Abstract
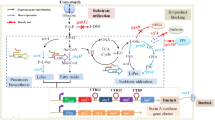
L-Xylulose is a rare ketopentose which inhibits α-glucosidase and is an indicator of hepatitis or liver cirrhosis. This pentose is also a precursor of other rare sugars such as L-xylose, L-ribose or L-lyxose. Recombinant E. coli expressing xylitol-4-dehydrogenase gene of Pantoea ananatis was constructed. A cost-effective culture media were used for L-xylulose production using the recombinant E. coli strain constructed. Response surface methodology was used to optimize these media components for L-xylulose production. A high conversion rate of 96.5% was achieved under an optimized pH and temperature using 20 g/L xylitol, which is the highest among the reports. The recombinant E. coli cells expressing the xdh gene were immobilized in calcium alginate to improve recycling of cells. Effective immobilization was achieved with 2% (w/v) sodium alginate and 3% (w/v) calcium chloride. The immobilized E. coli cells retained good stability and enzyme activity for 9 batches with conversion between 53 and 92% which would be beneficial for economical production of L-xylulose.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang W, Zhang T, Jiang B, Mu W (2017) Enzymatic approaches to rare sugar production. BiotechnolAdv 35:267–274
Bilal M, Iqbal HMN, Hu H, Wang W, Zhang X (2018) Metabolic engineering pathways for rare sugars biosynthesis, physiological functionalities, and applications—a review. Crit Rev Food SciNutr 58:2768–2778
Beerens K, Desmet T, Soetaert W (2012) Enzymes for the biocatalytic production of rare sugars. J IndMicrobiolBiotechnol 39:823–834
Meng Q, Zhang T, Jiang B, Mu W, Miao M (2016) Advances in applications, metabolism, and biotechnological production of L-xylulose. ApplMicrobiolBiotechnol 100:535–540
Muniruzzaman S, Pan YT, Zeng Y, Atkins B, Izumori K, Elbein AD (1996) Inhibition of glycoprotein processing by L-fructose and L-xylulose. Glycobiology 6:795–803
Fang Z, Zhang W, Zhang T, Guang C, Mu W (2018) Isomerases and epimerases for biotransformation of pentoses. ApplMicrobiolBiotechnol 102:7283–7292
Shabat D, List B, Lerner RA, Barbas CF (1999) A short enantioselective synthesis of l-deoxy-L-xylulose by antibody catalysis. Tetrahedron Lett 40:1437–1440
Glatthaar C, Reichstein T (1935) D-Adonose (D-Erythro-2-keto-pentose). HelvChimActa 18:80–81
Larson HW, Blatherwick N, Bradshaw PJ, Ewing ME, Sawyer SD (1941) The metabolism of L-xylulose. J BiolChem 138:353–360
Kim SJ, Kim YS, Yeom SJ (2020) Phosphate sugar isomerases and their potential for rare sugar bioconversion. J Microbiol 58:725–733
Drueckhammer DG, Durrwachter JR, Pederson RL, Crans DC, Daniels L, Wong CH (1989) Reversible and in situ formation of organic arsenates and vanadates as organic phosphate mimics in enzymatic reactions: mechanistic investigation of aldol reactions and synthetic applications. J Org Chem 54:70–77
Richard P, Londesborough J, Putkonen M, Kalkkinen N, Penttilä M (2001) Cloning and expression of a fungal L-arabinitol 4-dehydrogenase gene. J BiolChem 276:40631–40637
Suzuki T, Tran LH, Yogo M, Idota O, Kitamoto N, Kawai K, Takamizawa K (2005) Cloning and expression of NAD+-dependent L-arabinitol 4-dehydrogenase gene (ladA) of Aspergillus oryzae. J BiosciBioeng 100:472–474
Tiwari MK, Singh RK, Gao H, Kim T, Chang S, Kim HS, Lee JK (2014) pH-rate profiles of L-arabinitol 4-dehydrogenase from Hypocrea jecorina and its application in L-xylulose production. Bioorg Med ChemLett 24:173–176
Gao H, Kim IW, Choi JH, Khera E, Wen F, Lee JK (2015) Repeated production of L-xylulose by an immobilized whole-cell biocatalyst harboring L-arabinitol dehydrogenase coupled with an NAD+ regeneration system. BiochemEng J 96:23–28
Lu F, Xu W, Zhang W (2019) Polyol dehydrogenases: intermediate role in the bioconversion of rare sugars and alcohols. ApplMicrobiolBiotechnol 103:6473–6481
Hollmann S, Touster O (1957) The L-xylulose-xylitol enzyme and other polyol dehydrogenases of guinea pig liver mitochondria. J BiolChem 225:87–102
Doten RC, Mortlock RP (1985) Production of D-and L-xylulose by mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Erwinia uredovora. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:158–162
Khan AR, Tokunaga H, Yoshida K, Izumori K (1991) Conversion of xylitol to L-xylulose by Alcaligenes sp. 701B-cells. J Ferment Bioeng 72:488–490
Granstrom TB, Takata G, Morimoto K, Leisola M, Izumori K (2005) L-xylose and L-lyxose production from xylitol using Alcaligenes 701B strain and immobilized L-rhamnoseisomerase enzyme. EnzymeMicrobTechnol 36:976–981
Poonperm W, Takata G, Morimoto K, Granström TB, Izumori K (2007) Production of L-xylulose from xylitol by a newly isolated strain of Bacillus pallidus Y25 and characterization of its relevant enzyme xylitol dehydrogenase. Enzyme Microb Tech 40:1206–1212
Zhang Y, Zhao X, Yang L, Han Y, Liu J (2014) Isolation and identification of a novel L-xylulose-producing strain. Food Sci 35:99–203
Aarnikunnas J, Pihlajaniemi A, Palva A, Leisola M, Nyyssölä A (2006) Cloning and expression of a xylitol-4-dehydrogenase gene from Pantoea ananatis. Appl Environ Microb 72:368–377
