Abstract
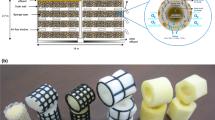
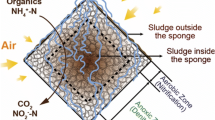
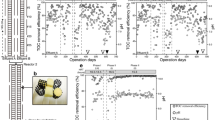
The down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor is advantageous for sewage treatment since it produces an effluent quality that complies with the standards for reuse and there is little excess sludge. A full-scale DHS module was efficiently employed for the treatment of domestic sewage (200 m3 day−1) flowing from a primary sedimentation basin (PSB), which was used to reduce the suspended solids loading rate and enhance the oxidation of organics by heterotrophs. The combined PSB-DHS was successfully operated at a total hydraulic retention time of 3.4 h (2.4 h for PSB and 1.0 h for DHS) for the relatively long period of 600 days at sewage temperatures of 10 °C to 32 °C. The PSB-DHS consistently produced an effluent quality with minimum values of chemical oxygen demand, biochemical oxygen demand, and suspended solids of 59 ± 15, 12 ± 3.0, and 15 ± 7 mg L−1, respectively. The proposed system performed exceptionally well at removing organics and particulate matter over a short hydraulic retention time.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tawfik A, El-Gohary F, Ohashi A, Harada H (2008) Optimization of the performance of an integrated anaerobic-aerobic system for domestic wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol 58(1):185–194. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2008.320
Tyagi VK, Ali M, Tawfik A, Maharjan N, Kazmi AA, Okubo T, Harada H (2021) Future perspectives of energy saving down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) technology for wastewater valorization—a review. Rev Environm Sci Bio/Technol 20:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-021-09573-1
Elnmer A, Khadr M, Kanae S, Tawfik A (2019) Mapping daily and seasonally evapotranspiration using remote sensing techniques over the Nile delta. Agric Water Manag 213:682–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.11.009
Tawfik A, Ohashi A, Harada H (2006) Sewage treatment in a combined up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB)-down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) system. Biochem Eng J 29(3):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2005.11.018
Okubo T, Iguchi A, Tanaka S, Uchida S, Tagawa T, Oshiki M, Araki N, Tawfik A, Takahashi M, Kubota K, Harada H, Uemura S (2019) Health impact of agricultural drainage water for farmers in the west Nile delta. Int J Environm Res 13(2):319–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00176-x
Drechsel P, Scott CA, Raschild L, Redwood M, Bahri A (2010) Wastewater irrigation and health -Assessing and mitigating risk in low income countries-. Earthscan, London
Tandukar M, Uemura S, Machdar I, Ohashi A, Harada H (2005) A low-cost municipal sewage treatment system with a combination of UASB and the “fourth-generation” downflow hanging sponge reactors. Water Sci Technol 52(1–2):323–329. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2005.0534
Beas REY, Kujawa-Roeleveld K, Zeeman G, Van Lier JB (2015) A downflow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor for faecal coliform removal from an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) effluent. Water Sci Technol 72(11):2034–2044. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.427
Uemura S, Harada H (2010) Application of UASB technology for sewage treatment with a novel post treatment process. In: Environmental Anaerobic Technology, Applications and New Developments (Fang HPH), (Ed) Imperial College Press, Singapore
Tanikawa D, Syutsubo K, Hatamoto M, Fukuda M, Takahashi M, Choeisai PK, Yamaguchi T (2016) Treatment of natural rubber processing wastewater using a combination system of a two-stage up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket and down-flow hanging sponge system. Water Sci Technol 73(8):1777–1784. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.019
Miyaoka Y, Yoochatchaval W, Sumino H, Banjongproo P, Yamaguchi T, Onodera T, Okadera T, Syutsubo K (2017) Evaluation of the process performance of a down-flow hanging sponge reactor for direct treatment of domestic wastewater in Bangkok, Thailand. J Environm Sci Health Part A 52(10):956–970. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2017.1324708
Okubo T, Onodera T, Uemura S, Yamaguchi T, Ohashi A, Harada H (2015) On-site evaluation of the performance of a full-scale down-flow hanging sponge reactor as a post-treatment process of an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor for treating sewage in India. Bioresource Technol 194:156–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.015
Okubo T, Kubota K, Yamaguchi T, Uemura S, Harada H (2016) Development of a new non-aeration based sewage treatment technology: Performance evaluation of a full-scale down-flow hanging sponge reactor employing third-generation sponge carriers. Water Res 102:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.035
