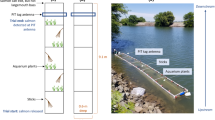
Abstract
Predator–prey relationships are altered by anthropogenic contaminants. Road salt is a widespread contaminant among freshwater ecosystems, yet a relatively understudied subject in community ecology. Unknown is whether road salt salinization interacts with predatory stress to influence the growth, behavior, or reproduction of freshwater organisms. Using rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and zooplankton (Daphnia pulex), we exposed them to variable levels of road salt (NaCl) crossed with the presence or absence of alarm cues or kairomones. Alarm cue reduced trout activity and aggression and increased shoaling behavior. Road salt reduced trout growth in the high compared to moderate salt concentration, but neither concentration was different from the control. There was no interaction between alarm cues and salt for trout. Road salt and predatory stress had an additive effect on Daphnia abundance. Predatory stress decreased Daphnia abundance by 11%. Compared to the control, salt decreased Daphnia abundance by 40% in 860 mg Cl−/L and 79% in 1300 mg Cl−/L, and by the final day abundance was reduced by 85% in 1300 mg Cl−/L. Road salt and predatory stress had an interactive effect on Daphnia reproduction. Predatory stress in control water and moderate salt levels (230 mg Cl−/L) increased sexual reproduction of Daphnia, but these responses disappeared at high salt concentrations. Thus, road salt could limit reproductive adaptations to natural and anthropogenic stressors in Daphnia. Our results indicate road salt salinization could alter zooplankton population dynamics directly and by interacting with predatory stress, which might affect energy flow through freshwater food webs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alekseev V, Lampert W (2001) Maternal control of resting-egg production in Daphnia. Nature 414:899–901
Arner M, Koivisto S (1993) Effects of salinity on metabolism and life history characteristics of Daphnia magna. Hydrobiologia 259:69–77
Baldwin CM, Beauchamp DA, Van Tassell JJ (2000) Bioenergetic assessment of temporal food supply and consumption demand by salmonids in the Strawberry Reservoir food web. Trans Am Fish Soc 129:429–450
Boeuf G, Payan P (2001) How should salinity influence fish growth? Comp Biochem Phys 130:411–423
Brown GE (2003) Learning about danger: chemical alarm cues and local risk assessment in prey fishes. Fish Fish 4:227–234
Brown GE, Smith RJF (1998) Acquired predator recognition in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): conditioning hatchery-reared fish to recognize chemical cues of a predator. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:611–617
Brown GE, Ferrari MCO, Malka PH, Oligny M-A, Romano M, Chivers DP (2011) Growth rate and retention of learned predator cues by juvenile rainbow trout: faster-growing fish forget sooner. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 65:1267–1276
Canada Environment (2011) Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: chloride. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Gatineau
Cañedo-Argüelles M, Hawkins CP, Kefford BJ, Schaefer RB, Dyack BJ, Brucet S, Buchwalter D, Dunlop J, Froer O, Lazorchak J, Coring E, Fernandez HR, Goodfellow W, Gonzalez Achem AL, Hatfield-Dodds S, Karimov BK, Mensah P, Olson JR, Piscart C, Prat N, Ponsa S, Schulz CJ, Timpano AJ (2016) Saving freshwater from salts. Science 351:914–916
Chapman DW (1962) Aggressive behavior in juvenile coho salmon as a cause of emigration. J Fish Res Board Can 19:1047–1080
Cherkauer DS, Ostenso NA (1976) The effect of salt on small artificial lakes. J Am Water Resour Assoc 12:1259–1267
Corsi SR, Graczyk DJ, Geis SW, Booth NL, Richards KD (2010) A fresh look at road salt: aquatic toxicity and water-quality impacts on local, regional, and national scales. Environ Sci Tech 44:7376–7382
Corsi SR, De Cicco LA, Lutz MA, Hirsch RM (2015) River chloride trends in snow-affected urban watersheds: increasing concentrations outpace urban growth rate and are common among all seasons. Sci Total Environ 508:488–497
Evans M, Frick C (2001) The effects of road salts on aquatic ecosystems. Environment Canada-Water Science and Technology Directorate
