Abstract
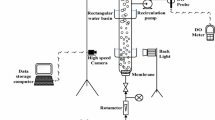
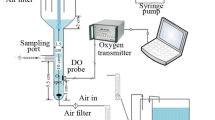
Two gas spargers, a novel membrane-tube sparger and a perforated plate sparger, were compared in terms of hydrodynamics and mass transfer (or oxygen transfer) performance in an internal-loop airlift bioreactor. The overall gas holdup ε T, downcomer liquid velocity V d, and volumetric mass transfer coefficient K L a were examined depending on superficial gas velocity U G increased in Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids for the both spargers. Compared with the perforated plate sparger, the bioreactor with the membrane-tube sparger increased the values of ε T by 4.9–48.8 % in air–water system when the U G was from 0.004 to 0.04 m/s, and by 65.1–512.6 % in air–CMC solution system. The V d value for the membrane-tube sparger was improved by 40.0–86.3 %. The value of K L a was increased by 52.8–84.4 % in air–water system, and by 63.3–836.3 % in air–CMC solution system. Empirical correlations of ε T, V d, and K L a were proposed, and well corresponding with the experimental data with the deviation of 10 %.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Specific interfacial area (m−1)
- A r :
-
Cross-sectional area in riser (m2)
- A d :
-
Cross-sectional area in riser (m2)
- K :
-
Consistency index, Pa sn
- n :
-
Flow index
- \(C_{\text{OL}}^{t}\) :
-
Instantaneous dissolved oxygen concentration (mg/L)
- \(C_{\text{OL}}^{*}\) :
-
Saturation dissolved oxygen concentration (mg/L)
- \(C_{OL}^{0}\) :
-
Initial dissolved oxygen concentration (mg/L)
- CMC:
-
Carboxymethyl cellulose
- C X :
-
Biomass concentration (kg/m3)
- K L a :
-
Volumetric mass transfer coefficient (s−1)
- Q :
-
Gas flow rate (m3/h)
- U G :
-
Superficial gas velocity (m/s)
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (m/s2)
- ε i :
-
Gas holdup, i = r, d, T
- τ :
-
Shear force, N/m2
- γ :
-
Shear rate, s−1
- γ av :
-
Average shear rate, s−1
- ρ i :
-
Density of fluid (kg/m3), i = G, L
- Δp :
-
Pressure difference between two measuring ports (Pa)
- h :
-
Distance between two measuring points (m)
- ν d :
-
Liquid velocity in downcomer (m/s)
- H :
-
Distance between two conductivity probe’s location
- Δt :
-
Time difference of two conductivity signal peak (s)
- ν :
-
Bubble velocity (m/s)
- μ ap :
-
Apparent viscosity (Pa s)
- d B :
-
Bubble diameter (m)
- α, α V, α K :
-
Exponent depends on the geometry of bioreactor for ε T, V d, and K L a correlation, respectively
- β, β V, β K :
-
Exponent depends on U G for ε T, V d, and K L a correlation, respectively
- γ, γ V, γ K :
-
Exponent depends on the apparent viscosity of liquid for ε T, V d, and K L a correlation, respectively
- ap:
-
Apparent
- r:
-
Riser
- d:
-
Downcomer
- T:
-
Total
- G:
-
Gas phase
- L:
-
Liquid phase
- B:
-
Bubble
References
Luo LJ, Liu FN, Xu YY, Yuan JQ (2011) Hydrodynamics and mass transfer characteristics in an internal loop airlift bioreactor with different spargers. Chem Eng J 175:494–504
Lin TJ, Chen PCH (2005) Studies on hydrodynamics of an internal-loop airlift bioreactor in gas entrainment regime by particle image analyzer. Chem Eng J 108:69–79
Krichnavaruk S, Pavasant P (2002) Analysis of gas-liquid mass transfer in an airlift contactor with perforated plates. Chem Eng J 89:203–211
Gavrilescu M, Roman RV, Tudose RZ (1997) Hydrodynamics in external-loop airlift bioreactors with static mixers. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 16:93–99
Chisti Y, Kasper M, Moo-Young M (1990) Mass transfer in internal-loop airlift bioreactors by using static mixers. Can J Chem Eng 68:45–50
Xu YY, Luo LJ, Yuan JQ (2011) CFD simulations to portray the bubble distribution and the hydrodynamics in an annulus sparged air-lift bioreactor. Can J Chem Eng 89:360–368
Garcia-Ochoa F, Gomez E (2009) Bioreactor scale-up and oxygen transfer rate in microbial processes: an overview. Biotechnol Adv 27:153–176
Wang TF, Wang JF (2007) Numerical simulations of gas–liquid mass transfer in bubble columns with a CFD–PBM coupled model. Chem Eng Sci 62:7107–7118
Šijački IM et al (2011) Sparger type influence on the hydrodynamics of the draft tube airlift bioreactor with diluted alcohol solutions. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:3580–3591
Merchuk JC, Contreras A, Garcia F, Molina E (1998) Studies of mixing in a concentric tube airlift bioreactor with different spargers. Chem Eng Sci 53:709–719
Fadavi A, Chisti Y (2007) Gas holdup and mixing characteristics of a novel forced circulation loop bioreactor. Chem Eng J 131:105–111
Fadavi A, Chisti Y (2005) Gas–liquid mass transfer in a novel forced circulation loop bioreactor. Chem Eng J 112:73–80
Chisti Y, Halard B, Moo-Young M (1988) Liquid circulation in airlift bioreactors. Chem Eng Sci 43:451–457
Merchuk JC, Berzin I (1995) Distribution of energy dissipation in airlift bioreactors. Chem Eng Sci 50:2225–2233