Usvalampi A, Kiviharju K, Leisola M, Nyyssölä A (2009) Factors affecting the production of L-xylulose by resting cells of recombinant Escherichia coli. J IndMicrobiolBiot 36:1323–2133
Han Qi, Eiteman MA (2017) Coupling xylitol dehydrogenase with NADH oxidase improves L-xylulose production in Escherichia coli culture. Enzyme Microb Tech 106:106–113
Takata G, Poonperm W, Morimoto K, Izumori K (2010) Cloning and overexpression of the xylitol dehydrogenase gene from Bacillus pallidus and its application to L-xylulose production. Biosci Biotech Bioch 74:1807–1813
Arsenis C, Touster O (1969) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked xylitol dehydrogenase in guinea pig liver cytosol. J BiolChem 244:3895–3899
Ishikura S, Isaji T, Usami N., Kitahara K, Nakagawa J and Hara A (2001) Molecular cloning, expression and tissue distribution of hamster diacetyl reductase. Identity with L-xylulose reductase, Chemico-Biol Int 879–889
Nakagawa J, Ishikura S, Asami J, Isaji T, Usami N, Hara A, Sakurai T, Tsuritani K, Oda K, Takahashi M, Yoshimoto M, Otsuka N, Kitamura K (2002) Molecular characterization of mammalian dicarbonyl/L-xylulose reductase and its localization in kidney. J BiolChem 277:17883–17891
Verho R, Putkonen M, Londesborough J, Penttilä M, Richard P (2004) A novel NADH-linked L-xylulose reductase in the L-arabinose catabolic pathway of yeast. J BiolChem 279:14746–14751
Ye Q, Li XM, Yan M, Cao H, Xu L, Zhang YY, Chen Y, Xiong J, Ouyang PK, Ying HJ (2010) High-level production of heterologous proteins using untreated cane molasses and corn steep liquor in Escherichia coli medium. ApplMicrobiolBiotechnol 87:517–525
Li S, Xu H, Yu J, Wang Y, Feng X, Ouyang P (2013) Enhancing isomaltulose production by recombinant Escherichia coli producing sucrose isomerase: culture medium optimization containing agricultural wastes and cell immobilization. Bioprocess BiosystEng 36:1395–1405
Lunzer R, Mamnun Y, Haltrich D, Kulbe KD, Nidetzky B (1998) Structural and functional properties of a yeast xylitol dehydrogenase, a Zn2+-containing metalloenzyme similar to medium-chain sorbitol dehydrogenases. Biochem J 336:91–99
Kim TS, Gao H, Li J, Kalia VC, Muthusamy K, Sohng JK, Kim IW, Lee JK (2019) Overcoming NADPH product inhibition improves D-sorbitol conversion to L-sorbose. Sci Rep 9:1–9
Cor FBW, Frans W, Ronald B, Jaap V (1994) Isolation and characterization of two xylitol dehydrogenases from Aspergillus niger. Microbiol 140:1679–1685
Erian AM, Gibisch M, Pflügl S (2018) Engineered E. coli W enables efficient 2,3-butanediol production from glucose and sugar beet molasses using defined minimal medium as economic basis. Microb Cell Fact 17:1–17
Mendonça EHM, Avanci NC, Romano LH, Branco DL, de Pádua AX, Ward RJ, Neto ÁdB, Lourenzoni MR (2020) Recombinant xylanase production by Escherichia coli using a non-induced expression system with different nutrient sources Braz. J ChemEng 37:29–39
Agarwal L, Isar J, Dutt K, Saxena RK (2007) Statistical optimization for succinic acid production from E. coli in a cost-effective medium. ApplBiochemBiotechnol 142:158–167
Agarwal L, Isar J, Meghwanshi GK, Saxena RK (2006) A cost effective fermentative production of succinic acid from cane molasses and corn steep liquor by Escherichia coli. J ApplMicrobiol 100:1348–1354
Jahreis K, Bentler L, Bockmann J, Hans S, Meyer A, Siepelmeyer J, Lengeler JW (2002) Adaptation of sucrose metabolism in the Escherichia coli wild-type strain EC3132. J Bacteriol 184:5307–5316
Lee PC, Lee SY, Hong SH, Chang HN, Park SC (2003) Biological conversion of wood hydrolysate to succinic acid by Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens. BiotechnolLett 25:111–114
Smrdel P, Bogataj M, Mrhar A (2008) The influence of selected parameters on the size and shape of alginate beads prepared by ionotropic Gelation. Sci Pharm 76(1):77–89
Idris A, Wahidin S (2006) Effect of sodium alginate concentration, bead diameter, initial pH and temperature on lactic acid production from pineapple waste using immobilized Lactobacillus delbrueckii. Process Biochem 41:1117–1123
Lee KY, Mooney DJ (2012) Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. ProgPolymSci 37:106–126
Chen XH, Wang XT et al (2012) Immobilization of Acetobacter sp. CCTCC M209061 for efficient asymmetric reduction of ketones and biocatalyst recycling. Microb Cell Fact 11:119–131
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Key R & D Plan of Shandong Province in 2019 (2019GSF107015), Shandong Province Science and Technology Development Project of China (2015GSF121016) and National Key Research and Development project of China (2017YFC1701502,2017YFC1701504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
The authors declare that there are no studies conducted with human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tesfay, M.A., Wen, X., Liu, Y. et al. Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli expressing xylitol-4-dehydrogenase and optimization for enhanced L-xylulose biotransformation from xylitol. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44, 1021–1032 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02505-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02505-3