. Then, P. pastoris X-33 cells were transformed with linearized recombinant DNA and a yeast clone was cultivated for extracellular recombinant HRP A2A (rHRP A2A) enzyme production. Then, the purification of this enzyme was performed in a single step by affinity chromatography. The molecular mass of purified rHRP A2A enzyme was found to be about 40 kDa. According to characterization studies of the purified enzyme, the optimum pH and ionic strength for the rHRP A2A isoenzyme were determined to be 6.0 and 0.04 M, respectively, and o-dianisidine had the highest specificity with the lowest Km and Vmax values. Thus, this is an economical procedure to purify HRP A2A isoenzyme without time-consuming and laborious isolation from an isoenzyme mixture.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Huystee RBV (1987) Some molecular aspects of plant peroxidase biosynthetic studies. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 38:205–219. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.38.060187.001225
Singh N, Gade WN, Singh J (2002) Purification of turnip peroxidase and its kinetic proPERTIES. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 32:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1081/PB-120013160
Zámocký M, Obinger C (2010) Molecular phylogeny of heme peroxidases. Biocatalysis based on heme peroxidases. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 7–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12627-7_2
Khurshid S (2012) Production and purification of horseradish peroxidase in Pakistan. Int J Phys Sci. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJPS11.724
Gholami-Borujeni F, Mahvi AH, Naseri S et al (2011) Application of immobilized horseradish peroxidase for removal and detoxification of azo dye from aqueous solution. Res J Chem Environ 15:217–222
Krieg R, Halbhuber KJ (2003) Recent advances in catalytic peroxidase histochemistry. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 49:547–563
Litescu SC, Eremia S, Radu GL (2010) Biosensors for the determination of phenolic metabolites. Adv Exp Med Biol 698:234–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-7347-4_17
Marquette CA, Blum LJ (2009) Chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassays: a review of bioanalytical applications. Bioanalysis 1:1259–1269. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.09.69
Ryan BJ, Carolan N, Ó’Fágáin C (2006) Horseradish and soybean peroxidases: comparable tools for alternative niches? Trends Biotechnol 24:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIBTECH.2006.06.007
Vasileva N, Godjevargova T, Ivanova D, Gabrovska K (2009) Application of immobilized horseradish peroxidase onto modified acrylonitrile copolymer membrane in removing of phenol from water. Int J Biol Macromol 44:190–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2008.12.002
Yang H (2012) Enzyme-based ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensors. Curr Opin Chem Biol 16:422–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CBPA.2012.03.015
Passardi F, Cosio C, Penel C, Dunand C (2005) Peroxidases have more functions than a Swiss army knife. Plant Cell Rep 24:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-005-0972-6
Jermyn MA, Thomas R (1954) Multiple components in horse-radish peroxidase. Biochem J 56:631–639. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0560631
Krainer FW, Glieder A (2015) An updated view on horseradish peroxidases: recombinant production and biotechnological applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1611–1625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6346-7
Hartmann C, Ortiz de Montellano PR (1992) Baculovirus expression and characterization of catalytically active horseradish peroxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(92)90641-9
Morawski B, Lin Z, Cirino P et al (2000) Functional expression of horseradish peroxidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris. Protein Eng 13:377–384. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/13.5.377
Zalai D, Dietzsch C, Herwig C, Spadiut O (2012) A dynamic fed batch strategy for a Pichia pastoris mixed feed system to increase process understanding. Biotechnol Prog. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.1551
Cos O, Ramón R, Montesinos JL, Valero F (2006) Operational strategies, monitoring and control of heterologous protein production in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris under different promoters: a review. Microb Cell Fact 5:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-5-17
Tenzer S, Docter D, Kuharev J et al (2013) Rapid formation of plasma protein corona critically affects nanoparticle pathophysiology. Nat Nanotechnol 8:772–781. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2013.181
Bensadoun A, Weinstein D (1976) Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem 70:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2697(76)80064-4
Greco O, Folkes LK, Wardman P et al (2000) Development of a novel enzyme/prodrug combination for gene therapy of cancer: Horseradish peroxidase/indole-3-acetic acid. Cancer Gene Ther. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700258
Connell-Crowley L, Nguyen T, Bach J et al (2012) ARTICLE cation exchange chromatography provides effective retrovirus clearance for antibody purification processes. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23300
Holland T, Sack M, Rademacher T et al (2010) Optimal nitrogen supply as a key to increased and sustained production of a monoclonal full-size antibody in BY-2 suspension culture. Biotechnol Bioeng. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22800
Krainer FW, Pletzenauer R, Rossetti L et al (2014) Purification and basic biochemical characterization of 19 recombinant plant peroxidase isoenzymes produced in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 95:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2013.12.003
Porath J, Carlsson J, Olsson I, Belfrage G (1975) Metal chelate affinity chromatography, a new approach to protein fractionation. Nature 258:598–599. https://doi.org/10.1038/258598a0
