Abstract
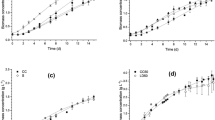
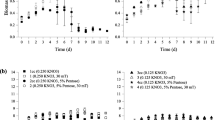
Increasing evidence shows that static magnetic fields (SMFs) can affect microbial growth metabolism, but the specific mechanism is still unclear. In this study, we have investigated the effect of moderate-strength SMFs on growth and vitamin K2 biosynthesis of Flavobacterium sp. m1-14. First, we designed a series of different moderate-strength magnetic field intensities (0, 50, 100, 150, 190 mT) and exposure times (0, 24, 48, 72, 120 h). With the optimization of static magnetic field intensity and exposure time, biomass and vitamin K2 production significantly increased compared to control. The maximum vitamin K2 concentration and biomass were achieved when exposed to 100 mT SMF for 48 h; compared with the control group, they increased by 71.3% and 86.8%, respectively. Interestingly, it was found that both the cell viability and morphology changed significantly after SMF treatment. Second, the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) metabolism is more vigorous after exposed to 100 mT SMF. This change affects the cell energy metabolism and fermentation behavior, and may partially explain the changes in bacterial biomass and vitamin K2 production. The results show that moderate-strength SMFs may be a promising method to promote bacterial growth and secondary metabolite synthesis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carbonell MV, Martinez E, Amaya JM (2000) Stimulation of germination in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by a static magnetic field. J Bioelectr 19(1):121–128
Flórez M, Carbonell MV, Martínez E (2004) Early sprouting and first stages of growth of rice seeds exposed to a magnetic field. J Bioelectr 23(2):10
Pinzon-Rodriguez A, Muheim R (2017) Zebra finches have a light-dependent magnetic compass similar to migratory birds. J Exp Biol 220(7):1202–1209
Yao-Ching H, Jia-Huey L, Huang-Meng C, Guewha Steven H (2010) Effects of static magnetic fields on the development and aging of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Exp Biol 213(6):2079–2085
Loghmannia J, Heidari B, Rozati SA, Kazemi S (2015) The physiological responses of the Caspian kutum (Rutilus frisii kutum) fry to the static magnetic fields with different intensities during acute and subacute exposures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 111(111):215–219
Bajpai I, Saha N, Basu B (2012) Moderate intensity static magnetic field has bactericidal effect on E. coli and S. epidermidis on sintered hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res Part B 100B(5):1206–1217
Potenza L, Ubaldi L, De Sanctis R, De Bellis R, Cucchiarini L, Dacha M (2004) Effects of a static magnetic field on cell growth and gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 561(1–2):53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2004.03.009
El May A, Snoussi S, Ben Miloud N, Maatouk I, Abdelmelek H, Ben Aissa R, Landoulsi A (2009) Effects of static magnetic field on cell growth, viability, and differential gene expression in Salmonella. Foodborne Pathog Dis 6(5):547–552. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2008.0244
Santos LO, Alegre RM, Garcia-Diego C, Cuellar J (2010) Effects of magnetic fields on biomass and glutathione production by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Process Biochem 45(8):1362–1367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.05.008
Da Motta MA, Muniz JBF, Schuler A, Da Motta M (2004) Static magnetic fields enhancement of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ethanolic fermentation. Biotechnol Prog 20(1):393–396. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp034263j
Konopacka A, Rakoczy R, Konopacki M (2019) The effect of rotating magnetic field on bioethanol production by yeast strain modified by ferrimagnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 473:176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.10.053
Deamici KM, Santos LO, Costa JAV (2018) Magnetic field action on outdoor and indoor cultures of Spirulina: evaluation of growth, medium consumption and protein profile. Bioresour Technol 249:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.185
Deamici KM, Cardias BB, Costa JAV, Santos LO (2016) Static magnetic fields in culture of Chlorella fusca: bioeffects on growth and biomass composition. Process Biochem 51(7):912–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.04.005
Tani Y, Asahi S, Yamada H (1986) Menaquinone (vitamin-K2)-6 production by mutants of Flavobacterium meningosepticum. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 32(2):137–145
Taguchi H, Kita S, Tani Y (1991) Enzymatic alteration in the shikimate pathway during derivation of menaquinone-4-producing mutants of Flavobacterium sp. 238-7. Agric Biol Chem 55(3):769–773. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1991.10870680
Fang X, Yang Q, Liu H, Wang P, Wang L, Zheng Z, Zhao G (2019) Effects of a combined processing technology involving ultrasound and surfactant on the metabolic synthesis of vitamin K2 by Flavobacterium sp. M1–14. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 135:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2018.09.010
Wei H, Zhao G, Liu H, Wang H, Ni W, Wang P, Zheng Z (2018) A simple and efficient method for the extraction and separation of menaquinone homologs from wet biomass of Flavobacterium. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 41(1):107–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1851-6
Zamani S, Hoseini AZ, Namin AM (2019) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity can modulate macrophage response to Leishmania major infection. Int Immunopharmacol 69:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.01.028
Hideyuki O, Hiroyuki I, Yu O, Toshiaki O, Hozumi T (2012) The effects of moderate-intensity gradient static magnetic fields on nerve conduction. Bioelectromagnetics 33(6):518–526
