Abstract
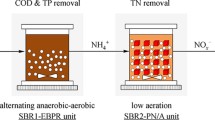
In this study, a novel laboratory-scale synchronous enhanced biological phosphorus removal and semi-nitritation (termed as EBPR-SN) combined with anammox process was put forward for achieving nutrient elimination from municipal wastewater at 27 ℃. This process consisted of two 10 L sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), i.e. EBPR-SN SBR followed by Anammox SBR. The EBPR-SN SBR was operated for 400 days with five periods and the Anammox SBR was operated starting on period IV. Eventually, for treating municipal wastewater containing low chemical oxygen demand/nitrogen (COD/N) of 3.2 (mg/mg), the EBPR-SN plus Anammox system performed advanced total inorganic nitrogen (TIN) and P removal, with TIN and P removal efficiencies of 81.4% and 94.3%, respectively. Further analysis suggested that the contributions of simultaneous partial nitrification denitrification, denitrification, and anammox to TIN removal were 15.0%, 45.0%, and 40.0%, respectively. The enriched phosphorus-accumulating organisms (PAOs) in the EBPR-SN SBR facilitated P removal. Besides, the EBPR-SN SBR achieved P removal and provided stable anammox substrates, suggesting a short sludge retention time (SRT 12 d) could achieve synergy between ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and PAOs. These results provided an alternative process for treating municipal wastewater with limited organics.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AOB:
-
Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria
- C/N:
-
Carbon/nitrogen
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- DN:
-
Denitrification
- DO:
-
Dissolved oxygen
- EBPR-SN:
-
Enhanced biological phosphorus removal and semi-nitritation
- FNA:
-
Free nitrite acid
- GAOs:
-
Glycogen-accumulating organisms
- Gly:
-
Glycogen
- MLSS:
-
Mixed liquor suspended solids
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- NAR:
-
Nitrite accumulation ratio
- NOB:
-
Nitrite-oxidizing bacteria
- OHO:
-
Ordinary heterotrophic organisms
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- PAOs:
-
Phosphorus-accumulating organisms
- PHAs:
-
Polyhydroxyalkanoates
- PHB:
-
Poly-b-hydroxybutyrate
- PHV:
-
Poly-b-hydroxyvalerate
- PRA:
-
Phosphorus release amount
- PUA:
-
Phosphorus uptake amount
- SBR:
-
Sequencing batch reactor
- SPND:
-
Simultaneous partial nitrification denitrification
- SRT:
-
Sludge retention time
- TIN:
-
Total inorganic nitrogen
- WWTP:
-
Wastewater treatment plants
References
Li J, Li J, Gao R et al (2018) A critical review of one-stage anammox processes for treating industrial wastewater: optimization strategies based on key functional microorganisms. Bioresource Technol 265:498–505
Li J, Peng Y, Zhang L et al (2019) Quantify the contribution of anammox for enhanced nitrogen removal through metagenomic analysis and mass balance in an anoxic moving bed biofilm reactor. Water Res 160:178–187
Mulder A, Vandegraaf AA, Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1995) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized-bed reactor. Fems Microbiol Ecol 16(3):177–183
Ma B, Wang S, Cao S et al (2016) Biological nitrogen removal from sewage via anammox: Recent advances. Bioresour Technol 200:981–990
Oehmen A, Lemos PC, Carvalho G et al (2007) Advances in enhanced biological phosphorus removal: From micro to macro scale. Water Res 41(11):2271–2300
Tuszynska A, Kaszubowska M, Kowal P, Ciesielski S, Makinia J (2019) The metabolic activity of denitrifying microorganisms accumulating polyphosphate in response to addition of fusel oil. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 42(1):143–155
Miao Y, Peng Y, Zhang L et al (2018) Partial nitrification-anammox (PNA) treating sewage with intermittent aeration mode: effect of influent C/N ratios. Chem Eng J 334:664–672
Mino T, Van Loosdrecht M, Heijnen JJ (1998) Microbiology and biochemistry of the enhanced biological phosphate removal process. Water Res 32(11):3193–3207
Yang Y, Zhang L, Shao H, Zhang S, Gu P, Peng Y (2017) Enhanced nutrients removal from municipal wastewater through biological phosphorus removal followed by partial nitritation/anammox. Front Env Sci Eng 11:82
