Abstract
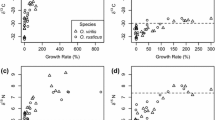
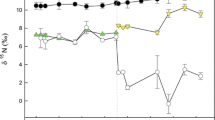
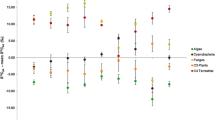
The stable isotope compositions (C and N) of plants and animals of a marsh dominated by Spartina alterniflora in the Delaware Estuary were determined. The study focused on the juvenile stage of the Atlantic blue crab, Callinectes sapidus, and the importance of marsh-derived diets in supporting growth during this stage. Laboratory growth experiments and field data indicated that early juvenile blue crabs living in the Delaware Bay habitat fed primarily on zooplankton, while marsh-dwelling crabs, which were enriched in 13C relative to bay juveniles, utilized marsh-derived carbon for growth. In laboratory experiments, the degree to which juvenile blue crabs isotopically fractionated dietary nitrogen, as well as the growth rate, depended on the protein quality of the diet. The range of δ13C of amino acids in laboratory-reared crabs and their diets was almost 20‰, similar to the isotopic range of amino acids of other organisms. In laboratory studies, the δ13C of nonessential and essential amino acids in the diet were compared to those in juvenile crabs. Isotopic fractionation at the molecular level depended on diet quality and the crabs' physiological requirements. Comparison of whole-animal isotope data with individual amino acid C isotope measurements of wild juvenile blue crabs from the bay and marsh suggested a different source of total dietary carbon, yet a shared protein component, such as zooplankton.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 July 1998 / Accepted: 15 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fantle, M., Dittel, A., Schwalm, S. et al. A food web analysis of the juvenile blue crab, Callinectes sapidus, using stable isotopes in whole animals and individual amino acids. Oecologia 120, 416–426 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050874
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050874