Findlay SEG, Kelly VR (2011) Emerging indirect and long-term road salt effects on ecosystems. Ann NY Acad Sci 1223:58–68
Galbraith MG (1967) Size-selective predation on Daphnia by rainbow trout and yellow perch. Trans Am Fish Soc 96:1–10
Gallagher AJ, Creel S, Wilson RP, Cooke SJ (2017) Energy landscapes and the landscape of fear. Trends Ecol Evol 32:88–96
Herbert ER, Boon P, Burgin AJ, Neubauer SC, Franklin RB, Ardon M, Hopfensperger KN, Lamers LPM, Gell P (2015) A global perspective on wetland salinization: ecological consequences of a growing threat to freshwater wetlands. Ecosphere 6:206
Hintz WD, Relyea RA (2017) Impacts of road deicing salts on the early-life growth and development of a stream salmonid: salt type matters. Environ Pollut 223:409–415
Hintz WD, Mattes BM, Schuler MS, Jones DK, Stoler AB, Lind LA, Relyea RA (2017) Salinization triggeres a trophic cascade in experimental freshwater communities with varying food-chain length. Ecol Appl 27:833–844
Hoover Z, Ferrari MCO, Chivers DP (2013) The effects of sub-lethal salinity concentrations on the anti-predator responses of fathead minnows. Chemosphere 90:1047–1052
Hopkins GR, French SS, Brodie ED Jr (2013) Potential for local adaptation in response to an anthropogenic agent of selection: effects of road deicing salts on amphibian embryonic survival and development. Evol Appl 6:384–392
Innes DJ (1997) Sexual reproduction of Daphnia pulex in a temporary habitat. Oecologia 111:53–60
Jeppesen E, Sondergaard M, Jensen JP, Mortensen E, Hansen AM, Jorgensen T (1998) Cascading trophic interactions from fish to bacteria and nutrients after reduced sewage loading: an 18-year study of a shallow hypertrophic lake. Ecosystems 1:250–267
Jeppesen E, Jensen JP, Amsinck S, Landkildehus F, Lauridsen T, Mitchell SF (2002) Reconstructing the historical changes in Daphnia mean size and planktivorous fish abundance in lakes from the size of Daphnia ephippia in the sediment. J Paleolimnol 27:133–143
Jones DK, Mattes BM, Hintz WD, Schuler MS, Stoler AB, Lind LA, Cooper RO, Relyea RA (2017) Investigation of road salts and biotic stressors on freshwater wetland communities. Environ Pollut 221:159–167
Karraker NE, Gibbs JP, Vonesh JR (2008) Impacts of road deicing salt on the demography of vernal pool-breeding amphibians. Ecol Appl 18:724–734
Kaushal SS, Groffman PM, Likens GE, Belt KT, Stack WP, Kelly VR, Band LE, Fisher GT (2005) Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern US. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13517–13520
Kelly WR, Panno SV, Hackley KC (2012) Impacts of road salt runoff on water quality of the Chicago, Illinois, Region. Environ Eng Geosci 18:65–81
Kelting DL, Laxson CL, Yerger EC (2012) Regional analysis of the effect of paved roads on sodium and chloride in lakes. Water Res 46:2749–2758
Kim JW, Brown GE, Grant JWA (2004) Interactions between patch size and predation risk affect competitive aggression and size variation in juvenile convict cichlids. Anim Behav 68:1181–1187
Kjensmo J (1997) The influence of road salts on the salinity and the meromictic stability of Lake Svinsjoen, southeastern Norway. Hydrobiologia 347:151–158
Kleiven OT, Larsson P, Hobaek A (1992) Sexual reproduction in Daphnia magna requires three stimuli. Oikos 65:197–206
Lass S, Spaak P (2003) Chemically induced anti-predator defences in plankton: a review. Hydrobiologia 491:221–239
Meuthen D, Baldauf SA, Bakker TCM, Thuenken T (2016) Conspecific alarm cues affect interspecific aggression in cichlid fishes. Hydrobiologia 767:37–49
Mullaney JR, Lorenz DL, Arnston AD (2009) Chloride in groundwater and surface water in areas underlain by the glacial aquifer system, northern US. United States Geological Survey
Novotny EV, Stefan HG (2012) Road salt impact on lake stratification and water quality. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 138:1069–1080
Novotny EV, Murphy D, Stefan HG (2008) Increase of urban lake salinity by road deicing salt. Sci Total Environ 406:131–144
Pestana JLT, Loureiro S, Baird DJ, Soares AMVM (2009) Fear and loathing in the benthos: responses of aquatic insect larvae to the pesticide imidacloprid in the presence of chemical signals of predation risk. Aquat Toxicol 93:138–149