Garcia Calvo E (1989) A fluid dynamic model for airlift loop bioreactors. Chem Eng Sci 44:321–323
Chisti MY, Moo-Young M (1987) Airlift bioreactors: characteristics, applications and design considerations. Chem Eng Commun 60:195–242
Snape JB, Zahradnik J, Fialova M, Thomas NH (1995) Liquid-phase properties and sparger design effects in an external-loop airlift bioreactor. Chem Eng Sci 50:3175–3186
Lin J, Han M, Wang T, Zhang T, Wang J, Jin Y (2004) Influence of the gas distributor on the local hydrodynamic behavior of an external loop airlift bioreactor. Chem Eng J 102:51–59
Smith BC, Skidmore DR (1990) Mass transfer phenomena in an airlift bioreactor: effects of solids loading and temperature. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:483–491
Mouza AA, Dalakoglou GK, Paras SV (2005) Effect of liquid properties on the performance of bubble column reactors with fine pore spargers. Chem Eng Sci 60:1465–1475
Kazakis NA, Papadopoulos ID, Mouza AA (2007) Bubble columns with fine pore sparger operating in the pseudo-homogeneous regime: gas hold up prediction and a criterion for the transition to the heterogeneous regime. Chem Eng Sci 62:3092–3103
Moraveji MK, Sajjadi B, Davarnejad R (2011) Gas-liquid hydrodynamics and mass transfer in aqueous alcohol solutions in a split-cylinder airlift bioreactor. Chem Eng Technol 34:465–474
Kimono PM, Margaritis A, Bergougnou MA (2010) Hydrodynamic characteristics in an inverse internal-loop airlift-driven fibrous-bed bioreactor. Chem Eng Sci 65:692–707
Lehrer LH (1968) Gas agitation of liquids. Ind Eng Chem Res 7:226–239
Freitas C, Teixeira JA (2001) Oxygen mass transfer in a high solids loading three-phase internal-loop airlift bioreactor. Chem Eng J 84:57–61
Bannari R, Bannari A, Selma B, Proulx P (2011) Mass transfer and shear in an airlift bioreactor: using a mathematical model to improve bioreactor design and performance. Chem Eng Sci 66:2057–2067
Deng Z, Wang T, Zhang N, Wang Z (2010) Gas holdup, bubble behavior and mass transfer in a 5 m high internal-loop airlift bioreactor with non-Newtonian fluid. Chem Eng J 160:729–737
Li GQ, Yang SZ, Cai ZL, Chen JY (1995) Mass transfer and gas-liquid circulation in an airlift bioreactor with viscous non-Newtonian fluids. Chem Eng J 56:B101–B107
Loimer T, Machu G, Schaflinger U (2004) Inviscid bubble formation on porous plates and sieve plates. Chem Eng Sci 59:809–818
Contreras A, Garcia F, Molina E, Merchuk JC (1999) Influence of sparger on energy dissipation, shear rate, and mass transfer to sea water in a concentric-tube airlift bioreactor. Enzyme Microb Technol 25:820–830
Anastasiou AD, Passos AD, Mouza AA (2013) Bubble columns with fine pore sparger and non-Newtonian liquid phase: prediction of gas holdup. Chem Eng Sci 98:331–338
Vitankar VS, Dhotre MT, Joshi JB (2002) A low Reynolds number k–ε model for the prediction of flow pattern and pressure drop in bubble column reactors. Chem Eng Sci 57:3235–3250
Bouaifi M, Hebrard G, Bastoul D, Roustan M (2001) A comparative study of gas hold-up, bubble size, interfacial area and mass transfer coefficients in stirred gas–liquid reactors and bubble columns. Chem Eng Proc 40:97–111
Gavrilescu M, Tudose RZ (1995) Study of the liquid circulation velocity in external-loop airlift bioreactors. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 14:33–39
Zahradnik J, Fialova M, Ruzicka M, Drahos J, Kastanek F, Thomas NH (1997) Duality of the gas–liquid flow regimes in bubble column bioreactors. Chem Eng Sci 52:3811–3826
Cerri MO, Futiwaki L, Jesus CDF, Cruz AJG, Badino AC (2008) Average shear rate for non-Newtonian fluids in a concentric-tube airlift bioreactor. Biochem Eng J 39(1):51–57
Shi LK, Riba JP, Angelino H (1990) Estimation of effective shear rate for aerated non-Newtonian liquids in airlift bioreactor. Chem Eng Commun 89:25–35
Kawase Y, Kumagai T (1991) Apparent viscosity for non-Newtonian fermentation media in bioreactors. Bioprocess Eng 7:25–28
Al-Masry WA (1999) Effect of scale-up on average shear rates for aerated non-Newtonian liquids in external loop airlift reactors. Biotechnol Bioeng 62(4):494–498
Gavrilescu M, Tudose RZ (1997) Hydrodynamics of non-Newtonian liquids in external-loop airlift bioreactors. Bioprocess Eng 18:17–26
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by The National Key Technology R&D Program (No. 2012BAI44G00) and The National High-Tech R&D Program (No. 2014AA021703).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
C. Wei and B. Wu had contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, C., Wu, B., Li, G. et al. Comparison of the hydrodynamics and mass transfer characteristics in internal-loop airlift bioreactors utilizing either a novel membrane-tube sparger or perforated plate sparger. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37, 2289–2304 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1207-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1207-4