Abstract
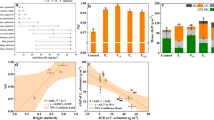
Increased availability of monomeric aluminum (Al3+) in forest soils is an important adverse effect of acidic deposition that reduces root growth and inhibits nutrient uptake. There is evidence that Al3+ exposure interferes with NO3 − uptake. If true for overstory trees, the reduction in stand demand for NO3 − could increase NO3 − discharge in stream water. These effects may also differ between species that tolerate different levels of soil acidity. To examine these ideas, we measured changes in relative uptake of NO3 − and NH4 + by six tree species in situ under increased soil Al3+ using a 15N-labeling technique, and measured soluble soil Al levels in a separate whole-watershed acidification experiment in the Fernow Experimental Forest (WV). When exposed to added Al3+, the proportion of inorganic N acquired as NO3 − dropped 14% across species, but we did not detect a reduction in overall N uptake, nor did tree species differ in this response. In the long-term acidification experiment, we found that soluble soil Al was mostly in the free Al3+ form, and the concentration of Al3+ was ~65 μM higher (~250%) in the mineral soil of the acidified watershed vs. an untreated watershed. Thus, increased levels of soil Al3+ under acidic deposition cause a reduction in uptake of NO3 − by mature trees. When our 15N uptake results were applied to the watershed acidification experiment, they suggest that increased Al3+ exposure could reduce tree uptake of NO3 − by 7.73 kg N ha−1 year−1, and thus increase watershed NO3 − discharge.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber J, McDowell W, Nadelhoffer K, Magill A, Bernston G, Kamakea M, McNulty S, Currie W, Rustad L, Fernandez I (1998) Nitrogen saturation in temperate forest ecosystems. Bioscience 48:921–934
Adams MB, Angradi TR, Kochenderfer JN (1997) Stream water and soil solution responses to 5 years of nitrogen and sulfur additions at the Fernow Experimental Forest, West Virginia. For Ecol Manag 95:79–91
Adams M, Peterjohn W, Gilliam F (2006) Acidification and Nutrient cycling. In: Adams M, DeWalle D, Hom J (eds) The Fernow watershed acidification study. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 207–236
Andresen L, Michelsen A (2005) Off-season uptake of nitrogen in temperate heath vegetation. Oecologia 144:585–597
Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2005) Nitrogen acquisition, PEP carboxylase, and cellular pH homeostasis: new views on old paradigms. Plant Cell Environ 28:1396–1409. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01372.x
Brumme R, Meesenburg H, Bredemeier M, Jacobsen C, Schonfelder E, Meiwes K, Eichhorn J (2009) Changes in soil solution chemistry, seepage, losses, and input–output budgets at three beech forests in response to atmospheric depositions. In: Brumme R, Khanna P (eds) Functioning and management of European Beech Ecosystems. Berlin, p 499
Buchmann N, Schultz E, Gebauer G (1995) 15N-ammonium and 15N-nitrate uptake of a 15-year-old Picea abies plantation. Oecologia 102:361–370
Calba H, Jaillard B (1997) Effect of aluminum on ion uptake and H+ release by maize. New Phytol 137:607–616
Chapman N, Miller AJ, Lindsey K, Whalley WR (2012) Roots, water, and nutrient acquisition: let’s get physical. Trends Plant Sci 17:701–710. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2012.08.001
Cumming JR (1990) Nitrogen source effects on Al toxicity in nonmycorrhizal and mycorrhizal pitch pine (Pinus rigida) seedlings. II. Nitrate reduction and NO3 − uptake. Can J Bot 68:2653–2659
Cumming J, Weinstein L (1990) Nitrogen source effects on Al toxicity in nonmycorrhizal and mycorrhizal pitch pine (Pinus rigida) seedlings. I. Growth and nutrition. Can J Bot 68:2644–2652
de Vries W, Reinds G, Vel E (2003) Intensive monitoring of forest ecosystems in Europe 2: atmospheric deposition and its impacts on soil solution chemistry. For Ecol Manag 174:97–115. doi:10.1016/S0378-1127(02)00030-0
de Wit HA, Eldhuset TD, Mulder J (2010) Dissolved Al reduces Mg uptake in Norway spruce forest: results from a long-term field manipulation experiment in Norway. For Ecol Manag 259:2072–2082. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2010.02.018
Delhaize E, Ryan P (1995) Aluminum toxicity and tolerance in plants. Plant Physiol 107:315–321
DeWalle D, Kochenderfer J, Adams M, Miller G, Gilliam F, Wood F, Odenwald-Clemens S, Sharpe W (2006) Vegetation and acidification. In: Adams M, DeWalle D, Hom J (eds) The Fernow watershed acidification study. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 137–188
Driscoll CT, Lawrence GB, Bulger AJ, Butler TJ, Cronan CS, Eagar C, Lambert KF, Likens GE, Stoddard JL, Weathers KC (2001) Acidic deposition in the northeastern US: sources and inputs, ecosystems effects, and management strategies. Bioscience 51:180–198. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0180:ADITNU]2.0.CO;2
Durieux R, Jackson W, Kamprath E, Moll R (1993) Inhibition of nitrate uptake by aluminum in maize. Plant Soil 151:97–104
