Abstract
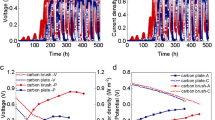
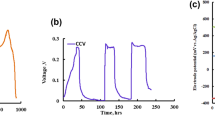
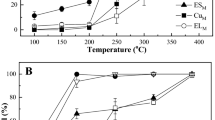
The formation of electroactive biofilm from activated sludge on electrode surface is a key step to construct a bio-electrochemical system, yet it is greatly limited by the poor affinity between the bacteria and the electrode interface. Herein, we report a new method to promote the formation of electroactive biofilm by regulating the extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) content in activated sludge with lysozyme. The investigation of the effect of lysozyme treatment on the content of extracellular polymers and the biofilm formation of electroactive bacteria suggests that lysozyme can improve the permeability of the positive bacterial cell membrane and thus increase the EPS content in the activated sludge. The characterizations of electrochemical activity, surface morphology and community structure of the anode biofilm indicate that increasing EPS content promotes the adhesion of the mixed bacteria in the activated sludge on the electrode and results in denser biofilms with better conductivities. The microbial fuel cell (MFC) inoculated with the sludge of high EPS content exhibits the power density up to 2.195 W/m2, much higher than that inoculated with the untreated sludge (1.545 W/m2). The strategy of adjusting EPS content in activated sludge with a biological enzyme can effectively enhance the ability of the bacterial community to form biofilms and exhibits great application potentials in the construction of high efficiency bio-electrochemical systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ji J, Gao T, Salama ES, El-Dalatony MM, Peng L, Gong Y, Liu P, Li X (2021) Using aspergillus niger whole-cell biocatalyst mycelial aerobic granular sludge to treat pharmaceutical wastewater containing β-lactam antibiotics. Chem Eng J 412:128665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128665
Izadi P, Izadi P, Eldyasti A (2021) Holistic insights into extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) in anammosx bacterial matrix and the potential sustainable biopolymer recovery: a review. Chemosphere 274:129703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129703
Li Z, Zhang P, Qiu Y, Zhang Z, Wang X, Yu Y, Feng Y (2021) Biosynthetic FeS/BC hybrid particles enhanced the electroactive bacteria enrichment in microbial electrochemical systems. Sci Total Env 762:143142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143142
Modestra JA, Reddy C, Krishna K, Min B, Mohan SV (2020) Regulated surface potential impacts bioelectrogenic activity, interfacial electron transfer and microbial dynamics in microbial fuel cell. Renew Energy 149:424–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.12.018
Taskan B, Taskan E (2021) Inhibition of AHL-mediated quorum sensing to control biofilm thickness in microbial fuel cell by using Rhodococcus sp. BH4. Chemosphere 285:131538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131538
Cecconet D, Sabba F, Devecseri M, Callegari A, Capodaglio AG (2020) In situ groundwater remediation with bioelectrochemical systems: a critical review and future perspectives. Env Int 137:105550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105550
Logan BE, Rossi R, Ragab A, Saikaly PE (2019) Electroactive microorganisms in bioelectrochemical systems. Nat Rev Microb 17(5):307–319. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-019-0173-x
Greenman J, Gajda I, You J, Mendis BA, Obata O, Pasternak G, Ieropoulos I (2021) Microbial fuel cells and their electrified biofilms. Biofilm 3:100057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioflm.2021.100057
Zhuang Z, Yang G, Zhuang L (2022) Exopolysaccharides matrix affects the process of extracellular electron transfer in electroactive biofilm. Sci Total Env 806:150713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150713
Wu D, Sun F, Chua F, Zhou Y (2020) Enhanced power generation in microbial fuel cell by an agonist of electroactive biofilm–sulfamethoxazole. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123238
Melo A, Costa J, Quintelas C, Ferreira EC, Mesquita DP (2021) Effect of ibuprofen on extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production and composition, and assessment of microbial structure by quantitative image analysis. J Env Manage 293:112852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112852
Chen S, Fang Y, Jing X, Luo H, Chen J, Zhou S (2018) Enhanced electrosynthesis performance of Moorella thermoautotrophica by improving cell permeability. Bioelectrochemistry 121:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2018.02.003
