Abstract
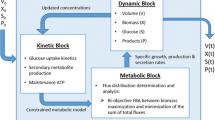
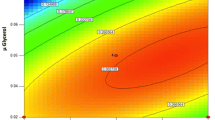
In this paper, we implemented a model-based optimization platform for fast development of Pichia pastoris cultures employing batch-to-batch control and hybrid semi-parametric modeling. We illustrate the methodology with a P. pastoris GS115 strain expressing a single-chain antibody fragment (scFv) by determining the optimal time profiles of temperature, pH, glycerol feeding and methanol feeding that maximize the endpoint scFv titer. The first hybrid model was identified from data of six exploratory experiments carried out in a pilot 50-L reactor. This model was subsequently used to maximize the final scFv titer of the proceeding batch employing a dynamic optimization program. Thereupon, the optimized time profiles of control variables were implemented in the pilot reactor and the resulting new data set was used to re-identify the hybrid model and to re-optimize the next batch. The iterative batch-to-batch optimization was stopped after 4 complete optimized batches with the final scFv titer stabilizing at 49.5 mg/L. In relation to the baseline batch (executed according to the Pichia fermentation guidelines by Invitrogen) a more than fourfold increase in scFv titer was achieved. The biomass concentration at induction and the methanol feeding rate profile were found to be the most critical control degrees of freedom to maximize scFv titer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teixeira AP, Clemente JJ, Cunha AE, Carrondo MJT, Oliveira R (2006) Bioprocess iterative batch-to-batch optimization based on hybrid parametric/nonparametric models. Biotechnol Prog 22(1):247–258
Teixeira AP, Alves C, Alves PM, Carrondo MJT, Oliveira R (2007) Hybrid elementary flux analysis/nonparametric modeling: application for bioprocess control. Bmc Bioinforma 8
Cregg JM, Madden KR, Barringer KJ, Thill GP, Stillman CA (1989) Functional-characterization of the 2 alcohol oxidase genes from the yeast Pichia pastoris. Mol Cell Biol 9(3):1316–1323
Cregg JM, Tschopp JF, Stillman C, Siegel R, Akong M, Craig WS, Buckholz RG, Madden KR, Kellaris PA, Davis GR, Smiley BL, Cruze J, Torregrossa R, Velicelebi G, Thill GP (1987) High-level expression and efficient assembly of hepatitis-B surface-antigen in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology 5(5):479–485
Jin H, Liu GQ, Ye XF, Duan ZY, Li Z, Shi ZP (2010) Enhanced porcine interferon-alpha production by recombinant Pichia pastoris with a combinational control strategy of low induction temperature and high dissolved oxygen concentration. Biochem Eng J 52(1):91–98
Cunha AE, Clemente JJ, Gomes R, Pinto F, Thomaz M, Miranda S, Pinto R, Moosmayer D, Donner P, Carrondo MJT (2004) Methanol induction optimization for scFv antibody fragment production in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Bioeng 86(4):458–467
Moon H, Kim SW, Lee J, Rhee SK, Choi ES, Kang HA, Kim IH, Hong SI (2003) Independent exponential feeding of glycerol and methanol for fed-batch culture of recombinant Hansenula polymorpha DL-1. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 111(2):65–79
Plantz BA, Sinha J, Villarete L, Nickerson KW, Schlegel VL (2006) Pichia pastoris fermentation optimization: energy state and testing a growth-associated model. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72(2):297–305
Ren HT, Yuan JQ (2005) Model-based specific growth rate control for Pichia pastoris to improve recombinant protein production. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80(11):1268–1272
Zhang WH, Bevins MA, Plantz BA, Smith LA, Meagher MM (2000) Modeling Pichia pastoris growth on methanol and optimizing the production of a recombinant protein, the heavy-chain fragment C of botulinum neurotoxin, serotype A. Biotechnol Bioeng 70(1):1–8
