Abstract
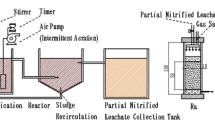
Leachates from municipal landfill ‘Lublinek‘ in Lodz city (Poland) were treated in two-sludge sequence batch reactor systems (type ND). The external carbon source—sodium acetate was used in denitrification. Two versions were tested—with and without supernatant recirculation from D-SBR to N-SBR. The 99% removal of inorganic nitrogen compounds was achieved in both versions. Due to recirculation, the buffering (by means of sodium bicarbonate) was not necessary. Kinetic models for nitrification and denitrification processes were proposed. Kinetic parameters of the models were estimated by the optimization method. The experimental results of both nitrification steps (oxidation of ammonia to nitrites and nitrites to nitrates) were best fitted with the interactive limitation model of nitrogen compounds and oxygen. The denitrification process was limited only by the concentration of nitrogen compounds.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Activated sludge
- BOD:
-
Biological oxygen demand
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- CSTR:
-
Continuous stirred tank reactor
- DF:
-
Down flow
- D-SBR:
-
Denitrification sequence batch reactor
- MLVSS:
-
Mixed liquor volatile suspended solids
- N-SBR:
-
Nitrification sequence batch reactor
- RBC:
-
Rotating bed contactor
- SBR:
-
Sequence batch reactor
- UASB:
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket
- UF:
-
Up flow
- c :
-
concentration (mg dm−3)
- c*:
-
equilibrium concentration (mg dm−3)
- K I :
-
inhibition coefficient (mg dm−3)
- k L a :
-
oxygen volumetric mass transfer coefficient in the liquid phase (h−1)
- K S :
-
saturation coefficient (mg dm−3)
- r :
-
substrate utilization rate (mg N dm−3 day−1)
- X :
-
biomass concentration (gMLVSS dm−3)
- Y :
-
yield coefficient (–)
- ν:
-
substrate utilization rate (mg gMLVSS−1 dm−3 day−1)
- νmax :
-
maximum substrate utilization rate (mg gMLVSS−1 dm−3 day−1)
- 0:
-
initial value
- A:
-
autotrophic biomass
- H:
-
heterotrophic biomass
- MLVSS:
-
mixed liquor volatile suspended solids
- NH3/NO2 :
-
ammonia inhibition to nitrites utilization
- N-NH:
-
the sum of ammonia and ammonium ion
- N-NH3 :
-
ammonia
- N-NH +4 :
-
ammonium ion
- N-HNO2 :
-
nitrous acid
- N-NO2 :
-
the sum of nitrites and nitrous acid
- N-NO −2 :
-
nitrite
- N-NO −3 :
-
nitrate
- O2 :
-
oxygen
References
Dichtl N, Kayser R, Steensen M (1997) Weitergehende Reinigung von Deponiesickerwässern durch chemische Oxidation/UV-Bestrahlung mit biologischer Vor- und Nachbehandlung. Abschlussbericht, TU Braunschweig
Burton SAQ, Watson-Craik IA (1998) Ammonia and nitrogen fluxes in landfill sites: applicability to sustainable landfilling. Waste Manage Res 16:41–53
Kjeldsen P, Christensen TH (2001) A simple model for the distribution and fate of organic chemicals in a landfill: MOCLA. Waste Manage Res 19:201–216
Wiesmann U (1994) Biological nitrogen removal from wastewater. Adv Biochem Eng/Biotechnol 51:113–154
Zart D, Stüven R, Bock E (1999) Nitrification and denitrification—microbial fundamentals and consequences for application. Biotechnology, vol 11. Weinheim, NY, USA, pp 56–65
Zumft WG (1997) Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:533–616
Whittaker M, Bergmann D, Arciero D, Hooper AB (2000) Electron transfer during the oxidation of ammonia by the chemolitotrophic bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Biochim Biophys Acta 1459:346–355
Wagner M, Loy A (2002) Bacterial community composition and function in sewage treatment systems. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13(1):218–227
Wett B, Rauch W (2003) The role of inorganic carbon limitation in biological nitrogen removal of extremely ammonia concentrated wastewater. Water Res 37:1100–1110
Robinson KG, Dionisi HM, Harms G, Layton AC, Gregory IR, Sayler GS (2003) Molecular assessment of ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in full-scale activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci Technol 48(8):103–110
Islas-Lima S, Thalasso F, Gomez-Hernandez J (2004) Evidence of anoxic methane oxidation coupled to denitrification. Water Res 38:13–16
Gujer W, Henze M, Mino T, van Loosdrecht M (1999) Activated sludge model no. 3. Water Sci Technol 39(1):183–193
Chang HN, Moon RK, Park BG, Lim S-J, Choi DW, Lee WG, Song SL, Ahn YH (2000) Simulation of sequential batch reactor (SBR) operation for simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus. Bioprocess Eng 23:513–521
