Abstract
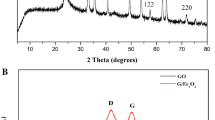
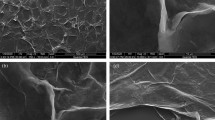
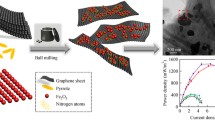
The properties of the anode material and structure are critical to the microbial growth and interfacial electron transfer between the biofilm and the anode. In this paper, we prepared the nitrogen-doped 3D expanded graphite foam (NEGF) by simple, rapid and inexpensive methods of liquid nitrogen expansion and hydrothermal treatment from commercial graphite foil (GF). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy confirmed the success of nitrogen doping on expanded graphite foam (EGF). Using cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, the NEGF and EGF electrode exhibited increased electrochemical active surface area and fast interfacial electron transfer ability than that of pristine GF, and NEGF electrode performed even better. Scanning electron microscopy revealed that NEGF and EGF possessed graphene-like structure and large surface area. MFCs equipped with NEGF or EGF anodes, respectively, achieved maximum power density of 0.739 and 0.536 W m−2, which was about 17.4 and 12.6 times larger than that of MFCs with GF anodes (0.0451 W m−2). The anode and cathode polarization curves further confirmed that the different anode other than the cathode was responsible for the advanced performance of MFCs. The morphology of the biofilm on three kinds of anodes proved the densest biofilm formed on NEGF anode. All the results indicated the synergistic effect of 3D graphene-like structure and N-doped surface on the performance of MFCs, which might provide special insights into designing simple and efficient route for anode construction to achieve promising electricity generation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logan BE, Rabaey K (2012) Conversion of wastes into bioelectricity and chemicals by using microbial electrochemical technologies. Science 337:686–690
Li WW, Yu HQ, He Z (2014) Towards sustainable wastewater treatment by using microbial fuel cells-centered technologies. Energy Environ Sci 7:911–924
Zhao CE, Gai PP, Song RB, Chen Y, Zhang JR, Zhu JJ (2017) Nanostructured material-based biofuel cells: recent advances and future prospects. Chem Soc Rev 46:1545–1564
Sonawane JM, Yadav A, Ghosh PC, Adeloju SB (2017) Recent advances in the development and utilization of modern anode materials for high performance microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 90:558–576
He Z, Liu J, Qiao Y, Li CM, Tan TTY (2012) Architecture engineering of hierarchically porous chitosan/vacuum-stripped graphene scaffold as bioanode for high performance microbial fuel cell. Nano Lett 12:4738–4741
Logan BE (2007) Microbial fuel cells. Wiley, New York
Wang RW, Yan M, Li HD, Zhang L, Peng BQ, Sun JZ, Liu D, Liu SQ (2018) FeS2 nanoparticles decorated graphene as microbial fuel cell anode achieving high power density. Adv Mater 30:e1800618
Wu GM, Bao H, Xia Z, Yang B, Lei LC, Lia ZJ, Liu CX (2018) Polypyrrole/sargassum activated carbon modified stainless-steel sponge as high-performance and low-cost bioanode for microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 384:86–92
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal RA, Schrorder U, Keller J, Freguia S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40:5181–5192
Wang X, Cheng SA, Feng YJ, Merrill MD, Saito T, Logan BE (2009) Use of carbon mesh anodes and the effect of different pretreatment methods on power production in microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 43:6870–6874
Hidalgo D, Tommasi T, Bocchini S, Chiolerio A, Chiodoni A, Mazzarino I, Ruggeri B (2016) Surface modification of commercial carbon felt used as anode for microbial fuel cells. Energy 99:193–201
Deng LF, Dong G, Zhang YY, Li DN, Lu T, Chen Y, Yuan HR, Chen Y (2019) Lysine-modified TiO2 nanotube array for optimizing bioelectricity generation in microbial fuel cells. Electrochim Acta 300:163–170
Cai H, Wang J, Bu YF, Zhong Q (2013) Treatment of carbon cloth anodes for improving power generation in a dual-chamber microbial fuel cell. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:623–628
Ci SQ, Wen ZH, Chen JH, He Z (2012) Decorating anode with bamboo-like nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes for microbial fuel cells. Electrochem Commun 14:71–74
Yang Y, Liu TY, Zhu X, Zhang F, Ye DD, Liao Q, Li Y (2016) Boosting power density of microbial fuel cells with 3D nitrogen-doped graphene aerogel electrode. Adv Sci 3:1600097
Xie X, Ye M, Hu LB, Liu N, McDonough JR, Chen W, Alshareef HN, Criddle CS, Cui Y (2012) Carbon nanotube-coated macroporous sponge for microbialfuel cell electrodes. Energy Environ Sci 5:5265–5270
Xie X, Yu GH, Liu N, Bao ZN, Criddle CS, Cui Y (2012) Graphene sponges as high-performance low-cost anodes for microbial fuel cells. Energy Environ Sci 5:6862–6866
Xie X, Hu LB, Pasta M, Wells GF, Kong DS, Criddle CS, Cui Y (2011) Three-dimensional carbon nanotube-textile anode for high-performance microbial fuel cells. Nano Lett 11:291–296
Yong YC, Dong XC, Chan-Park MB, Song H, Chen P (2012) Macroporous and monolithic anode based on polyaniline hybridized three-dimensional graphene for high-performance microbial fuel cells. ACS Nano 6:2394–2400
Wang H, Wang G, Ling Y, Qian F, Song Y, Lu X, Chen SW, Tong Y, Li Y (2013) High power density microbial fuel cell with flexible 3D graphene-nickel foam as anode. Nanoscale 5:10283–10290
Lu M, Qian Y, Yang C, Huang X, Li H, Xie X, Huang L, Huang W (2016) Nitrogen-enriched pseudographitic anode derived from silk cocoon with tunable flexibility for microbial fuel cells. Nano Energy 32(Complete):382–388.