Gaberc-Porekar V, Menart V (2001) Perspectives of immobilized-metal affinity chromatography. J Biochem Biophys Methods 49:335–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-022X(01)00207-X
Keha EE, Küfrevioğlu Öİ (2009) Biyokimya. Aktif Yayınevi
Kettle AJ, Gedye CA, Winterbourn CC (1997) Mechanism of inactivation of myeloperoxidase by 4-aminobenzoic acid hydrazide. Biochem J. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3210503
Kalin R, Atasever A, Özdemir H (2014) Single-step purification of peroxidase by 4-aminobenzohydrazide from Turkish blackradish and Turnip roots. Food Chem 150:335–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2013.10.125
Oztekin A, Almaz Z, Gerni S et al (2019) Purification of peroxidase enzyme from radish species in fast and high yield with affinity chromatography technique. J Chromatogr B 1114–1115:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCHROMB.2019.03.035
Almaz Z, Oztekin A, Abul N et al (2021) A new approach for affinity-based purification of horseradish peroxidase. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1899
Unver Y, Yildiz M, Kilic D et al (2018) Efficient expression of recombinant human telomerase inhibitor 1 (hPinX1) in Pichia pastoris. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 48:535–540. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2018.1466160
Yamada H, Kojo M, Nakahara T et al (2012) Development of a fluorescent chelating ligand for scandium ion having a Schiff base moiety. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 90:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.01.014
Whitney PL (1974) Affinity chromatography of carbonic anhydrase. Anal Biochem 57:467–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(74)90102-X
Bradford M (1976) A Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Lineweaver H, Burk D (1934) The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J Am Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01318a036
Macauley-Patrick S, Fazenda ML, McNeil B, Harvey LM (2005) Heterologous protein production using thePichia pastoris expression system. Yeast 22:249–270. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1208
Mchunu NP, Singh S, Permaul K (2009) Expression of an alkalo-tolerant fungal xylanase enhanced by directed evolution in Pichia pastoris and Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 141:26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.02.021
Wang M, Jiang S, Liu X, Wang Y (2013) Expression, purification, and immunogenic characterization of Epstein-Barr virus recombinant EBNA1 protein in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:6251–6262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4967-x
Yang J, Liu L (2010) Codon optimization through a two-step gene synthesis leads to a high-level expression of Aspergillus niger lip2 gene in Pichia pastoris. J Mol Catal B Enzym 63:164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2010.01.011
De Schutter K, Lin YC, Tiels P et al (2009) Genome sequence of the recombinant protein production host Pichia pastoris. Nat Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1544
Jia H, Fan G, Yan Q et al (2012) High-level expression of a hyperthermostable Thermotoga maritima xylanase in Pichia pastoris by codon optimization. J Mol Catal B Enzym 78:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2012.02.009
Zhao S, Huang J, Zhang C et al (2010) High-level expression of an aspergillus niger endo-β-1,4-glucanase in Pichia pastoris through gene codon optimization and synthesis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:467–473. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.0908.08028
Unver Y, Sensoy Gun B, Acar M, Yildiz S (2021) Heterologous expression of azurin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 51:723–730. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2020.1855444
Dewi KS, Chairunnisa S, Swasthikawati S et al (2022) Production of codon-optimized Human papillomavirus type 52 L1 virus-like particles in Pichia pastoris BG10 expression system. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2022.2048262
Vogl T, Gebbie L, Palfreyman RW, Speight R (2018) Effect of plasmid design and type of integration event on recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02712-17
Sunga AJ, Tolstorukov I, Cregg JM (2008) Posttransformational vector amplification in the yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Yeast Res 8:870–876. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1567-1364.2008.00410.x
Zheng J, Guo N, Lin F et al (2014) Screening of multi-copy mannanase recombinants of Pichia pastoris based on colony size. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:579–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1479-x
Lu Y, Fang C, Wang Q et al (2016) High-level expression of improved thermo-stable alkaline xylanase variant in Pichia pastoris through codon optimization, multiple gene insertion and high-density fermentation. Sci Rep 6:37869. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37869
Vlamis-Gardikas A, Smith AT, Clements JM, Burke JF (1992) Expression of active horseradish peroxidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Soc Trans 20:111S-111S. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst020111s
Balamurugan V, Reddy GR, Suryanarayana VVS (2007) Pichia pastoris: a notable heterologous expression system for the production of foreign proteins - Vaccines. Indian J Biotechnol 6:175–186
Kaewthai N, Harvey AJ, Hrmova M et al (2010) Heterologous expression of diverse barley XTH genes in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Plant Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.27.251
Yang S, Kuang Y, Li H et al (2013) Enhanced production of recombinant secretory proteins in Pichia pastoris by optimizing Kex2 P1’ site. PLoS ONE 8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075347
