Abstract
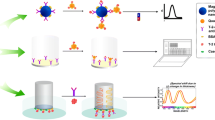
A flow-through quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) immunoassay method has been developed based on aflatoxin B1 antibody (anti-AFB1)-functionalized magnetic core-shell Fe3O4/SiO2 composite nanoparticles (bionanoparticles) in this study. To construct such an assay protocol, anti-AFB1, as a model protein, was initially covalently immobilized onto the Fe3O4/SiO2 surface, and then the functionalized nanoparticles were attached to the surface of the QCM probe with an external magnet. The binding of target molecules onto the immobilized antibodies decreased the sensor’s resonant frequency, and the frequency shift was proportional to the AFB1 concentration in the range of 0.3–7.0 ng/ml. The regeneration of the developed immunosensor was carried out via attaching or detaching the external magnet from the detection cell. In addition, the selectivity, reproducibility, and stability of the proposed immunoassay system were acceptable. Compared with the conventional ELISAs, the proposed immunoassay system was simple and rapid without multiple labeling and separation steps. Importantly, the proposed immunoassay method could be further developed for the immobilization of other antigens or biocompounds.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kriz K, Ibraimi F, Lu M, Hansson LO, Kriz D (2005) Anal Chem 77:5920
Tang D, Yuan R, Chai Y (2006) J Phys Chem B 110:11640
Stiens M, Schneiker S, Puhler A, Schluter A (2007) FEMS Microbiol Lett 271:297
Diaz-Gonzalez M, Garcia M, Costa-Garcia A (2005) Electroanalysis 17:1909
Mulchandani A, Chen W, Mulchandani P, Wang J, Rogers K (2001) Biosens Bioelectron 16:225
Tang D, Yuan R, Chai Y, Dai J, Zhong X, Liu Y (2004) Bioelectrochemistry 65:15
Won B, Choi H, Kim K, Byun S, Kim H, Yoon H (2005) Biotechnol Bioeng 89:815
Melikhova E, Kalmykova E, Eremin S, Ermolaeva T (2006) J Anal Chem 61:682
Mao X, Yang L, Su X, Li Y (2006) Biosens Bioelectron 21:1178
Gerdon A, Wright D, Cliffel D (2005) Anal Chem 77:304
Zhang Q, Huang Y, Zhao R, Liu G, Chen Y (2008) J Colloid Interface Sci 319:94
Palanianppan A, Moochhala S, Tay F, Su X, Phua N (2008) Sens Actuators B Chem 129:184
Martin SJ, Granstaff VE, Frye GC (1991) Anal Chem 63:2272
Sauerbrey G (1959) Z Phys 155:2333
Luppa P, Sokoll L, Chan D (2001) Clin Chim Acta 314:1
Deng T, Li J, Wang H, Sheng G, Yu R (2005) J Immunol Methods 299:1
Tang D, Yuan R, Chai Y, An H (2007) Adv Func Mater 17:976
Pejcic B, Marco R (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:6217
Wang J, Liu G, Munge B, Lin L, Zhu Q (2004) Agew Chem Int Ed Engl 43:2158
Katayama S, Nonaka Y, Lwata K, Kubo Y, Yamada N (2005) Adv Mater 17:2596
Park H, Lee Y (2005) Adv Mater 17:477
Adanyi N, Levkovets I, Rodriguez-Gil S, Ronald A, Varadi M, Szendro I (2007) Biosens Bioelectron 22:797
Monaci L, Palmisano F (2004) Anal Bioanal Chem 378:96
Ho J, Wauchope R (2002) Anal Chem 74:1493
Daly S, Keating G, Dillon P, Manning B, O’Kennedy R, Lee H, Morgan M (2000) J Agric Food Chem 48:5097
Pal A, Dhar T (2004) Anal Chem 76:98
Goryacheva I, Saeger S, Delmulle B, Lobeau M, Eremin S, Barna-Vetro I, Peteghem C (2007) Anal Chim Acta 590:118
Ma M, Zang Y, Yu W, Shen H, Zhang H, Gu N (2003) Colloids Surf A 212:219
Sakai K, Teng T, Katada A, Harada T, Yoshida K, Yamanaka K, Asami Y, Sakata M, Hirayama C, Kunitake M (2003) Chem Mater 15:4091
Liu Y, Qin Z, Wu X, Jiang H (2006) Biochem Eng J 32:211
European Commission Regulation No 194/97, Amended by European Commission Regulation No 1525/98, L201, 1998, p 43
Ammida N, Micheli L, Palleschi G (2004) Anal Chim Acta 520:159
Thevenot D, Toth K, Durst R, Wilson G (2001) Biosens Bioelectron 16:121
Kolosova A, Shim W, Yang Z, Eremin S, Chung D (2006) Anal Bioanal Chem 384:286
Piermarini S, Micheli L, Ammida N, Palleschi G, Moscone D (2007) Biosens Bioelectron 22:1434
Ammida N, Micheli L, Piermarini S, Moscone D, Palleschi G (2006) Anal Lett 39:1559
Pemberton R, Pittson R, Biddle N, Drago G, Hart J (2006) Anal Lett 39:1573
Dunne L, Daly S, Baxter A, Haughey S, O′Kennedy R (2005) Spectrosc Lett 38:229
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Specialized Research Funds for the Excellent Young Teachers from Yibin University, China. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from Postgraduate Science and Technology Innovation Program of YBU, and NSF of Sichuan, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Gan, XX. Biomolecule-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for flow-through quartz crystal microbalance immunoassay of aflatoxin B1 . Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 32, 109–116 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-008-0228-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-008-0228-2