Nomoto N, Hatamoto M, Ali M, Jayaswal K, Iguchi A, Okubo T, Takahashi M, Kubota K, Tagawa T, Uemura S, Yamaguchi T, Harada H (2018) Characteristics of sludge properties for sewage treatment in a practical-scale down-flow hanging sponge reactor: Oxygen consumption and removal of organic matter, ammonium, and sulfur. Water Sci Technol 77(3):608–616. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.557
Ismail S, Tawfik A (2016) Performance of passive aerated immobilized biomass reactor coupled with Fenton process for treatment of landfill leachate. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 111:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.04.010
United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and Government of Egypt (2010) Integrated Water Resource Management II, Feasibility of wastewater reuse, June 2010, USAID and Government of Egypt
Mahmoud M, Tawfik A, Goharya FL (2011) Use of down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor as a promising post-treatment system for municipal wastewater. Chem Eng J 168:535–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.019
Hatamoto M, Okubo T, Kubota K, Yamaguchi T (2018) Characterization of downflow hanging sponge reactors with regard to structure, process function, and microbial community compositions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:10345–10352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9406-6
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Metcalf L, Eddy HP (2003) Wastewater engineering: Treatment and reuse, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Nomoto N, Hatamoto M, Hirakata Y, Ali M, Jayaswal K, Iguchi A, Okubo T, Takahashi M, Kubota K, Tagawa T, Uemura S, Yamaguchi T, Harada H (2018) Defining microbial community composition and seasonal variation in a sewage treatment plant in India using a down-flow hanging sponge reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:4381–4392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8864-1
Kubota K, Hayashi M, Matsunaga K, Iguchi A, Ohashi A, Li Y, Yamaguchi T, Harada H (2014) Microbial community composition of a down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor combined with an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor for the treatment of municipal sewage. Biores Technol 151:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.058
Fleifle A, Saavedra O, Yoshimura C, Elzeir M, Tawfik A (2014) Optimization of integrated water quality management for agricultural efficiency and environmental conservation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(13):8095–8111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2712-3
Adlin N, Matsuura N, Ohta Y, Hirakata Y, Maki S, Hatamoto M, Yamaguchi T (2018) A nitrogen removal system to limit water exchange for recirculating freshwater aquarium using DHS–USB reactor. Environ Technol 39(12):1577–1585. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1333530
Cao LTT, Kodera H, Abe K, Imachi H, Aoi Y, Kindaichi T, Ozaki N, Ohashi A (2015) Biological oxidation of Mn(II) coupled with nitrification for removal and recovery of minor metals by downflow hanging sponge reactor. Water Res 68:545–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.002
Choeisai P, Jitkam N, Silapanoraset K, Yubolsai C, Yoochatchaval W, Yamaguchi T, Onodera T, Syutsubo K (2014) Sugarcane molasses-based bio-ethanol wastewater treatment by two-phase multi-staged up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) combination with up-flow UASB and down-flow hanging sponge. Water Sci Technol 69(6):1174–1180. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.794
Tandukar M, Machdar I, Uemura S, Ohashi A, Harada H (2006) Potential of a combination of UASB and DHS reactor as a novel sewage treatment system for developing countries: long-term evaluation. J Environ Eng 132(2):166–172. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2006)132:2(166)
Mahmoud M, Tawfik A, El-Gohary F (2010) Simultaneous organic and nutrient removal in a naturally ventilated biotower treating presettled municipal wastewater. J Environ Eng 136(3):301–307. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000148
Onodera T, Tandukar M, Sugiyana D, Uemura S, Ohashi A, Harada H (2014) Development of a sixth-generation down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor using rigid sponge media for post-treatment of UASB treating municipal sewage. Biores Technol 152:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.106
Sato N, Okubo T, Onodera T, Ohashi A, Harada H (2006) Prospects for a self-sustainable sewage treatment system: A case study on full-scale UASB system in India’s Yamuna River Basin. J Environ Manage 80:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.08.025
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant no. 17H04590) and the Program for the Strategic Promotion of International Cooperation to Accelerate Innovation in Developing Countries of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okubo, T., Tagawa, T., Takahashi, M. et al. Full-scale application of a down-flow hanging sponge reactor combined with a primary sedimentation basin for domestic sewage treatment. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 45, 701–709 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-022-02689-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-022-02689-w