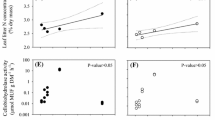
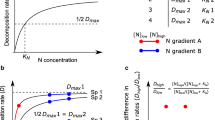
Abstract
Leaf litter decomposition plays a major role in nutrient dynamics in forested streams. The chemical composition of litter affects its processing by microorganisms, which obtain nutrients from litter and from the water column. The balance of these fluxes is not well known, because they occur simultaneously and thus are difficult to quantify separately. Here, we examined C and N flow from streamwater and leaf litter to microbial biofilms during decomposition. We used isotopically enriched leaves (13C and 15N) from two riparian foundation tree species: fast-decomposing Populus fremontii and slow-decomposing Populus angustifolia, which differed in their concentration of recalcitrant compounds. We adapted the isotope pool dilution method to estimate gross elemental fluxes into litter microbes. Three key findings emerged: litter type strongly affected biomass and stoichiometry of microbial assemblages growing on litter; the proportion of C and N in microorganisms derived from the streamwater, as opposed to the litter, did not differ between litter types, but increased throughout decomposition; gross immobilization of N from the streamwater was higher for P. fremontii compared to P. angustifolia, probably as a consequence of the higher microbial biomass on P. fremontii. In contrast, gross immobilization of C from the streamwater was higher for P. angustifolia, suggesting that dissolved organic C in streamwater was used as an additional energy source by microbial assemblages growing on slow-decomposing litter. These results indicate that biofilms on decomposing litter have specific element requirements driven by litter characteristics, which might have implications for whole-stream nutrient retention.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argerich A, Martí E, Sabater F, Ribot M, von Schiller D, Riera JL (2008) Combined effects of leaf litter inputs and a flood on nutrient retention in a Mediterranean mountain stream during fall. Limnol Oceanogr 53:631–641
Battin TJ, Kaplan LA, Findlay S, Hopkinson CS, Mart E, Packman AI, Newbold JD, Sabater F (2009) Biophysical controls on organic carbon fluxes in fluvial networks. Nat Geosci 2:595
Benfield EF (2006) Decompostion of leaf material. In: Hauer FR, Lamberti GA (eds) Methods in stream ecology. Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 711–720
Boecklen WJ, Yarnes CT, Cook BA, James AC (2011) On the use of stable isotopes in trophic ecology. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 42:411–440
Bott TL, Kaplan LA, Kuserk FT (1984) Benthic bacterial biomass supported by streamwater dissolved organic matter. Microb Ecol 10:335–344
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842
Caraco NF, Lampman G, Cole JJ et al (1998) Microbial assimilation of DIN in a nitrogen rich estuary: implications for food quality and isotope studies. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 167:59–71
Carreiro MM, Sinsabaugh RL, Repert DA, Parkhurst DF (2000) Microbial enzyme shifts explain litter decay responses to simulated nitrogen deposition. Ecology 81:2359–2365
Casciotti KL, Sigman DM, Galanter Hastings M, Böhlke K, Hilkert A (2002) Measurement of the oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate in seawater and freshwater using the denitrifier method. Anal Chem 74:4905–4912
Cheever BM, Webster JR, Bilger EE, Thomas SA (2013) The relative importance of exogenous and substrate-derived nitrogen for microbial growth during leaf decomposition. Ecology 94:1614–1625
Compson Z, Hungate B, Koch G, Hart S, Maestas J, Adams K, Whitham T, Marks J (2014) Closely related tree species differentially influence the transfer of carbon and nitrogen from leaf litter up the aquatic food web. Ecosystems (in revision)
