Abstract.
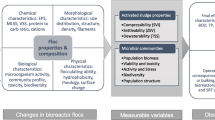
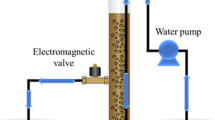
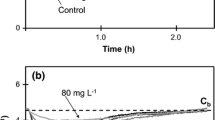
This paper summarizes the methodology utilized for measuring the toxic and inhibitory effects of azo-reactive dyes on the activity of activated sludge. The microbial sensor employed in this study consisted of a small-fluidized bed reactor in which the microbial mass was immobilized on spherical (diameter =1–2 mm) reticulated sinter glass carriers. To sustain a highly dense population of aerobic microbes, pure oxygen was supplied via a cylindrical chamber, which comprised part of the sample re-circulation system. The mean hydraulic retention time in the microbial sensor ranged between 30 and 40 min, while temperature was maintained at 30°C and pH at 6.4. Inhibition of microbial activity (toxicity) was determined as the mean percent reduction in carbon dioxide production from microorganisms' respiration. Several azo-reactive dyes demonstrated toxicity when applied at a high concentration (2 g/l), however, a portion of the microbes showed tolerance to the dyes. Moreover, textile wastewater demonstrated very efficient biodegradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georgiou, .D., Melidis, .P. & Aivasidis, .A. Use of a microbial sensor: inhibition effect of azo-reactive dyes on activated sludge. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 25, 79–83 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-002-0290-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-002-0290-0