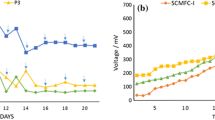
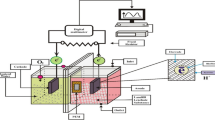
Abstract
Waters contaminated with naphthenic acids (NAs) and associated tailings are one of the major environmental challenges associated with the processing of oil sands and production of heavy oil. In the current work biodegradation of linear and cyclic naphthenic acids, namely octanoic acid and 4-methyl-1-cyclohexane carboxylic acid (trans-4MCHCA), individually and in mixture were evaluated in microbial fuel cells (MFCs). In batch MFCs with single rod electrodes and freely suspended bacteria, biodegradation rate increased as NA initial concentration increased from 100 to 250 mg L−1 with no further improvement when a concentration of 500 mg L−1 was evaluated. During the co-biodegradation, diauxic microbial growth and preferential use of octanoic acid were observed. Moreover, the presence of octanoic acid enhanced the biodegradation of trans-4MCHCA. In the continuous flow MFCs with granular graphite electrodes and biofilm, increases in NA concentration and loading rate led to higher biodegradation rates and improvement of electrochemical output. Furthermore, MFC operated with octanoic acid outperformed its counterpart that was fed with trans-4MCHCA, with the maximum biodegradation rate, current and power densities for octanoic acid and trans-4MCHCA being 49.9 and 36.5 mg L−1 h−1, 6000.0 and 4296.3 mA m−3, and 963.0 and 481.5 mW m−3, respectively. Co-biodegradation of NAs in continuous flow MFCs with biofilm acclimated to octanoic acid or trans-4MCHCA revealed development of distinctly different microbial communities, simultaneous biodegradation of NAs albeit at faster rates for octanoic acid, and superior performance of MFC with the biofilm developed with trans-4MCHCA.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oíl Sands Fact Sheet (2017) Canadian association of petroleum producers. http://www.capp.ca/publications-and-statistics/publications/305711. Accessed 21 Sept 2017
Holowenko FM, MacKinnon MD, Fedorak PM (2001) Naphthenic acids and surrogate naphthenic acids in methanogenic microcosms. Water Res 35:2595–2606
Allen EW (2008) Process water treatment in Canada’s oil sands industry: I. Target pollutants and treatment objectives. J Environ Eng Sci 7:123–138
MacKinnon MD, Boerger H (1986) Description of two treatment methods for detoxifying oil sand tailing pond water. Water Pollut Res J Canada 21:496–512
Pourrezaei P, Drzewicz P, Wang Y, Gamal El-Din M, Perez-Estrada LA, Martin JW, Anderson J, Wiseman S, Liber K, Giesy JP (2011) The impact of metallic coagulants on the removal of organic compounds from oil sands process-affected water. Environ Sci Technol 45:8452–8459
Alpatova A, Kim ES, Dong S, Sun N, Chelme-Ayala P, Gamal El-Din M (2014) Treatment of oil sands process-affected water with ceramic ultrafiltration membrane: effects of operating conditions on membrane performance. Sep Purif Technol 122:170–182
Mohamed MH, Wilson LD, Headley JV, Peru KM (2008) Novel materials for environmental remediation of tailing pond waters containing naphthenic acids. Process Saf Environ Prot 86:237–243
Pérez-Estrada LA, Han X, Drzewicz P, Gamal El-Din M, Fedorak PM, Martin JW (2011) Structure-reactivity of naphthenic acids in the ozonation process. Environ Sci Technol 45:7431–7437
Toor NS, Franz ED, Fedorak PM, MacKinnon MD, Liber K (2013) Degradation and aquatic toxicity of naphthenic acids in oil sands process-affected waters using simulated wetlands. Chemosphere 90:449–458
Allen EW (2008) Process water treatment in Canada’s oil sands industry: II. A review of emerging technologies. J Environ Eng Sci 7:499–524
Quagraine EK, Peterson HG, Headley JV (2005) In situ bioremediation of naphthenic acids contaminated tailing pond waters in the Athabasca oil sands region—demonstrated field studies and plausible options: a review. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 40:685–722
Xue J, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Gamal El-Din M (2016) Treatment of oil sands process-affected water (OSPW) using a membrane bioreactor with a submerged flat-sheet ceramic microfiltration membrane. Water Res 88:1–11
Demeter MA, Lemire J, George I, Yue G, Ceri H, Turner RJ (2014) Harnessing oil sands microbial communities for use in ex situ naphthenic acid bioremediation. Chemosphere 97:78–85
McKenzie N, Yue S, Liu X, Ramsay BA, Ramsay JA (2014) Biodegradation of naphthenic acids in oils sands process waters in an immobilized soil/sediment bioreactor. Chemosphere 109:164–172
Whitby C (2010) Microbial naphthenic Acid degradation. Adv Appl Microbiol 70:93–125