Cornwell WK, Cornelissen JHC, Amatangelo K, Dorrepaal E, Eviner VT, Godoy O, Hobbie SE, Hoorens B, Kurokawa H, Pérez-Harguindeguy N, Quested HM, Santiago LS, Wardle DA, Wright IJ, Aerts R, Allison SD, van Bodegom P, Brovkin V, Chatain A, Callaghan TV, Díaz S, Garnier E, Gurvich DE, Kazakou E, Klein JA, Read J, Reich PB, Soudzilovskaia NA, Vaieretti MV, Westoby M (2008) Plant species traits are the predominant control on litter decomposition rates within biomes worldwide. Ecol Lett 11:1065–1071
Danger M, Cornut J, Chauvet E, Chavez P, Elger A, Lecerf A (2013) Benthic algae stimulate leaf litter decomposition in detritus-based headwater streams: a case of aquatic priming effect? Ecology 94:1604–1613
De Boer W, Folman LB, Summerbell RC, Boddy L (2005) Living in a fungal world: impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:795–811
Dodds WK, Martí E, Tank JL, Pontius J, Hamilton SK, Grimm NB, Bowden WB, McDowell WH, Peterson BJ, Valett HM, Webster JR, Gregory S (2004) Carbon and nitrogen stoichiometry and nitrogen cycling rates in streams. Oecologia 140:458–467
Driebe EM, Whitham TG (2000) Cottonwood hybridization affects tannin and nitrogen content of leaf litter and alters decomposition. Oecologia 123:99–107
Enriquez S, Duarte CM, Sand-Jensen K (1993) Patterns in decomposition rates among photosynthetic organisms: the importance of detritus C:N:P content. Oecologia 94:457–471
Ferreira V, Castagneyrol B, Koricheva, Gulis JV, Chauvet E, and Graça MAS (2014) A meta-analysis of the effects of nutrient enrichment on litter decomposition in streams. Biol Rev (in press)
Findlay S, Strayer D, Goumbala C, Gould K (1993) Metabolism of streamwater dissolved organic carbon in the shallow hyporheic zone. Limnol Oceanogr 38:1493–1499
Findlay S, Tank JL, Valett HM, Mulholland PJ, McDowell WH, Johnson SL, Hamilton S, Edmonds J, Dodds WK, Bowden WB (2002) A cross-system comparison of bacterial and fungal biomass in detritus pools of headwater streams. Microb Ecol 43:55–66
Fischer H, Sachse A, Steinberg CEW, Pusch M (2002) Differential retention and utilization of dissolved organic carbon by bacteria in river sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 47:1702–1711
Fisher SG, Likens GE (1973) Energy flow in bear brook, new hampshire: an integrative approach to stream ecosystem metabolism. Ecol Monogr 43:421–439
Frossard A, Gerull L, Mutz M, Gessner MO (2013) Litter supply as a driver of microbial activity and community structure on decomposing leaves: a test in experimental streams. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4965–4973
Gessner MO (1997) Fungal biomass, production and sporulation associated with particulate organic matter in streams. Limnetica 13:33–44
Gessner MO, Chauvet E (1994) Importance of stream microfungi in controlling breakdown rates of leaf litter. Ecology 75:1807–1817
Gessner MO, Swan CM, Dang CK, McKie BG, Bardgett RD, Wall DH, Hättenschwiler S (2010) Diversity meets decomposition. Trends Ecol Evol 25:372–380
Gruber N, Galloway JN (2008) An Earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451:293–296
Gulis V, Suberkropp K (2003) Leaf litter decomposition and microbial activity in nutrient-enriched and unaltered reaches of a headwater stream. Freshwater Biol 48:123–134
Hart SC, Nason GE, Myrold DD, Perry DA (1994) Dynamics of gross nitrogen transformations in an old-growth forest: the carbon connection. Ecology 75:880–891
Holeski LM, Hillstrom ML, Whitham TG, Lindroth RL (2012) Relative importance of genetic, ontogenetic, induction, and seasonal variation in producing a multivariate defense phenotype in a foundation tree species. Oecologia 170:695–707
Holmes RM, McClelland JW, Sigman DM, Fry B, Peterson BJ (1998) Measuring 15N−NH4 + in marine, estuarine and fresh waters: an adaptation of the ammonia diffusion method for samples with low ammonium concentrations. Mar Chem 60:235–243
Kaplan LA, Wiegner TN, Newbold JD, Ostrom PH, Gandhi H (2008) Untangling the complex issue of dissolved organic carbon uptake: a stable isotope approach. Freshwater Biol 53:855–864