Zhang P, Zhou X, Qi R, Gai P, Liu L, Lv F, Wang S (2019) Conductive polymer–exoelectrogen hybrid bioelectrode with improved biofilm formation and extracellular electron transport. Adv—Electronic Mater 5(8):1900320. https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.201900320
Gomaa OM, Selim N, Fathy R, Maghrawy HH, Gamal M, Kareem HA, Kyazze G, Keshavarz T (2021) Characterization of a biosurfactant producing electroactive Bacillus sp. for enhanced microbial fuel cell dye decolourisation. Enzyme Microb Technol 147:109767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2021.109767
Zhou X, Zhai S, Zhao Y, Liu D, Wang Q, Ji M (2021) Rapid recovery of inhibited denitrification with cascade Cr(VI) exposure by bio-accelerant: characterization of chromium distributions, EPS compositions and denitrifying communities. Hazard Mater 411:125087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125087
Wang S, Zhi L, Shan W, Lu H, Xu Q, Li J (2020) Correlation of extracellular polymeric substances and microbial community structure in denitrification biofilm exposed to adverse conditions. Microb Biotechnol 13(6):1889–1903. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13633
Ray G, Noori M, Ghangrekar M (2017) Novel application of peptaibiotics derived from Trichoderma sp. for methanogenic suppression and enhanced power generation in microbial fuel cells. RSC Adv 7:10707–10717. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA27763B
Lin ZQ, Shao W, Xu J, Sheng GP (2019) Accurately quantifying the reductive capacity of microbial extracellular polymeric substance by mediated electrochemical oxidation method. Sci Total Env 673:541–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.130
Shen WR, Zhao X, Wang X, Yang S, Jia X, Yu X, Yang J, Yang Q, Zhao H (2020) Improving the power generation performances of gram-positive electricigens by regulating the peptidoglycan layer with lysozyme. Env Res 185:109463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109463
Yang QZ, Zhou B, Liu JW, Shen WR, Jia XD, He XJ, Zhao HZ (2020) Nitrate removal from water via self-flocculation of genetically engineered bacteria. Chem Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2021.116750
Zhang L, Zhu X, Li J, Liao Q, Liao Q, Ye D (2011) Biofilm formation and electricity generation of a microbial fuel cell started up under different external resistances. J Power Sources 196(15):6029–6035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.04.013
Zhang Q, Zhang W, He Q, Li M, Li Y, Huang W (2020) Effects of dissolved oxygen concentrations on a bioaugmented sequencing batch rector treating aniline-laden wastewater: reactor performance, microbial dynamics and functional genes. Bioresour Technol 313:123598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123598
Lian Z, Yang Z, Song W, Sun M, Gan Y, Bai X (2022) Effects of different exogenous cadmium compounds on the chemical composition and adsorption properties of two gram-negative bacterial EPS. Sci Total Env 806:150511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150511
Wang D, Pan J, Met Xu, Liu B, Hu J, Hu S, Hou H (2021) Surface modification of shewanella oneidensis MR-1 with polypyrrole-dopamine coating for improvement of power generation in microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229220
Lin F, Zhu X, Li J, Yu P, Luo Y, Liu M (2019) Effect of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) conditioned by combined lysozyme and cationic polyacrylamide on the dewatering performance of activated sludge. Chemosphere 235:679–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.220
Lin F, Li J, Liu M, Yu P, Zhang Z, Zhu X (2020) New insights into the effect of extracellular polymeric substance on the sludge dewaterability based on interaction energy and viscoelastic acoustic response analysis. Chemosphere 261:127929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127929
He JG, Xin XD, Qiu W, Zhang J, Wen ZD, Tang J (2014) Performance of the lysozyme for promoting the waste activated sludge biodegradability. Bioresour Technol 170:108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.07.095
Jia F, Yang Q, Liu X, Li X, Li B, Zhang L, Peng Y (2017) Stratification of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) for aggregated anammox microorganisms. Env Sci Technol 51:3260–3268. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05761
Stockl M, Teubner NC, Holtmann D, Mangold KM, Sand W (2019) Extracellular polymeric substances from geobacter sulfurreducens biofilms in microbial fuel cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:8961–8968. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b14340
Yang G, Lin J, Zeng EY, Zhuang L (2019) Extraction and characterization of stratified extracellular polymeric substances in geobacter biofilms. Bioresour Technol 276:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.12.100
