Abstract
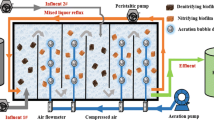
This study investigated the effects of the internal recycling rate on nutrients removal in a sequential anoxic/anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SAM). Microbial community structure in sludge from the SAM was studied using quinone profile method. Above 98% COD, 68% nitrogen, and 55% phosphorus removal efficiencies were achieved when the internal recycling rate was 2.5 times influent flow. At that rate, the optimum specific nitrate loading rate and COD/NO3-N ratio were found to be 2.24 mgNO3-N g−1 MLSS h−1 and 9.13, respectively. Batch tests demonstrated that anoxic condition suppressed phosphorus release, and that denitrification was also influenced by initial substrate concentration. Denitrification appeared to have some priority over phosphorus release for substrate uptake. Microbial community analysis revealed a predominance of the subclass β-Proteobacteria. Furthermore, it was found that Rhodocyclus-related bacteria were efficient at phosphorus removal than Actinobacteria.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn K-H, Song K-G, Choa E, Cho J, Yun H, Lee S, Me J (2003) Enhanced biological phosphorus and nitrogen removal using a sequencing anoxic/anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SAM) process. Desalination 157(1–3):345–352
Cho J, Song K-G, Lee SH, Ahn K-H (2005) Sequencing anoxic/anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SAM) pilot plant for advanced wastewater treatment. Desalination 178(1–3):219–225
Zhang B, Yamamoto K, Ohgaki S, Kamiko N (1997) Floc size distribution and bacterial activities in membrane separation activated sludge processes for small-scale wastewater treatment/reclamation. Wat Sci Technol 35(6):37–44
Fan X-J, Urbain V, Qian Y, Manem J (1996) Nitrification and mass balance with a membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment. Wat Sci Technol 34(1–2):129–136
Hofken MWA, Huber P, Schafer M, Steiner R (1996) Membrane aerators and stirring systems for the operation in large and small wastewater treatment plants. Wat Sci Technol 34(3–4):329–338
de Silva DGV, Urbain V, Abeysinghe DH, Rittmann BE (1998) Advanced analysis of membrane-bioreactor performance with aerobic-anoxic cycling. Wat Sci Technol 38(4–5):505–512
Louie TM, Mah TJ, Oldham W, Ramey WD (2000) Use of metabolic inhibitors and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry to study poly-[beta]-hydroxyalkanoates metabolism involving cryptic nutrients in enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Wat Res 34(5):1507–1514
Shin J-H, Lee S-M, Jung J-Y, Chung Y-C, Noh S-H (2005) Enhanced COD and nitrogen removals for the treatment of swine wastewater by combining submerged membrane bioreactor (MBR) and anaerobic upflow bed filter (AUBF) reactor. Process Biochem 40(12):3769–3776
Hu H-Y, Fujie K, Nakagome H, Urano K, Katayama A (1999) Quantitative analyses of the change in microbial diversity in a bioreactor for wastewater treatment based on respiratory quinones. Wat Res 33(15):3263–3270
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59(1):143–169
Wagner M, Amann R, Lemmer H, Schleifer KH (1993) Probing activated sludge with oligonucleotides specific for proteobacteria: inadequacy of culture-dependent methods for describing microbial community structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(5):1520–1525
Fang J, Barcelona MJ (1998) Structural determination and quantitative analysis of bacterial phospholipids using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization/mass spectrometry. J Microbiol Methods 33(1):23–35
Macnaughton SJ, Jenkins TL, Wimpee MH, Cormier MR, White DC (1997) Rapid extraction of lipid biomarkers from pure culture and environmental samples using pressurized accelerated hot solvent extraction. J Microbiol Methods 31(1–2):19–27
Hu H-Y, Lim B-R, Goto N, Fujie K (2001) Analytical precision and repeatability of respiratory quinones for quantitative study of microbial community structure in environmental samples. J Microbiol Methods 47(1):17–24
Hiraishi A, Ueda Y, Ishihara J, Mori T (1996) Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J Gen Appl Microbiol 42(6):457–469
Hiraishi A, Ueda Y, Ishihara J (1998) Quinone Profiling of Bacterial Communities in Natural and Synthetic Sewage Activated Sludge for Enhanced Phosphate Removal. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(3):992–998
Hiraishi A (1999) Isoprenoid quinones as biomarkers of microbial populations in the environment. J Biosci Bioeng 88(5):449–460
Lim B-R, Ahn K-H (2004) Analysis of microbial community structure in a biofilm on membrane surface in the submerged membrane bioreactor treating domestic wastewater on the basis of respiratory quinone profiles. J Gen Appl Microbiol 50(4):197–202
Hedrick DB, White DC (1986) Microbial respiratory quinones in the environment : I. A sensitive liquid chromatographic method. J Microbiol Methods 5(5–6):243–254
Lim B-R, Ahn K-H, Songprasert P, Lee S-H, Kim M-J (2004) Microbial community structure in an intermittently aerated submerged membrane bioreactor treating domestic wastewater. Desalination 161(2):145–153
Merkel W, Manz W, Szewzyk U, Krauth K (1999) Population dynamics in anaerobic wastewater reactors: modelling and in situ characterization. Wat Res 33(10):2392–2402
APHA (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. APHA-AWWA-WEF
Kuba T, Smolders G, van Loosdrecht MCM, Heijnen JJ (1993) Biological phosphorus removal from wastewater by anaerobic-anoxic batch reactors. Wat Sci Technol 27:241–252
Hascoet MC, Florentz M (1985) Influence of nitrate on biological phosphorus removal from wastewater. Water SA 11(1):1–8
Gerber A, Mostert ES, Winter CT, Villiers RH (1987) Interaction between phosphate, nitrate and organic substrate in biological nutrient removal processes. Wat Sci Technol 19:183–194
Chuang S-H, Ouyang C-F, Wang Y-B (1996) Kinetic competition between phosphorus release and denitrification on sludge under anoxic condition. Wat Res 30(12):2961–2968
Orhan D, Artan N (1994) Modelling of activated sludge systems. Technomic Publication Company Inc 61–69:482–492
Li H, Yang M, Zhang Y, Yu T, Kamagata Y (2006) Nitrification performance and microbial community dynamics in a submerged membrane bioreactor with complete sludge retention. J Biotech 123(1):60–70
Zilles JL, Peccia J, Kim M-W, Hung C-H, Noguera DR (2002) Involvement of rhodocyclus-related organisms in phosphorus removal in full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(6):2763–2769
Kurisu F, Satoh H, Mino T, Matsuo T (2002) Microbial community analysis of thermophilic contact oxidation process by using ribosomal RNA approaches and the quinone profile method. Wat Res 36(2):429–438
Tang J-C, Kanamori T, Inoue Y, Yasuta T, Yoshida S, Katayama A (2004) Changes in the microbial community structure during thermophilic composting of manure as detected by the quinone profile method. Process Biochem 39(12):1999–2006
Hanada S, Liu WT, Shintani T, Kamagata Y, Nakamura K (2002) Tetrasphaera elongata sp. nov., a polyphosphate-accumulating bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52(3):883–887
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, Z., Lim, BR., Cho, J. et al. Effects of the internal recycling rate on biological nutrient removal and microbial community structure in a sequential anoxic/anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 30, 61–69 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-006-0098-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-006-0098-4