Eddy WC, Zak DR, Holmes WE, Pregitzer KS (2008) Chronic atmospheric NO3 − deposition does not induce NO3 − use by Acer saccharum Marsh. Ecosystems 11:469–477. doi:10.1007/s10021-008-9134-3
Edwards PJ, Kochenderfer JN, Coble DW, Adams MB (2002) Soil leachate responses during 10 years of induced whole-watershed acidification. Water Air Soil Pollut 140:99–118. doi:10.1023/A:1020181800320
Edwards PJ, Williard KWJ, Wood F, Sharpe WE (2006) Soil water and stream water chemical responses. In: Adams M, DeWalle D, Hom J (eds) The Fernow watershed acidification study. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 71–136
Fahey TJ, Yavitt JB (2005) An in situ approach for measuring root-associated respiration and nitrate uptake of forest trees. Plant Soil 272:125–131. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-4212-6
Fry B (2006) Stable isotope ecology, 1st edn. Springer, New York
Galloway J, Dentener F, Capone D, Boyer E, Howarth R, Seitzinger S, Asner G, Cleveland C, Green P, Holland E, Karl D, Michaels A, Porter J, Townsend A, Vorosmarty C (2004) Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry 70:153–226
Gessler A, Schneider S, Von Sengbusch D, Weber P, Haneman U, Huber C, Rothe A, Kreutzer K, Rennenberg H (1998) Field and laboratory experiments on net uptake of nitrate and ammonium by the roots of spruce (Picea abies) and beech (Fagus sylvatica) trees. New Phytol 138:275–285
Halman JM, Schaberg PG, Hawley GJ, Hansen CF, Fahey TJ (2015) Differential impacts of calcium and aluminum treatments on sugar maple and American beech growth dynamics. Can J For Res 45:52–59. doi:10.1139/cjfr-2014-0250
Jarvis SC, Hatch DJ (1986) The effects of low concentrations of aluminum on the growth and uptake of nitrate-N by white clover. Plant Soil 95:43–55
Jerzykiewicz J (2001) Aluminum effect on nitrate assimilation in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) roots. Acta Physioligiae Plant 23:213–219
Kochenderfer JN (2006) Fernow and the Appalachian Hardwood region. In: Adams M, DeWalle D, Hom J (eds) The Fernow watershed acidification study. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 17–39
Kochian LV (1995) Cellular mechanisms of aluminum toxicity and resistance in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 46:237–260. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.46.060195.001321
Kronzucker HJ, Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM (1997) Conifer root discrimination against soil nitrate and the ecology of forest succession. Nature 385:59–61
Li W, Johnson CE (2016) Relationships among pH, aluminum solubility and aluminum complexation with organic matter in acid forest soils of the Northeastern US. Geoderma 271:234–242. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.02.030
Lovett G, Mitchell M (2004) Sugar maple and nitrogen cycling in the forests of Eastern North America. Front Ecol Environ 2:81–88
Lovett GM, Tear TH, Evers DC, Findlay SEG, Cosby BJ, Dunscomb JK, Driscoll CT, Weathers KC (2009) Effects of air pollution on ecosystems and biological diversity in the eastern US. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1162:99–135. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04153.x
Lux HB (1999) The effects of aluminum and nitrogen on mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal tulip poplar. MS Thesis, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV, USA
Lux HB, Cumming JR (1999) Effect of aluminum on the growth and nutrition of tulip-poplar seedlings. Can J For Res 29:2003–2007. doi:10.1139/cjfr-29-12-2003
Malagoli M, Canal AD, Quaggiotti S, Pegoraro P, Bottacin A (2000) Differences in nitrate and ammonium uptake between Scots pine and European larch. Plant Soil 221:1–3
McFarlane KJ, Yanai RD (2006) Measuring nitrogen and phosphorus uptake by intact roots of mature Acer saccharum Marsh., Pinus resinosa Ait., and Picea abies (L.) Karst. Plant Soil 279:163–172. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-0838-2
McKane R, Grigal D, Russelle M (1990) Spatiotemporal differences in 15N uptake and the organization of an old-field plant community. Ecology 71:1126–1132
McKane RB, Johnson LC, Shaver GR, Nadelhoffer KJ, Rastetter EB, Fry B, Giblin AE, Kielland K, Kwiatkowski BL, Laundre JA, Murray G (2002) Resource-based niches provide a basis for plant species diversity and dominance in arctic tundra. Nature 415:68–71. doi:10.1038/415068a
Min X, Siddiqi MY, Guy RD, Glass ADM, Kronzucker HJ (2000) A comparative kinetic analysis of nitrate and ammonium influx in two early-successional tree species of temperate and boreal forest ecosystems. Plant Cell Environ 23:321–328. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3040.2000.00546.x
Monterroso C, Alvarez E, Fernandez-Marcos M, Macias F (1999) Geochemistry of aluminium and iron in mine soils from As Pontes, Galicia (N.W. Spain). Water Air Soil Pollut 110:81–102. doi:10.1023/A:1005055704392
Mulder J, Stein A (1994) The solubility of aluminum in acidic forest soils: long-term changes due to acid deposition. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:85–94. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(94)90448-0