Xiao Y, Zhao F (2017) Electrochemical roles of extracellular polymeric substances in biofilms. Curr Opin Electrochem 4:206–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2017.09.016
Liu Y, Climent V, Berná A, Feliu JM (2011) Effect of temperature on the catalytic ability of electrochemically active biofilm as anode catalyst in microbial fuel cells. Electroanalysis 23:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201000499
Molognoni D, Puig S, Balaguer MD, Capodaglio AG, Callegari A, Colprim J (2016) Multiparametric control for enhanced biofilm selection in microbial fuel cells. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91(6):1720–1727. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4760
Modestra JA, Mohan SV (2014) Bio-electrocatalyzed electron efflux in gram positive and gram negative bacteria: an insight into disparity in electron transfer kinetics. RSC Adv 4(64):34045–34055. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra03489a
Sathishkumar K, Li Y, Sanganyado E (2020) Electrochemical behavior of biochar and its effects on microbial nitrate reduction: role of extracellular polymeric substances in extracellular electron transfer. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125077
Tsuneda S, Aikawa H, Hayashi H, Yuasa A, Hirata A (2003) Extracellular polymeric substances responsible for bacterial adhesion onto solid surface. FEMS Microb Lett 223:287–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00399-9
Li Y, Xin M, Xie D, Fan S, Ma J, Liu K, Yu F (2021) Variation in extracellular polymeric substances from Enterobacter sp. and their Pb(2+) adsorption behaviors. ACS Omega 6:9617–9628. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00185
Arabski M, Konieczna I, Tusinska E, Wasik S, Relich I, Zajac K, Zbigniew Z, Kaca W (2015) The use of lysozyme modified with fluorescein for the detection of gram-positive bacteria. Microb Res 170:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2014.05.004
Luo J, Li M, Zhou M, Hu Y (2015) Characterization of a novel strain phylogenetically related to Kocuria rhizophila and its chemical modification to improve performance of microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 69:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.02.025
Gustave W, Yuan ZF, Sekar R, Toppin V, Liu JY, Ren YX, Zhang J, Chen Z (2019) Relic DNA does not obscure the microbial community of paddy soil microbial fuel cells. Res Microb 170(2):97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2018.11.002
Alatraktchi FAa, Zhang Y, Angelidaki I (2014) Nanomodification of the electrodes in microbial fuel cell: Impact of nanoparticle density on electricity production and microbial community. Appl Energy 116:216–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.11.058
Chen G-W, Choi S-J, Cha J-H, Lee TH, Kim CW (2010) Microbial community dynamics and electron transfer of a biocathode in microbial fuel cells. Korean J Chem Eng 27:1513–1520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0231-6
Jiang Q, Xing D, Sun R, Zhang L, Feng Y, Ren N (2016) Anode biofilm communities and the performance of microbial fuel cells with different reactor configurations. RSC Adv 6:85149–85155. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA08790F
Kim GT, Webster G, Wimpenny JW, Kim BH, Kim HJ, Weightman AJ (2006) Bacterial community structure, compartmentalization and activity in a microbial fuel cell. J Appl Microb 101:698–710. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.02923.x
Park HS, Kim BH, Kim HS, Kim HJ, Kim GT, Kim M, Chang IS, Park YK, Chang HI (2001) A novel electrochemically active and Fe(III)-reducing bacterium phylogenetically related to clostridium butyricum Isolated from a microbial fuel cell. Anaerobe 7:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1006/anae.2001.0399
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Local College Student (No. S202010431030 and No. S202010431046), Foundation of Qilu University of Technology of Cultivating Subject for Biology and Biochemistry (No. 202017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XJ Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-Original draft preparation. XL Visualization, Writing-Original draft preparation. KZ: Software, Data curation, Writing-Original draft preparation. XZ and ZY Investigation, Validation. XY and YH Supervision, Methodology. QY Methodology, Writing-Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent for participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, X., Liu, X., Zhu, K. et al. Lysozyme regulates the extracellular polymer of activated sludge and promotes the formation of electroactive biofilm. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 45, 1065–1074 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-022-02727-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-022-02727-7