Lei Z, Hou Y, Li Z, Ji X, Wang Z, Wang H, Tian X, Yu F, Yang Z, Li P (2017) 27 T ultra-high static magnetic field changes orientation and morphology of mitotic spindles in human cells. eLife 6:e22911
Grassi C, D’Ascenzo M, Torsello A, Martinotti G, Wolf F, Cittadini A, Azzena GB (2004) Effects of 50 Hz electromagnetic fields on voltage-gated Ca channels and their role in modulation of neuroendocrine cell proliferation and death. Cell Calcium 35(4):307–315
Rosen AD, Chastney EE (2010) Effect of long term exposure to 0.5 T static magnetic fields on growth and size of GH3 cells. Bioelectromagnetics 30(2):114–119
Xin Z, Yarema K, An X (2017) Impact of static magnetic fields (SMFs) on cells
Katherine S, Balin AK, Allen RG (2011) Effects of static magnetic fields on the growth of various types of human cells. Bioelectromagnetics 32(2):140–147
Chionna A, Dwikat M, Panzarini E, Tenuzzo B, Carlà EC, Verri T, Pagliara P, Abbro L, Dini L (2003) Cell shape and plasma membrane alterations after static magnetic fields exposure. Eur J Histochem 47(4):299–308
Moore RL (1979) Biological effects of magnetic-fields with microorganisms. Can J Microbiol 25(10):1145–1151. https://doi.org/10.1139/m79-178
Morrow AC, Dunstan RH, King BV, Roberts TK (2007) Metabolic effects of static magnetic fields on Streptococcus pyogenes. Bioelectromagnetics 28(6):439–445. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20332
Egami S, Naruse Y, Watarai H (2010) Effect of static magnetic fields on the budding of yeast cells. Bioelectromagnetics 31(8):622–629. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20599
Rosen AD, Chastney EE (2009) Effect of long term exposure to 0.5 T static magnetic fields on growth and size of GH3 cells. Bioelectromagnetics 30(2):114–119. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20452
Kobayashi T, Dedem G, Ven Moo-Young M (2010) Oxygen transfer into mycelial pellets. Biotechnol Bioeng 15(1):27–45
Sun X, Wu H, Zhao G, Li Z, Wu X, Liu H, Zheng Z (2018) Morphological regulation of Aspergillus niger to improve citric acid production by chsC gene silencing. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 41(2):1–10
Lucia P, Roberta S, Emanuela P, Paola C, Antonella A, Sabrina Z, Alessandra Z, Vilberto S (2012) Effect of 300 mT static and 50 Hz 0.1 mT extremely low frequency magnetic fields on Tuber borchii mycelium. Revue Canadienne De Microbiologie 58(58):1174–1182
Blanquer-Rossello MDM, Oliver J, Sastre-Serra J, Valle A, Roca P (2016) Leptin regulates energy metabolism in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 72:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2016.01.002
Santoro M, Guido C, De Amicis F, Sisci D, Cione E, Vincenza D, Dona A, Panno ML, Aquila S (2016) Bergapten induces metabolic reprogramming in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep 35(1):568–576. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4327
Buchachenko AL, Kuznetsov DA (2008) Magnetic field affects enzymatic ATP synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 130(39):12868–12869
Zhao G, Chen S, Wang L, Zhao Y, Wang J, Wang X, Zhang W, Wu R, Wu L, Wu Y (2011) Cellular ATP content was decreased by a homogeneous 8.5 T static magnetic field exposure: role of reactive oxygen species. Bioelectromagnetics 32(2):94–101
Aydin B (2017) Effects of argan oil on the mitochondrial function, antioxidant system and the activity of NADPH-generating enzymes in acrylamide treated rat brain. Biomedicine Pharmacother Biomedecine pharmacotherapie 87:476–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.124
Kahani SA, Yagini Z (2014) A comparison between chemical synthesis magnetite nanoparticles and biosynthesis magnetite. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2014(4):384–984
Mirabello G, Lenders JJ, Sommerdijk NA (2016) Bioinspired synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 45(18):5085–5106. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00432f
Wiltschko R, Wiltschko W (2012) The magnetite-based receptors in the beak of birds and their role in avian navigation. J Comp Physiol A 199(2):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-012-0769-3
Ritz T, Adem S, Schulten K (2000) A model for photoreceptor-based magnetoreception in birds. Biophys J 78(2):707–718
Braganza LF, Blott BH, Melville TJ (1984) The superdiamagnetic effect of magnetic fields on one and two component multilamellar liposomes. BBA Gen Subj 801(1):66–75
De NM, Cordisco S, Cerella C, Albertini MC, D'Alessio M, Accorsi A, Bergamaschi A, Magrini A, Ghibelli L (2010) Magnetic fields protect from apoptosis via redox alteration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1090(1):59–68
Rosen AD (2003) Effect of a 125 mT static magnetic field on the kinetics of voltage activated Na+ channels in GH3 cells. Bioelectromagnetics 24(7):517–523. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.10124
Braganza LF, Blott BH, Coe TJ, Melville D (1984) The superdiamagnetic effect of magnetic-fields on one and two component multilamellar liposomes. Biochem Biophys Acta 801(1):66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(84)90213-7
Bhalerao S, Clandinin TR (2012) Vitamin K-2 takes charge. Science 336(6086):1241–1242. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1223812
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Key Research and Development Plan of Anhui Province (1804b06020342), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1608085QC46), Major Projects of Science and Technology of Anhui Province (17030801036), and “Development and Demonstration of Vitamin K2 Functional Food” Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1908085MB43).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Hengfang Tang and Peng Wang contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, H., Wang, P., Wang, H. et al. Effect of static magnetic field on morphology and growth metabolism of Flavobacterium sp. m1-14. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42, 1923–1933 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02186-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02186-7