Petranka JW, Doyle EJ (2010) Effects of road salts on the composition of seasonal pond communities: can the use of road salts enhance mosquito recruitment? Aquat Ecol 44:155–166
Petranka JW, Francis RA (2013) Effects of road salts on seasonal wetlands: poor prey performance may compromise growth of predatory salamanders. Wetlands 33:707–715
Pijanowska J, Stolpe G (1996) Summer diapause in Daphnia as a reaction to the presence of fish. J Plankton Res 18:1407–1412
Pitcher TJ (1983) Heuristic definitions of fish shoaling behavior. Anim Behav 31:611–613
Relyea RA (2003) Predator cues and pesticides: a double dose of danger for amphibians. Ecol Appl 13:1515–1521
Relyea RA (2004) Synergistic impacts of malathion and predatory stress on six species of North American tadpoles. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1080–1084
Relyea RA (2005) The lethal impacts of roundup and predatory stress on six species of North American tadpoles. Arch Environ Con Tox 48:351–357
Relyea RA, Mills N (2001) Predator-induced stress makes the pesticide carbaryl more deadly to gray treefrog tadpoles (Hyla versicolor). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2491–2496
Sanzo D, Hecnar SJ (2006) Effects of road de-icing salt (NaCl) on larval wood frogs (Rana sylvatica). Environ Pollut 140:247–256
Scott GR, Sloman KA (2004) The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat Toxicol 68:369–392
Searle CL, Shaw CL, Hunsberger KK, Prado M, Duffy MA (2016) Salinization decreases population densities of the freshwater crustacean, Daphnia dentifera. Hydrobiologia 770:165–172
Slusarczyk M (1999) Predator-induced diapause in Daphnia magna may require two chemical cues. Oecologia 119:159–165
Stoler AB, Walker BM, Hintz WD, Jones DK, Lind L, Mattes BM, Schuler MS, Relyea RA (2017) Combined effects of road salt and an insecticide on wetland communities. Environ Toxicol Chem 36:771–779
Thunqvist EL (2004) Regional increase of mean chloride concentration in water due to the application of deicing salt. Sci Total Environ 325:29–37
USEPA (1988) Ambient water quality criteria for chloride—1988. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington
Van Meter RJ, Swan CM, Leips J, Snodgrass JW (2011a) Road salt stress induces novel food web structure and interactions. Wetlands 31:843–851
Van Meter RJ, Swan CM, Snodgrass JW (2011b) Salinization alters ecosystem structure in urban stormwater detention ponds. Urban Ecosyst 14:723–736
Walsh JR, Carpenter SR, Vander Zanden MJ (2016) Invasive species triggers a massive loss of ecosystem services through a trophic cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:4081–4085
Wellborn GA, Skelly DK, Werner EE (1996) Mechanisms creating community structure across a freshwater habitat gradient. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 27:337–363
Wisenden BD, Sargent RC (1997) Antipredator behaviour and suppressed aggression by convict cichlids in response to injury-released chemical cues of conspecifics but not to those of an allopatric heterospecific. Ethology 103:283–291
Acknowledgements
We thank Jeff Inglee of the Warren County Fish Hatchery for providing experimental fish. This study was funded by the Jefferson Project at Lake George, a collaboration between Rensselear Polytechnic Institute, IBM, and The Fund for Lake George. We also thank Brian Mattes for culturing zooplankton and Justin Rappold, Jeevan Narendran, Skylar Carter, and Alex Brooks for their help setting up and taking down the experiments.
Data availability statement
The datasets during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contribution statement
WDH and RAR conceived and designed the experiments. WDH performed the experiments and analyzed the data. WDH and RAR wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Joel Trexler.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hintz, W.D., Relyea, R.A. A salty landscape of fear: responses of fish and zooplankton to freshwater salinization and predatory stress. Oecologia 185, 147–156 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-017-3925-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-017-3925-1