Mattanovich D, Graf A, Stadlmann J et al (2009) Genome, secretome and glucose transport highlight unique features of the protein production host Pichia pastoris. Microb Cell Fact 8:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-8-29
Huang C-J, Damasceno LM, Anderson KA et al (2011) A proteomic analysis of the Pichia pastoris secretome in methanol-induced cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:235–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3118-5
Eom GT, Lee SH, Song BK et al (2013) High-level extracellular production and characterization of Candida antarctica lipase B in Pichia pastoris. J Biosci Bioeng 116:165–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.02.016
Ünver Y, Kurbanoğlu EB, Erdoğan O (2015) Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant human paraoxonase 1 (rhPON1) in Pichia pastoris. Turkish J Biol 39:649–655. https://doi.org/10.3906/biy-1501-43
Maity N, Jaswal AS, Gautam A et al (2022) High level production of stable human serum albumin in Pichia pastoris and characterization of the recombinant product. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 45:409–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02670-z
Vinay DS, Ryan EP, Pawelec G et al (2015) Immune evasion in cancer: Mechanistic basis and therapeutic strategies. Semin Cancer Biol 35:S185–S198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.004
He D, Luo W, Wang Z et al (2015) Combined use of GAP and AOX1 promoters and optimization of culture conditions to enhance expression of Rhizomucor miehei lipase. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:1175–1182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1633-6
Thorpe ED, D’Anjou MC, Daugulis AJ (1999) Sorbitol as a non-repressing carbon source for fed-batch fermentation of recombinant Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Lett 21:669–672. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005585407601
Xie J, Zhou Q, Du P et al (2005) Use of different carbon sources in cultivation of recombinant Pichia pastoris for angiostatin production. Enzyme Microb Technol 36:210–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2004.06.010
Jungo C, Schenk J, Pasquier M et al (2007) A quantitative analysis of the benefits of mixed feeds of sorbitol and methanol for the production of recombinant avidin with Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 131:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.05.019
Zhu T, Hang H, Chu J et al (2013) Transcriptional investigation of the effect of mixed feeding to identify the main cellular stresses on recombinant Pichia pastoris. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1225-7
van den Hazel HB, Kielland-Brandt MC, Winther JR (1996) Review: Biosynthesis and function of yeast vacuolar proteases. Yeast 12:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(199601)12:1%3c1::AID-YEA902%3e3.0.CO;2-N
Zhou XS, Zhang YX (2002) Decrease of proteolytic degradation of recombinant hirudin produced by Pichia pastoris by controlling the specific growth rate. Biotechnol Lett 24:1449–1453. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019831406141
Grinna LS, Tschopp JF (1989) Size distribution and general structural features of N-linked oligosaccharides from the methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Yeast 5:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.320050206
Bretthauer RK, Castellino FJ (1999) Glycosylation of Pichia pastoris-derived proteins. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 30:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1470-8744.1999.tb00770.x
Zhu X, Wu S, Letchworth GJ (1997) Yeast-secreted bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein D has authentic conformational structure and immunogenicity. Vaccine 15:679–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-410X(96)00234-4
Hu X, Yuan X, He N et al (2019) Expression of Bacillus licheniformis α-amylase in Pichia pastoris without antibiotics-resistant gene and effects of glycosylation on the enzymic thermostability. 3 Biotech 9:427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1943-x
Greco O, Folkes LK, Wardman P et al (2000) Development of a novel enzyme/prodrug combination for gene therapy of cancer: horseradish peroxidase/indole-3-acetic acid. Cancer Gene Ther 7:1414–1420. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700258
Zhao W, Zheng J, Zhou H (2011) A thermotolerant and cold-active mannan endo-1,4-β-mannosidase from Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88: Constitutive overexpression and high-density fermentation in Pichia pastoris. Bioresour Technol 102:7538–7547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.070
Gurramkonda C, Adnan A, Gäbel T et al (2009) Simple high-cell density fed-batch technique for high-level recombinant protein production with Pichia pastoris: application to intracellular production of Hepatitis B surface antigen. Microb Cell Fact 8:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-8-13
Spadiut O, Rossetti L, Dietzsch C, Herwig C (2012) Purification of a recombinant plant peroxidase produced in Pichia pastoris by a simple 2-step strategy. Protein Expr Purif 86:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2012.09.008
Bonifert G, Folkes L, Gmeiner C et al (2016) Recombinant horseradish peroxidase variants for targeted cancer treatment. Cancer Med 5:1194–1203. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.668
Acknowledgements
The authors kindly acknowledge East Anatolia High Technology Application and Research Center (DAYTAM, Atatürk University, Erzurum, Turkey) for the equipment support. M.A. and E.D.T also thank The Council of Higher Education (CoHE, 100/2000) PhD Scholarship Program, Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Acar, M., Abul, N., Yildiz, S. et al. Affinity-based and in a single step purification of recombinant horseradish peroxidase A2A isoenzyme produced by Pichia pastoris. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 46, 523–534 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-022-02837-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-022-02837-2