Abstract
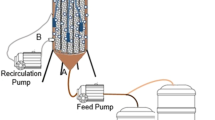
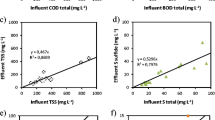
The performance of continuous flow intermittent decant type sequencing batch (CFID) reactor treating the effluent of an UASB reactor treating domestic wastewater and operated at 8 h hydraulic retention time (HRT) was investigated. The CFID was operated at three different HRTs (22, 8 and 6 h) and three different dissolved oxygen (DO) patterns (<0.5, 2.5–3.5 and 3.5–4.5 mg/L). The highest effluent quality was observed at the 8 h HRT and 2.5–3.5 mg/L DO concentration. At this operational condition, the average BOD, TSS, ammonia nitrogen and fecal coliform removal efficiencies were 83, 90, 74 and 99 %, respectively. The CFID is a promising post-treatment option for existing UASB systems, with a final effluent quality that comply with receiving water and effluent reuse criteria.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan AA, Gaur RZ, Tyagi VK, Khursheed A, Lew B, Kazmi AA, Mehrotra I (2011). Sustainable options of post treatment of UASB effluent treating sewage: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 55(12):1232–1251
Khan AA (2011) Post treatment of UASB effluent: aeration and variant of ASP; Ph.D. Thesis, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India
Aiyuk S, Amoako J, Raskin L, van Haandel A, Verstraete W (2004) Removal of carbon and nutrients from domestic wastewater using a low investment, integrated treatment concept. Water Res 38:3031–3042
Chernicharo CAL, Nascimento MCP (2001) Feasibility of a pilot-scale UASB/trickling filter system for domestic sewage treatment. Water Sci Technol 44(4):221–228
Tawfik A, Klapwijk B, El-Gohary F, Lettinga G (2002) Treatment of anaerobically treated domestic wastewater using rotating biological contactor. Water Sci Technol 45(10):371–376
Tawfik A, Klapwijk B, El-Gohary F, Lettinga G (2001) Treatment of anaerobically pretreated domestic sewage by a rotating biological contactor. Water Res 36(1):147–155
Goncalves RF, Araujo VL, Chernicharo CAL (1998) Association of a UASB reactor and a submerged aerated biofilter for domestic sewage treatment. Water Sci Technol 38(8–9):189–195
Goncalves RF, de Araujo VL, Bof VS (1999) Combining upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors and submerged aerated biofilters for secondary domestic wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol 40(8):71–79
Reali MAP, Penetra RG, Carvalho ME (2001) Flotation technique with coagulant and polymer application applied to the post-treatment of effluents from anaerobic rector treating sewage. Water Sci Technol 44(4):205–212
Tandukar M, Ohashi A, Harada H (2007) Performance comparison of a pilot-scale UASB and DHS system and activated sludge process for the treatment of municipal wastewater. Water Res 41(4):2697–2705
Sousa JT, Foresti E (1996) Domestic sewage treatment in an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket—sequential batch system. Water Sci Technol 33(3):73–84
Torres P, Foresti E (2001) Domestic sewage treatment in a pilot system composed of UASB and SBR reactors. Water Sci Technol 44(4):247–253
Moawad A, Mahmoud UF, El-Khateeb MA, El-Molla E (2009) Coupling of sequencing batch reactor and UASB reactor for domestic wastewater treatment. Desalination 242:325–335
Mbuligwe SE (2004) Comparative effectiveness of engineered wetland systems in the treatment of anaerobically pre-treated domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 23:269–284
Tandukar M, Ohashi A, Harada H (2007) Performance comparison of a pilot scale UASB and DHS and activated sludge process for treatment of municipal wastewater. Water Res 41(4):2697–2705
von Sperling M, Freire VH, Chernicharo CAL (2001) Performance evaluation of a UASB-activated sludge system treating municipal wastewater. Water Sci Technol 43(11):323–328
von Sperling M, Mascarenhas LCAM (2005) Performance of very shallow ponds treating effluents from UASB reactors. Water Sci Technol 12(51):83–90
Khan AA, Gaur RZ, Lew B, Diamantis V, Mehrotra I, Kazmi AA (2011) UASB/flash aeration enable complete treatment of municipal wastewater for reuse. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35(6):907–913. doi:10.1007/s00449-011-0675-z
Lettinga G, Roersma R, Grin P, de Zeeuw W, Hulshoff Pol L, van Velsen L, Hovma S, Zeeman G (1981) Anaerobic treatment of sewage and low strength waste waters. In: Proceedings of the second international symposium on anaerobic digestion, Travemunde, Germany, pp 271–291
APHA, AWWA, WEF (1998) Standards methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20th edition, American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation, Washington, DC, USA
Ozer C, Yassar S, Metin K, Demiroz K, Yigit NO, Kitis M (2008) Effect of cycle time on biodegradation of azo dye in sequencing batch reactor. Process Saf Environ Protect 86:455–460
Martins Antonio MP, Pagilla K, Heijnen JJ, Mark CM, Loosdrechta van (2003) Filamentous bulking sludge—a critical review. Water Res. doi:10.1016794-811
Metcalf and Eddy (2003) Wastewater engineering treatment and reuse, 3rd edn. Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi
Arceivala SJ (2001) Wastewater treatment for pollution control, 2nd edn. Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi
Khan AA, Gaur RZ, Lew B, Mehrotra I, Kazmi AA (2011) Effect of aeration on the quality of effluent from UASB reactor treating sewage. J Environ Eng ASCE 137(6):464–471
Draaijer H, Maas JAW, Schaapman JE, Khan A (1992) Performance of the 5 MLD UASB reactor for sewage treatment at Kanpur, India. Water Sci Technol 25(7):123–133
Chen KY, Morris JC (1972) Kinetics of oxidation of aqueous sulfide by O2. Environ Sci Technol 6(6):529–537
Eckenfelder WW (1989) Industrial pollution control. McGraw Hill, Singapore
Hegazy Talaat A, Abdel-Magied MA, Al-Asmar A, Ibrahim MS (2011) Environmental studies of domestic wastewater treatment using integrated anaerobic/aerobic system. J Am Sci 7(3):485–492
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Marvyn C. Goronszy, for his critical suggestions and comments made during this study. The authors also extend thanks to the Petroleum Conservation Research Association, an autonomous body of Ministry of Petroleum & Gas, Govt. of India, New Delhi, India for financial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A.A., Gaur, R.Z., Diamantis, V. et al. Continuous fill intermittent decant type sequencing batch reactor application to upgrade the UASB treated sewage. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36, 627–634 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0831-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0831-0