Abstract
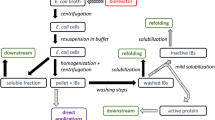
Many recombinant proteins are often over-expressed in host cells, such as Escherichia coli, and are found as insoluble and inactive protein aggregates known as inclusion bodies (IBs). Recently, a novel process for IB extraction and solubilisation, based on chemical extraction, has been reported. While this method has the potential to radically intensify traditional IB processing, the process economics of the new technique have yet to be reported. This study focuses on the evaluation of process economics for several IB processing schemes based on chemical extraction and/or traditional techniques. Simulations and economic analysis were conducted at various processing conditions using granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor, expressed as IBs in E. coli, as a model protein. In most cases, IB processing schemes based on chemical extraction having a shorter downstream cascade demonstrated a competitive economic edge over the conventional route, validating the new process as an economically more viable alternative for IB processing.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baneyx F, Mujacic M (2004) Recombinant protein folding and misfolding in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 22:1399
Blanch HW, Clark DS (1997) Biochemical engineering. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 453–577
Burgess RR (1991) Use of polyethyleneimine in purification of DNA-binding proteins. Methods Enzymol 208:3–10
Choe WS, Middelberg APJ (2001) Direct chemical extraction of a recombinant viral coat protein from Escherichia coli at high cell density. Biotechnol Bioeng 75:451–455
Choe WS, Middelberg APJ (2001) Selective precipitation of DNA by spermine during chemical extraction of insoluble cytoplasmic protein. Biotechnol Prog 17:1107–1113
Choe WS, Clemmitt RH, Rito-Palomares M, Chase HA, Middelberg APJ (2002a) Bioprocess intensification: a radical new process for recovering inclusion body protein. Trans IChemE 80:45–50
Choe WS, Clemmitt RH, Chase HA, Middelberg APJ (2002b) Comparison of histidine-tag capture chemistries for purification following chemical extraction. J Chromatogr A 953:111–121
Choe WS, Clemmitt RH, Chase HA, Middleberg APJ (2003) Coupling of chemical extraction and expanded-bed adsorption for simplified inclusion-body processing: optimization using surface plasmon resonance. Biotechnol Bioeng 8:221–232
Clark EDB (1998) Refolding of recombinant proteins. Curr Opin Biotechnol 9:157–163
Clark EDB, Schwarz E, Rudolph R (1999) Inhibition of aggregation side reactions during in vitro protein refolding. Methods Enzymol 309:217–236
Clemmitt RH, Chase HA (2000) Immobilised metal affinity chromatography of b-galactosidase from unclarified Escherichia coli homogenates using expanded bed adsorption. J Chromatogr A 874:27–43
Colangeli R, Heijbel A, Williams AM, Manca C, Chan J, Lyashchenko K, Gennaro ML (1998) Three-step purification of lipopolysaccharide-free, polyhistidine-tagged recombinant antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Chromatogr B 714:223–235
Cooke GD, Cranenburgh RM, Hanak JAJ, Ward JM (2003) A modified Escherichia coli protein production strain expressing staphylococcal nuclease, capable of auto-hydrolysing host nucleic acid. J Biotechnol 101:229–239
Demidov V (2004) Proper refolding helps express ‘difficult’ proteins. Drug Discov Dev 7:41
DeWalt BW, Murphy JC, Fox GE, Willson RC (2003) Compaction agent clarification of microbial lysates. Protein Expr Purif 28:220–223
Expanded bed adsorption principles and methods, 18-1124-26 Edition AB, Amersham Pharmacia Biotech
Falconer RJ, O’Neill BK, Middelberg AP (1997) Chemical treatment of Escherichia coli: 1. Extraction of intracellular protein from uninduced cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 53:453–458
Falconer RJ, O’Neill BK, Middelberg AP (1998) Chemical treatment of Escherichia coli: II. Direct extraction of a recombinant protein from cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in intact cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:381–386