Holmes WJ, Darby RAJ, Wilks MDB, Smith R, Bill RM (2009) Developing a scalable model of recombinant protein yield from Pichia pastoris: the influence of culture conditions, biomass and induction regime. Microbial Cell Factories 8
Kupesulik B, Sevella B (2005) Optimization of specific product formation rate by statistical and formal kinetic model descriptions of an HSA producing Pichia pastoris Mut(S) strain. Chem Biochem Eng Q 19(1):99–108
Schenk J, Balazs K, Jungo C, Urfer J, Wegmann C, Zocchi A, Marison IW, von Stockar U (2008) Influence of specific growth rate on specific productivity and glycosylation of a recombinant avidin produced by a Pichia pastoris Mut(+) strain. Biotechnol Bioeng 99(2):368–377
Sinha J, Inan M, Fanders S, Taoka S, Gouthro M, Swanson T, Barent R, Barthuli A, Loveless BM, Smith LA, Smith T, Henderson I, Ross J, Meagher MM (2007) Cell bank characterization and fermentation optimization for production of recombinant heavy chain C-terminal fragment of botulinum neurotoxin serotype E (rBoNTE(H-c): Antigen E) by Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 127(3):462–474
Sinha J, Plantz BA, Zhang WH, Gouthro M, Schlegel V, Liu CP, Meagher MM (2003) Improved production of recombinant ovine interferon-tau by Mut(+) strain of Pichia pastoris using an optimized methanol feed profile. Biotechnol Prog 19(3):794–802
Modak J, Konde K (2009) Multiobjective optimization of Pichia pastoris fermentations. New Biotechnol 25:S241
Zhang W, Sinha J, Smith LA, Inan M, Meagher MM (2005) Maximization of production of secreted recombinant proteins in Pichia pastoris fed-batch fermentation. Biotechnol Prog 21(2):386–393
(2000) Pichia fermentation process guidelines. Invitrogen Corporation
Cos O, Ramon R, Montesinos JL, Valero F (2006) Operational strategies, monitoring and control of heterologous protein production in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris under different promoters: a review. Microbial Cell Factories 5
Curvers S, Brixius P, Klauser T, Thommes J, Weuster-Botz D, Takors R, Wandrey C (2001) Human chymotrypsinogen B production with Pichia pastoris by integrated development of fermentation and downstream processing. Part 1. fermentation. Biotechnol Prog 17(3):495–502
Jahic M, Gustavsson M, Jansen AK, Martinelle M, Enfors SO (2003) Analysis and control of proteolysis of a fusion protein in Pichia pastoris fed-batch processes. J Biotechnol 102(1):45–53
Li ZJ, Xiong F, Lin QS, d’Anjou M, Daugulis AJ, Yang DSC, Hew CL (2001) Low-temperature increases the yield of biologically active herring antifreeze protein in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 21(3):438–445
Potgieter TI, Cukan M, Drummond JE, Houston-Cummings NR, Jiang YW, Li F, Lynaugh H, Mallem M, McKelvey TW, Mitchell T, Nylen A, Rittenhour A, Stadheim TA, Zha DX, d’Anjou M (2009) Production of monoclonal antibodies by glycoengineered Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 139(4):318–325
Cregg JM, Vedvick TS, Raschke WC (1993) Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology 11(8):905–910
Calik P, Bayraktar E, Inankur B, Soyaslan ES, Sahin M, Taspinar H, Acik E, Yilmaz R, Ozdamar TH (2010) Influence of pH on recombinant human growth hormone production by Pichia pastoris. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85(12):1628–1635
Brierley RA, Davis GR, Holtz GC, Gleeson MA, Howard BD (1997) Production of insulin-like growth factor-1 in methylotrophic yeast cells. US 5612198
Kobayashi K, Kuwae S, Ohya T, Ohda T, Ohyama M, Tomomitsu K (2000) High level secretion of recombinant human serum albumin by fed-batch fermentation of the methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris, based on optimal methanol feeding strategy. J Biosci Bioeng 90(3):280–288
Ohya T, Ohyama M, Kobayashi K (2005) Optimization of human serum albumin production in methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris by repeated fed-batch fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 90(7):876–887