Cao Y, Kwok BH, van Loosdrecht MCM et al (2017) The occurrence of enhanced biological phosphorus removal in a 200,000 m(3)/day partial nitration and Anammox activated sludge process at the Changi water reclamation plant. Singapore Water Sci Technol 75(3):741–751
Ma H, Xue Y, Zhang Y, Kobayashi T, Kubota K, Li Y (2020) Simultaneous nitrogen removal and phosphorus recovery using an anammox expanded reactor operated at 25 °C. Water Res 172:115510
Wen X, Zhou J, Li Y, Qing X, He Q (2016) A novel process combining simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) with denitrifying phosphorus removal (DPR) to treat sewage. Bioresour Technol 222:309–316
Yan Y, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhou S, Wang J, Guo J (2019) Comparison of short-term dosing ferrous ion and nanoscale zero-valent iron for rapid recovery of anammox activity from dissolved oxygen inhibition. Water Res 153:284–294
Zhang F, Peng Y, Miao L, Wang Z, Wang S, Li B (2017) A novel simultaneous partial nitrification Anammox and denitrification (SNAD) with intermittent aeration for cost-effective nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate. Chem Eng J 313:619–628
Ali M, Okabe S (2015) Anammox-based technologies for nitrogen removal: advances in process start-up and remaining issues. Chemosphere 141:144–153
Ma Y, Peng Y, Wang S, Yuan Z, Wang X (2009) Achieving nitrogen removal via nitrite in a pilot-scale continuous pre-denitrification plant. Water Res 43(3):563–572
Yang Q, Peng Y, Liu X, Zeng W, Mino T, Satoh H (2007) Nitrogen removal via nitrite from municipal wastewater at low temperatures using real-time control to optimize nitrifying communities. Environ Sci Technol 41(23):8159–8164
Winkler MKH, Kleerebezem R, Khunjar WO, de Bruin B, van Loosdrecht MCM (2012) Evaluating the solid retention time of bacteria in flocculent and granular sludge. Water Res 46(16):4973–4980
Liu W, Yang Q, Ma B et al (2017) Rapid achievement of nitritation using aerobic starvation. Environ Sci Technol 51(7):4001–4008
Ge S, Wang S, Yang X, Qiu S, Li B, Peng Y (2015) Detection of nitrifiers and evaluation of partial nitrification for wastewater treatment: a review. Chemosphere 140:85–98
APHAs (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington
Oehmen A, Zeng RJ, Saunders AM, Blackall LL, Keller J, Yuan Z (2006) Anaerobic and aerobic metabolism of glycogen-accumulating organisms selected with propionate as the sole carbon source. Microbiol-Sgm 152(9):2767–2778
Zeng RJ, van Loosdrecht M, Yuan ZG, Keller J (2003) Metabolic model for glycogen-accumulating organisms in anaerobic/aerobic activated sludge systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 81(1):92–105
Bernet N, Dangcong P, Delgenes JP, Moletta R (2001) Nitrification at low oxygen concentration in biofilm reactor. J Environ Eng 127(3):266–271
Wu J, He C, van Loosdrecht MCM, Perez J (2016) Selection of ammonium oxidizing bacteria, (AOB) over nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB) based on conversion rates. Chem Eng J 304:953–961
Du R, Cao S, Li B, Niu M, Wang S, Peng Y (2017) Performance and microbial community analysis of a novel DEAMOX based on partial-denitrification and anammox treating ammonia and nitrate wastewaters. Water Res 108:46–56
Fuessel J, Lam P, Lavik G et al (2012) Nitrite oxidation in the namibian oxygen minimum zone. Isme J 6(6):1200–1209
Veuger B, Pitcher A, Schouten S, Damste JSS, Middelburg JJ (2013) Nitrification and growth of autotrophic nitrifying bacteria and Thaumarchaeota in the coastal North Sea. Biogeosciences 10(3):1775–1785
Wang X, Wang S, Xue T, Li B, Dai X, Peng Y (2015) Treating low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) wastewater in simultaneous nitrification-endogenous denitrification and phosphorous removal (SNDPR) systems by strengthening anaerobic intracellular carbon storage. Water Res 77:191–200
Carucci A, Kuhni M, Brun R et al (1999) Microbial competition for the organic substrates and its impact on EBPR systems under conditions of changing carbon feed. Water Sci Technol 39(1):75–85
Smolders G, Vandermeij J, Vanloosdrecht M, Heijnen JJ (1994) Model of the anaerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process-stoichiometry and pH Influence. Biotechnol Bioeng 43(6):461–470
Filipe C, Daigger GT, Grady C (2001) A metabolic model for acetate uptake under anaerobic conditions by glycogen accumulating organisms: Stoichiometry, kinetics, and the effect of pH. Biotechnol Bioeng 76(1):17–31