Oyewole OA, Inselsbacher E, Nasholm T (2014) Direct estimation of mass flow and diffusion of nitrogen compounds in solution and soil. New Phytol 201:1056–1064. doi:10.1111/nph.12553
Pal’ove-Balang P, Mistrík I (2007) Impact of low pH and aluminium on nitrogen uptake and metabolism in roots of Lotus japonicus. Biologia (Bratisl) 62:715–719. doi:10.2478/s11756-007-0133-1
Patric J, Reinhart K (1971) Hydrologic effects of deforesting two mountain watersheds in West Virginia. Water Resour Res 7:1182–1188
Phillips RP, Yanai RD (2004) The effect of AlCl3 additions on rhizosphere soil and fine root chemistry of sugar maple (Acer saccharum). Water Air Soil Pollut 159:339–356. doi:10.1023/B:WATE.0000049187.35869.7d
Poschenrieder C, Amenos M, Corrales I, Doncheva S, Barcelo J (2009) Root behavior in response to aluminum toxicity. In: Baluska F (ed) Plant–environment interactions. Springer, Berlin, p 313
Rosenberg MB, Butcher DJ (2010) Investigation of acid deposition effects on southern Appalachian red spruce (Picea rubens) by determination of calcium, magnesium, and aluminum in foliage and surrounding soil using ICP-OES. Instrum Sci Technol 38:341–358. doi:10.1080/10739149.2010.508968
Rothstein DE, Zak DR, Pregitzer KS, Url S, Zak R (1996) Nitrate deposition in northern hardwood forests and the nitrogen metabolism of Acer saccharum marsh. Oecologia 108:338–344
Socci AM, Templer PH (2011) Temporal patterns of inorganic nitrogen uptake by mature sugar maple (Acer saccharum Marsh.) and red spruce (Picea rubens Sarg.) trees using two common approaches. Plant Ecol Divers 4:141–152. doi:10.1080/17550874.2011.624557
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1981) Biometry, 2nd edn. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York
Tang MH, Porder S, Lovett GM (2012) Species differences in nitrate reductase activity are unaffected by nitrogen enrichment in northeastern US forests. For Ecol Manag 275:52–59. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2012.03.006
Templer PH, Dawson TE (2004) Nitrogen uptake by four tree species of the Catskill Mountains, New York: implications for forest N dynamics. Plant Soil 262:251–261. doi:10.1023/B:PLSO.0000037047.16616.98
Thornton B, Osborne SM, Paterson E, Cash P (2007) A proteomic and targeted metabolomic approach to investigate change in Lolium perenne roots when challenged with glycine. J Exp Bot 58:1581–1590. doi:10.1093/jxb/erl294
Vanguelova EI, Hirano Y, Eldhuset TD, Sas-Paszt L, Bakker MR, Puttsepp U, Brunner I, Lohmus K, Godbold D (2007) Tree fine root Ca/Al molar ratio—indicator of Al and acidity stress. Plant Biosyst 141:460–480. doi:10.1080/11263500701626192
Watanabe T, Osaki M, Tadano T (1998) Effects of nitrogen source and aluminum on growth of tropical tree seedlings adapted to low pH soils. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 44:655–666. doi:10.1080/00380768.1998.10414489
Zhou X, Gu Z, Xu H, Chen L, Tao G, Yu Y, Li K (2016) The effects of exogenous ascorbic acid on the mechanism of physiological and biochemical responses to nitrate uptake in two rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) under aluminum stress. J Plant Growth Regul 35:1013–1024. doi:10.1007/s00344-016-9599-9
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Chris Walter, Joe Cararra, Katie Sesa, Hannah Hedrick, Leah Baldinger, Rachel Arrick, Jessica Graham, and Hoff Lindberg for their field and lab work on this project. We also thank Dr. Robert McKane for his aid in developing 15N labeling methods. We greatly appreciate Dr. James McGraw’s input on statistical analyses. Finally, we acknowledge the contributions of the USDA Forest Service Fernow Experimental Forest staff for the long-term management and support of this experiment. This work was supported by the Long-Term Research in Environmental Biology (LTREB) program at the National Science Foundation (Grant Nos. DEB-0417678 and DEB-1019522) and the WVU Department of Biology and Eberly College of Arts and Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions
MBB, JRC, and WTP conceived and designed the 15N-labeling experiment, MBA aided with site selection and soil analysis methodology for both the whole-watershed acidification study and the labeling experiment. MBB and WTP analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; MBA and JRC reviewed the manuscript and provided editorial advice and comments.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jason P. Kaye.
We found that soil solution Al reduces the uptake of NO3 by mature trees. This effect and the impact on watershed NO3 export are novel findings important in areas impacted by acid deposition.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burnham, M.B., Cumming, J.R., Adams, M.B. et al. Soluble soil aluminum alters the relative uptake of mineral nitrogen forms by six mature temperate broadleaf tree species: possible implications for watershed nitrate retention. Oecologia 185, 327–337 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-017-3955-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-017-3955-8