Abstract.
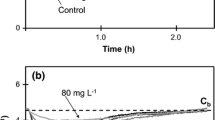
This paper presents a new method for the measurement of inhibitory effects in wastewater treatment plants on the basis of a continuous measurement of the microbial respiration product (CO2). The microbial sensor developed for this purpose consists of a small conical fluidized bed reactor connected to a cylindrical chamber that comprises part of the sample recirculation system. Activated sludge microbes are immobilized on spherical (diameter=1–2 mm) reticulated sinter glass carriers. Pure oxygen is supplied via the cylindrical chamber in order to sustain a highly dense population of microbial mass. The mean hydraulic retention time in the microbial sensor ranges between 30 and 40 min, while temperature is maintained at 30°C, and pH 6.4. Carbon dioxide in the off-gas, which reflects the microbial activity, is continuously analyzed by means of an infrared analyzer. Inhibition of microbial activity (toxicity) can be determined as the mean percent reduction in carbon dioxide concentration. Several substances were tested and proved toxic to the microbes. With this microbial sensor, early detection of toxic substances becomes feasible, preventing them from entering an activated sludge unit operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aivasidis, .A., Melidis, .P. & Georgiou, .D. Use of a microbial sensor: a new approach to the measurement of inhibitory effects on the microbial activity of activated sludge. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 25, 29–33 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-002-0283-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-002-0283-z