Pla IA, Damasceno LM, Vannelli T, Ritter G, Batt CA, Shuler ML (2006) Evaluation of Mut(+) and Mut(S) Pichia pastoris phenotypes for high level extracellular scFv expression under feedback control of the methanol concentration. Biotechnol Prog 22(3):881–888
Damasceno LM, Pla I, Chang HJ, Cohen L, Ritter G, Old LJ, Batt CA (2004) An optimized fermentation process for high-level production of a single-chain Fv antibody fragment in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 37(1):18–26
Guarna MM, Lesnicki GJ, Tam BM, Robinson J, Radziminski CZ, Hasenwinkle D, Boraston A, Jervis E, MacGillivray RTA, Turner RFB, Kilburn DG (1997) On-line monitoring and control of methanol concentration in shake-flask cultures of Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Bioeng 56(3):279–286
Katakura Y, Zhang WH, Zhuang GQ, Omasa T, Kishimoto M, Goto W, Suga KI (1998) Effect of methanol concentration on the production of human beta(2)-glycoprotein I domain V by a recombinant Pichia pastoris: a simple system for the control of methanol concentration using a semiconductor Gas Sensor. J Ferment Bioeng 86(5):482–487
Chung JD (2000) Design of metabolic feed controllers: application to high-density fermentations of Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Bioeng 68(3):298–307
Oliveira R, Clemente JJ, Cunha AE, Carrondo MJT (2005) Adaptive dissolved oxygen control through the glycerol feeding in a recombinant Pichia pastoris cultivation in conditions of oxygen transfer limitation. J Biotechnol 116(1):35–50
Zhang WH, Smith LA, Plantz BA, Schlegel VL, Meagher MM (2002) Design of methanol feed control in Pichia pastoris fermentations based upon a growth model. Biotechnol Prog 18(6):1392–1399
Dietzsch C, Spadiut O, Herwig C (2011) A dynamic method based on the specific substrate uptake rate to set up a feeding strategy for Pichia pastoris. Microbial Cell Factories 10
Ferreira A (2012) A systems biology framework for pathway level culture media engineering: application to Pichia pastoris cultures. Universidade Nova de Lisboa, Lisboa
Kunkel JP, Jan DCH, Jamieson JC, Butler M (1998) Dissolved oxygen concentration in serum-free continuous culture affects N-linked glycosylation of a monoclonal antibody. J Biotechnol 62(1):55–71
Oliveira R (2004) Combining first principles modelling and artificial neural networks: a general framework. Comput Chem Eng 28(5):755–766
Dimassimo C, Willis MJ, Montague GA, Tham MT, Morris AJ (1991) Bioprocess model-building using artificial neural networks. Bioprocess Eng 7(1–2):77–82
Inan M, Meagher MM (2001) The effect of ethanol and acetate on protein expression in Pichia pastoris. J Biosci Bioeng 92(4):337–341
Jahic M, Rotticci-Mulder JC, Martinelle M, Hult K, Enfors SO (2002) Modeling of growth and energy metabolism of Pichia pastoris producing a fusion protein. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 24(6):385–393
Zhang WH, Potter KJH, Plantz BA, Schlegel VL, Smith LA, Meagher MM (2003) Pichia pastoris fermentation with mixed-feeds of glycerol and methanol: growth kinetics and production improvement. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30(4):210–215
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was provided by the Portuguese Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia through projects PEst-C/EQB/LA0006/2011 and PTDC/EBB-EBI/103761/2008, PhD grants SFRH/BD/36285/2007 (A.R.F.) and SFRH/BD/36990/2007 (M.V.S.) and Post-Doc grant SFRH/BPD/46277/2008 (J.D.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, A.R., Dias, J.M.L., von Stosch, M. et al. Fast development of Pichia pastoris GS115 Mut+ cultures employing batch-to-batch control and hybrid semi-parametric modeling. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37, 629–639 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-1029-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-1029-9