Coelho MAZ, Russo C, Araujo OQF (2000) Optimization of a sequencing batch reactor for biological nitrogen removal. Water Res 34(10):2809–2817
Moussa MS, Hooijmans CM, Lubberding HJ, Gijzen HJ, van Loosdrecht MCM (2005) Modelling nitrification, heterotrophic growth and predation in activated sludge. Water Res 39(20):5080–5098
Surmacz-Górska J (2000) Usuwanie zanieczyszczeń organicznych oraz azotu z odcieków powstających w wysypiskach odpadów komunalnych (Removal of organics and nitrogen from landfill leachate). Inżynieria Środowiska, 44, Zeszyty Naukowe Politechniki Śląskiej
Pelkonen M, Kotro M, Rintala J (1999) Biological nitrogen removal from landfill leachate a pilot-scale study. Waste Manage Res 17:493–497
Hoilijoki TH, Kettunen RH, Rintala JA (2000) Nitrification of anaerobically pretreated municipal landfill leachate at low temperature. Water Res 34(5):1435–1446
Ilies P, Mavinic DS (2001) The effect of decreased ambient temperature on the biological nitrification and denitrification of a high ammonia landfill leachate. Water Res 35(8):2065–2072
Im J-H, Woo H-J, Choi M-W, Han K-B, Kim C-W (2001) Simultaneous organic and nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate using an anaerobic–aerobic system. Water Res 35(10):2403–2410
Martienssen M, Schöps R (1997) Biological treatment of leachate from solid waste landfill sites—alternations in the bacterial community during the denitrification process. Water Res 31(5):1164–1170
Jokela JPY, Kettunen RH, Sormunen KM, Rintala JA (2002) Biological nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate: low-cost nitrification in biofilters and laboratory scale in-situ denitrification. Water Res 36:4079–4087
Stephenson T, Pollard SJT, Cartmell E (2003) Feasability of biological aerated filters (BAFs) for leachate treatment. In: Proceedings Sardinia 2003, ninth international waste management and landfill symposium
Henderson JP, Besler DA, Atwater JA, Mavinic DS (1997) Treatment of methanogenic lanfill leachate to remove ammonia using a rotating biological contactor (RBC) and a sequencing batch reactor (SBR). Environ Technol 18:687–698
Welander U, Henrysson T, Welander T (1998) Biological nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate in a pilot scale suspended carrier biofilm process. Water Res 32(5):1564–1570
Schwarzenbeck N, Leonhard K, Wilderer PA (2003) Treatment of landfill leachate—high tech or low tech? A case study. Water Sci Technol 48(11–12):277–284
Luning L, Notenboom G (1997) The membrane bioreactor, advanced leachate treatment. In: Christensen TH, Cossu R, Stegmann R (eds) Proceedings of the sixth international landfill symposium. CISA, Cagliari, Italy, pp 275–281
Yalmaz G, Öztürk I (2001) Biological ammonia removal from anaerobically pre-treated landfill leachate in sequencing batch reactors (SBR). Water Sci Technol 43:307–314
Dockhorn T, Chang L, Dichtl N (1997) Removal of nitrogen from landfill leachate by using SBR-technology. In: Christensen TH, Cossu R, Stegmann R, (eds) Proceedings of the sixth international landfill symposium. CISA, Cagliari, Italy, pp 303–314
APHA (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. American Public Health Association (APHA), Washington, DC
Noophan P, Figureoa LA, Munakata-Marr J (2004) Nitrite oxidation inhibition by hydroxyloamine: experimental and model evaluation. Water Sci Technol 50(6):295–304
Maurer C, Steegmans R, Kraus S (1996) Reststoffarme Deponiesickerwasseraufbereitung nach dem Verfahren Biologie-Regenerative Aktivkohle-Ozon/UV-Biologie-Ionensustauscher (BAOUBI) fuer die Deponien Fernthal und Linkenbach in Landkreis Neuwied, RWTH Aachen
Gromadecki F, Chang L (1995) Stickstoffelimination mit Einstufigen Belebungsanlagen zur Behandlung von Sickerwasser aus Hausmuelldeponien, ATV-Seminar, Magdeburg
Anthonisen AC, Loehr RC, Prakasam TBS, Srinath EG (1976) Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J WPCF 48(5):835–852
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank Dr. Marcin Bizukojć for making the program Easyfit available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaczorek, K., Ledakowicz, S. Kinetics of nitrogen removal from sanitary landfill leachate. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 29, 291–304 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-006-0078-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-006-0078-8