Han X, Scott AC, Fedorak PM, Bataineh M, Martin JW (2008) Influence of molecular structure on the biodegradability of naphthenic acids. Environ Sci Technol 42:1290–1295
Herman DC, Fedorak PM, MacKinnon MD, Costerton JW (1994) Biodegradation of naphthenic acids by microbial populations indigenous to oil sands tailings. Can J Microbiol 40:467–477
Huang J, Nemati M, Hill G, Headley J (2012) Batch and continuous biodegradation of three model naphthenic acids in a circulating packed-bed bioreactor. J Hazard Mater 201:132–140
D’Souza L, Sami Y, Nemati M, Headley J (2014) Continuous Co-biodegradation of linear and cyclic naphthenic acids in circulating packed-bed bioreactors. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 33:835–843
Islam MS, Dong T, Sheng Z, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Gamal El-Din M (2014) Microbial community structure and operational performance of a fluidized bed biofilm reactor treating oil sands process-affected water. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 91:111–118
Folwell BD, McGenity TJ, Price A, Johnson RJ, Whitby C (2016) Exploring the capacity for anaerobic biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and naphthenic acids by microbes from oil-sands-process-affected waters. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 108:214–221
Clothier LN, Gieg LM (2016) Anaerobic biodegradation of surrogate naphthenic acids. Water Res 90:156–166
Dong F, Nemati M (2016) Anoxic biodegradation of a surrogate naphthenic acid coupled to reduction of nitrite. Biochem Eng J 110:84–94
Gunawan Y, Nemati M, Dalai A (2014) Biodegradation of a surrogate naphthenic acid under denitrifying conditions. Water Res 51:11–24
Martin JW, Barri T, Han X, Fedorak PM, El-Din MG, Perez L, Scott AC, Jiang JT (2010) Ozonation of oil sands process-affected water accelerates microbial bioremediation. Environ Sci Technol 44:8350–8356
Hwang G, Dong T, Islam MS, Sheng Z, Pérez-Estrada LA, Liu Y, Gamal El-Din M (2013) The impacts of ozonation on oil sands process-affected water biodegradability and biofilm formation characteristics in bioreactors. Bioresour Technol 130:269–277
Shi Y, Huang C, Rocha KC, El-Din MG, Liu Y (2015) Treatment of oil sands process-affected water using moving bed biofilm reactors: With and without ozone pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 192:219–227
Islam MS, Zhang Y, McPhedran KN, Liu Y, Gamal El-Din M (2016) Mechanistic investigation of industrial wastewater naphthenic acids removal using granular activated carbon (GAC) biofilm based processes. Sci Total Environ 541:238–246
Frankel ML, Bhuiyan TI, Veksha A, Demeter MA, Layzell DB, Helleur RJ, Hill JM, Turner RJ (2016) Removal and biodegradation of naphthenic acids by biochar and attached environmental biofilms in the presence of co-contaminating metals. Bioresour Technol 216:352–361
Jiang Y, Ulrich AC, Liu Y (2013) Coupling bioelectricity generation and oil sands tailings treatment using microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 139:349–354
Choi J, Liu Y (2014) Power generation and oil sands process-affected water treatment in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 169:581–587
Paslawski JC, Headley JV, Hill GA, Nemati M (2009) Biodegradation kinetics of trans-4-methyl-1-cyclohexane carboxylic acid. Biodegradation 20:125–133
Moreno L, Nemati M, Predicala B (2017) Biodegradation of phenol in batch and continuous flow microbial fuel cells with rod and granular graphite electrodes. Environ Technol 1–13
Logan BE (2008) Microbial fuel cells. Wiley, New York
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal E, Schroder U, Keller J, Freguia F, Alterman P, Verstraete L, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: Methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40:5181–5192
Aelterman P, Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2006) Continuous electricity generation at high voltages and currents using stacked microbial fuel cells. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci 40:3388–3394
Marsili E, Rollefson JB, Baron DB, Hozalski RM, Bond DR (2008) Microbial biofilm voltammetry: direct electrochemical characterization of catalytic electrode-attached biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7329–7337
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Discovery Grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valdes Labrada, G., Nemati, M. Biodegradation of surrogate naphthenic acids and electricity generation in microbial fuel cells: bioelectrochemical and microbial characterizations. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 41, 1635–1649 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-1989-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-1989-x