Smolders G, Vandermeij J, Vanloosdrecht M, Heijnen JJ (1994) Stoichiometric model of the aerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process. Biotechnol Bioeng 44(7):837–848
Coats ER, Brinkman CK, Lee S (2017) Characterizing and contrasting the microbial ecology of laboratory and full-scale EBPR systems cultured on synthetic and real wastewaters. Water Res 108:124–136
Saito T, Brdjanovic D, van Loosdrecht M (2004) Effect of nitrite on phosphate uptake by phosphate accumulating organisms. Water Res 38(17):3760–3768
Pijuan M, Ye L, Yuan Z (2010) Free nitrous acid inhibition on the aerobic metabolism of poly-phosphate accumulating organisms. Water Res 44(20):6063–6072
Zeng W, Yang Y, Li L, Wang X, Peng Y (2011) Effect of nitrite from nitritation on biological phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch reactor treating domestic wastewater. Bioresour Technol 102(12):6657–6664
Yuan Y, Peng Y, Liu Y, Jin B, Wang B, Wang S (2014) Change of pH during excess sludge fermentation under alkaline, acidic and neutral conditions. Bioresour Technol 174:1–5
Zhao W, Zhang Y, Lv P, Wang M, Peng Y, Li B (2016) Advanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal in the pre-denitrification anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic nitrification sequence batch reactor (pre-A(2)NSBR) treating low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) wastewater. Chem Eng J 302:296–304
Wang F, Lu S, Wei Y, Ji M (2009) Characteristics of aerobic granule and nitrogen and phosphorus removal in a SBR. J Hazard Mater 164(2–3):1223–1227
Rahimi Y, Torabian A, Mehrdadi N, Shahmoradi B (2011) Simultaneous nitrification-denitrification and phosphorus removal in a fixed bed sequencing batch reactor (FBSBR). J Hazard Mater 185(2–3):852–857
Lo IW, Lo KV, Mavinic DS, Shiskowski D, Ramey W (2010) Contributions of biofilm and suspended sludge to nitrogen transformation and nitrous oxide emission in hybrid sequencing batch system. J Environ Sci-China 22(7):953–960
Du R, Peng Y, Ji J, Shi L, Gao R, Li X (2019) Partial denitrification providing nitrite: Opportunities of extending application for anammox. Environ Int 131:105001
Du R, Cao S, Li B, Zhang H, Wang S, Peng Y (2019) Synergy of partial-denitrification and anammox in continuously fed upflow sludge blanket reactor for simultaneous nitrate and ammonia removal at room temperature. Bioresour Technol 274:386–394
Ji J, Peng Y, Li X, Zhang Q, Liu X (2020) A novel partial nitrification-synchronous anammox and endogenous partial denitrification (PN-SAEPD) process for advanced nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater at ambient temperatures. Water Res 175:115690
Gao D, Peng Y, Li B, Liang H (2008) Shortcut nitrification-denitrification by real-time control strategies. J Biotechnol 136S:S652
Ji J, Peng Y, Wang B, Li X, Zhang Q (2020) A novel SNPR process for advanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from mainstream wastewater based on anammox, endogenous partial-denitrification and denitrifying dephosphatation. Water Res 170:115363
Liu J, Yuan Y, Li B et al (2017) Enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater in an anaerobic-aerobic-anoxic sequencing batch reactor with sludge fermentation products as carbon source. Bioresour Technol 244:1158–1165
Jin B, Niu J, Zhang J et al (2020) Response of extracellular polymeric substances and enzymatic activity to salinity for the waste activated sludge anaerobic fermentation process. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 43(4):737–745
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0401103), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21806006), Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Project (D171100001017002), and the Funding Projects of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, C., Peng, Y., Ji, J. et al. Advanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater via simultaneous enhanced biological phosphorus removal and semi-nitritation (EBPR-SN) combined with anammox. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43, 2039–2052 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02392-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02392-8