Abstract
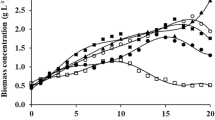
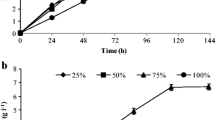
Cell retention culture of lactic acid bacterium Leuconostoc citreum was carried out in a fermentor equipped with an internal ceramic filtration system to co-produce biomass and metabolites. The filtration system was composed of porous ceramic filter module with pore size of 0.1 μm and total surface area of 330 cm2. High cell density cultivation of L. citreum was achieved within the fermentor, while extracellular metabolites such as mannitol and d-lactic acid were produced through the filter with high productivities. In batch culture of L. citreum using a medium containing 50 g/L of glucose and 100 g/L of fructose, the maximum optical density (OD) monitored at 660 nm was 13 with 65 g/L of mannitol and 38 g/L of lactic acid. In cell retention culture of L. citreum with dilution rate of 0.07 h−1, OD increased to 75, which was 6 times higher than that in batch culture. The concentrations of mannitol and lactic acid increased to 85 and 45 g/L, respectively, and were maintained throughout the cultivation to 105 h. By increasing dilution rate to 0.13 h−1, the productivities of mannitol and lactic acid increased to 8.5 and 4.2 g/L/h, respectively, which were 2.7 to 3 times higher than those in batch culture, suggesting that cell retention culture using internal filtration system is highly effective for co-production of useful cell biomass and various extracellular metabolites.







Similar content being viewed by others

References
Kim BS (2007) High cell density culture techniques for production of industrial products. In: Hou CT, Shaw J-F (eds) Biocatalysis and biotechnology for functional foods and industrial products. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 505–520
Ben Chaabane F, Aldiguier AS, Alfenore S, Cameleyre X, Blanc P, Bideaux C, Guillouet SE, Roux G, Molina-Jouve C (2006) Very high ethanol productivity in an innovative continuous two-stage bioreactor with cell recycle. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 29:49–57
Chang HN, Yoo I-K, Kim BS (1994) High density cell culture by membrane-based cell recycle. Biotechnol Adv 12:467–487
Chang HN, Kim N-J, Kang J, Jeong CM, Choi J, Fei Q, Kim BJ, Kwon S, Lee SY, Kim J (2011) Multi-stage high cell continuous fermentation for high productivity and titer. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 34:419–431
Chang HN, Lee WG, Kim BS (1993) Cell retention culture with an internal filter module: continuous ethanol fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 41:677–681
Suzuki T, Sato T, Kominami M (1994) A dense cell retention culture system using a stirred ceramic membrane reactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 44:1186–1192
Lee WG, Kim BS, Chang HN (1996) Microfiltration of yeast cells in an internal filter reactor. Korean J Chem Eng 13:404–408
Lee WG, Park BG, Chang YK, Chang HN, Lee JS, Park SC (2000) Continuous ethanol production from concentrated wood hydrolysates in an internal membrane-filtration bioreactor. Biotechnol Prog 16:302–304
Kang BC, Lee SY, Chang HN (1993) Production of Bacillus thuringiensis spores in total cell retention culture and two stage continuous culture using an internal ceramic filter system. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:1107–1112
Lee PC, Lee SY, Chang HN (2008) Cell recycled culture of succinic acid-producing Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens using an internal membrane filtration system. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:1252–1256
Otgonbayar G-E, Eom H-J, Kim BS, Ko J-H, Han NS (2011) Mannitol production by Leuconostoc citreum KACC 91348P isolated from kimchi. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:968–971
Eom H-J, Moon J-S, Seo E-Y, Han NS (2009) Heterologous expression and secretion of Lactobacillus amylovorus α-amylase in Leuconostoc citreum. Biotechnol Lett 31:1783–1788
Jin Q, Jung JY, Kim YJ, Eom H-J, Kim S-Y, Kim T-J, Han NS (2009) Production of l-lactate in Leuconostoc citreum via heterologous expression of l-lactate dehydrogenase gene. J Biotechnol 144:160–164
Hirayama S, Ueda R (2004) Production of optically pure d-lactic acid by Nannochlorum sp. 26A4. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 119:71–77
Kim H, Eom H-J, Lee J, Han J, Han NS (2004) Statistical optimization of medium composition for growth of Leuconostoc citreum. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 9:278–284
Saha BC, Racine FM (2011) Biotechnological production of mannitol and its application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:879–891
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2011-013-D00027) and by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy (MKE) and Korea Institute for Advancement in Technology (KIAT) through the Workforce Development Program in Strategic Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, IK., Han, N.S. & Kim, B.S. Co-production of biomass and metabolites by cell retention culture of Leuconostoc citreum . Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35, 715–720 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0651-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0651-7