Falconer RJ, O’Neill BK, Middelberg AP (1999) Chemical treatment of Escherichia coli: 3. Selective extraction of a recombinant protein from cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in intact cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 62:455–460
Fischer B, Sumner I, Goodenough P (1993) Isolation, renaturation, and formation of disulfide bonds of eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli as inclusion bodies. Biotechnol Bioeng 41:3–13
Harrison RG, Todd P, Rudge SR, Petrides DP (2002) Bioprocess design. In: Bioseparations science and engineering. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 319–372
Heebøll-Nielsen A, Choe WS, Middelberg APJ, Thomas ORT (2003) Efficient inclusion body processing using chemical extraction and high gradient magnetic fishing. Biotechnol Prog 19(3):887–898
Helander IM, Alakomi H-L, Latva-Kala K, Koski P (1997) Polyethyleneimine is an effective permeabilizer of Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology 143:3193–3199
Jungbauer A, Kaar W, Schlegl R (2004) Folding and refolding of proteins in chromatographic beds. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15:487–494
Langenhof M, Leong SSJ, Pattenden LK, Middelberg APJ (2005) Controlled oxidative protein refolding using an ion-exchange column. J Chromatogr A 1069:195–201
Lee SY (1996) High cell density culture of Escherichia coli. Trends Biotechnol 14:98–105
Lee CT, Morreale G, Middelberg APJ (2004) Combined in-fermenter extraction and cross-flow microfiltration for improved inclusion body processing. Biotechnol Bioeng 85:103–113
Lilie H, Schwarz E, Rudolph R (1998) Advances in refolding of proteins produced in E. coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 9:497–501
Ling Y, Wong HH, Thomas CJ, Williams DR, Middelberg APJ (1997) Pilot-scale extraction of PHB from recombinant E. coli by homogenization and centrifugation. Bioseparation 7:9–15
Lodish H, Baltimore D, Berk A, Zipursky SL, Matsudaira P, Darnell J (1995) Molecular cell biology, 3rd edn. Scientific American Books, Inc. p 145, Table 5.1
Maachupalli-Reddy J, Kelley BD, Clark ED (1997) Effect of inclusion body contaminants on the oxidative renaturation of hen egg white lysozyme. Biotechnol Prog 13:144–150
Marston FAO, Hartley DL (1990) Solubilisation of protein aggregates. Methods Enzymol 182:264
Middelberg APJ (2002) Preparative protein refolding. Trends Biotechnol 20:437–443
Middelberg APJ, O’Neill BK (1998) Harvesting recombinant protein inclusion bodies. In: Subramaniam G (ed) Bioseparation and bioprocessing: a handbook. Wiley-VCH, New York, pp 81–106
Petrides D, Cooney CL, Evans LB (1989) Bioprocess simulation: an integrated approach to process development. Comput Chem Eng 13:553–561
Schuler ML, Kargi F (1992) Bioprocess engineering: basic concepts. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, pp 395–430
Shepard SR, Boyd GA, Schrimsher JL (2001) Routine manufacture of recombinant proteins using expanded bed adsorption chromatography. Bioseparation 10:51–56
Speed MA, Wang DIC, King J (1996) Specific aggregation of partially folded polypeptide chains: the molecular basis of inclusion body composition. Nat Biotechnol 14:1283
Valax P, Georgiou G (1993) Molecular characterisation of β-lactamase inclusion bodies produced in Escherichia coli. 1. Composition. Biotechnol Prog 9:539
Vallejo LF, Rinas U (2004) Strategies for the recovery of active proteins through refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. Microb Cell Fact 3:11
Wong HH, O’Neill BK, Middelberg APJ (1997a) Cumulative sedimentation analysis of Escherichia coli debris size. Biotechnol Bioeng 55:556–564
Wong HH, O’Neill BK, Middelberg APJ (1997b) A mathematical model for Escherichia coli debris size reduction during high pressure homogenization based on grinding theory. Chem Eng Sci 52:2883–2890
Zhang Y, Qu XM, Lu JF, Yang SL (2000) Purification of recombinant GM-CSF/IL-3 fusion protein. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai) 32:235–238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, G.H., Cooney, D., Middelberg, A.P.J. et al. The economics of inclusion body processing. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 29, 73–90 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-006-0047-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-006-0047-2