Yuan Y, Zhou S, Liu Y, Tang J (2013) Nanostructured macroporous bioanode based on polyaniline-modified natural loofah sponge for high-performance microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 47:14525–14532
Chen SL, He GH, Liu Q, Harnisch F, Yan Zhou, Chen Y, Hanif M, Wang SQ, Peng XW, Hou HQ, Schroder U (2012) Layered corrugated electrode macrostructures boost microbial bioelectrocatalysis. Energy Environ Sci 5:9769–9772
Bian B, Shi D, Cai XB, Hu MJ, Guo QQ, Zhang CH, Wang Q, Sun XLA, Yang J (2018) 3D printed porous carbon anode for enhanced power generation in microbial fuel cell. Nano Energy 44:174–180
Zhao S, Li Y, Yin H, Liu Z, Luan E, Feng Z, Tang Z, Liu S (2015) Three-dimensional graphene/Pt nanoparticle composites as freestanding anode for enhancing performance of microbial fuel cells. Sci Adv 1:e1500372–e1500372
Zhang J, Wang G, Liao ZQ, Zhang PP, Wang FX, Zhuang XD, Zschech E, Feng XL (2017) Iridium Nanoparticles Anchored on 3D graphite foam as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for excellent overall water splitting in acidic solution. Nano Energy 40:27–33
Chen LY, Li YZ, Yao JN, Wu GM, Yang B, Lei LC, Hou Y, Li ZJ (2019) Fast expansion of graphite into superior three-dimensional anode for microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 412:86–92
Guo K, Freguia S, Dennis PG, Chen X, Donose BC, Keller J, Gooding JJ, Rabaey K (2013) Effects of surface charge and hydrophobicity on anodic biofilm formation, community composition, and current generation in bioelectrochemical systems. Environ Sci Technol 47:7563–7570
Santoro C, Guilizzoni M, Baena JC, Pasaogullari U, Casalegno A, Li B, Babanova S, Artyushkova K, Atanassov P (2014) The effects of carbon electrode surface properties on bacteria attachment and start up time of microbial fuel cells. Carbon 67:128–139
Bi LL, Ci SQ, Cai PW, Li H, Wen ZH (2018) One-step pyrolysis route to three dimensional nitrogen-doped porous carbon as anode materials for microbial fuel cells. Appl Surf Sci 427:10–16
Wu XS, Qiao Y, Shi ZZ, Tang W, Li CM (2018) Hierarchically porous N-doped CNTs/peduced graphene oxide composite for promoting flavin based interfacial electron transfer in microbial fuel cells. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10:11671–11677
Mohamed HO, Sayed ET, Cho H, Park M, Obaid M, Kim H-Y, Barakat NAM (2018) Effective strategies for anode surface modification for power harvesting and industrial wastewater treatment using microbial fuel cells. J Environ Manag 206:228–235
Kim JR, Cheng SA, Oh SE, Logan BE (2007) Power generation using different cation, anion, and ultrafiltration membranes in microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 41:1004–1009
Zhao CE, Li JX, Chen Y, Chen JY (2019) Nitrogen and sulfur dual-doped graphene as an efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cells. New J Chem 43:9389–9395
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Qiao Y, Li CM, Bao SJ, Bao QL (2007) Carbon nanotube/polyaniline composite as anode material for microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 170:79–84
Banks CE, Davies TJ, Wildgoose GG, Compton RG (2005) Electrocatalysis at graphite and carbon nanotube modified electrodes: edge-plane sites and tube ends are the reactive sites. Chem Commun 7:829–841
Ci SQ, Cai PW, Wen ZH, Li J (2015) Graphene-based electrode materials for microbial fuel cells. Sci China Mater 58:496–509
Lau CL, Moehlenbrock MJ, Arechederra RL, Falase A, Garcia K, Rincon R, Minteer SD, Banta S, Gupta G, Babanova S, Atanassov P (2015) Paper based biofuel cells: Incorporating enzymatic cascades for ethanol and methanol oxidation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:14661–14666
Feng CH, Ma L, Li FB, Mai HJ, Lang XM, Fan SS (2010) A polypyrrole/anthraquinone-2,6-disulphonic disodium salt (PPy/AQDS)-modified anode to improve performance of microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1516–1520
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21601151) and the Scientific and Technological Research Projects of Henan Province, China (Grant No. 172102210449).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Chao, S. & Chen, Q. Improved power generation using nitrogen-doped 3D graphite foam anodes in microbial fuel cells. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43, 143–151 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02212-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02212-8