Kirkham D, Bartholomew WV (1954) Equations for following nutrient transformations in soil, utilizing tracer data. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 18:33–34
Kohlmeier S, Smits THM, Ford RM, Keel C, Harms H, Wick LY (2005) Taking the fungal highway: mobilization of pollutant-degrading bacteria by fungi. Environ Sci Technol 39:4640–4646
LeRoy CJ, Whitham TG, Keim P, Marks JC (2006) Plant genes link forests and streams. Ecology 87:255–261
LeRoy CJ, Whitham TG, Wooley SC, Marks JC (2007) Within-species variation in foliar chemistry influences leaf-litter decomposition in a Utah river. J North Am Benthol Soc 26:426–438
Melillo JM, Naiman RJ, Aber JD, Linkins AE (1984) Factors controlling mass loss and nitrogen dynamics of plant litter decaying in northern streams. Bull Mar Sci 35:341–356
Meyer JL, Johnson C (1983) The influence of elevated nitrate concentration on rate of leaf decomposition in a stream. Freshwater Biol 13:177–183
Meyer JL, Wallace JB, Eggert SL (1998) Leaf litter as a source of dissolved organic carbon in streams. Ecosystems 1:240–249
Moorhead DL, Sinsabaugh RL (2006) A theoretical model of litter decay and microbial interaction. Ecol Monogr 76:151–174
Mulholland PJ, Newbold JD, Elwood JW, Ferren LA, Webster JR (1985) Phosphorus spiralling in a woodland stream: seasonal variations. Ecology 66:1012–1023
Mulholland PJ, Tank JL, Sanzone DM, Wollheim WM, Peterson BJ, Webster JR, Meyer JL (2000) Nitrogen cycling in a forest stream determined by a 15N tracer addition. Ecol Monogr 70:471–493
Murphy DV, Recous S, Stockdale EA, Fillery IRP, Jensen LS, Hatch DJ, Goulding KWT (2003) Gross nitrogen fluxes in soil: theory, measurement and application of 15 N pool dilution techniques. Adv Agron 79:69–118
Parton W, Silver WL, Burke IC, Grassens L, Harmon ME, Currie WS, King JY, Adair EC, Brandt LA, Hart SC, Fasth B (2007) Global-scale similarities in nitrogen release patterns during long-term decomposition. Science 315:361–364
Peterson BJ, Wollheim WM, Mulholland PJ, Webster JR, Meyer JL, Tank JL, Martí E, Bowden WD, Valett HM, Hershey AE, McDowell WH, Dodds WK, Hamilton SK, Gregory S, Morrall DD (2001) Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science 292:86–90
Phillips DL, Gregg JW (2003) Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too many sources. Oecologia 136:261–269
R Development Core Team (2012) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0. http://www.R-project.org
Rier ST, Shirvinski JM, Kinek KC (2014) In situ light and phosphorus manipulations reveal potential role of biofilm algae in enhancing enzyme-mediated decomposition of organic matter in streams. Freshwater Biol 59:1039–1051
Romaní AM, Fischer H, Mille-Lindblom C, Tranvik LJ (2006) Interactions of bacteria and fungi on decomposing litter: differential extracellular enzyme activities. Ecology 87:2559–2569
Sanzone DM, Tank JL, Meyer JL, Mulholland PJ, Findlay SEG (2001) Microbial incorporation of nitrogen in stream detritus. Hydrobiologia 464:27–35
Schweitzer JA, Bailey JK, Rehill BJ, et al. (2004) Genetically based trait in a dominant tree affects ecosystem processes. Ecol Lett 7:127–134
Schweitzer JA, Madritch MD, Bailey JK, Rehill BJ, Martinsen GD, Hart SC, Lindroth RL, Keim P, Whitham TG (2008) From genes to ecosystems: the genetic basis of condensed tannins and their role in nutrient regulation in a Populus model system. Ecosystems 11:1005–1020
Sinsabaugh RL, Antibus RK, Linkins AE, McClaugherty CA, Rayburn L, Weiland T (1993) Wood decomposition: nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in relation to extracellular enzyme activity. Ecology 74:1586–1593
Sobczak WV, Findlay S (2002) Variation in bioavailability of dissolved organic carbon among stream hyporheic flowpaths. Ecology 83:3194–3209
Stelzer RS, Heffernan J, Likens GE (2003) The influence of dissolved nutrients and particulate organic matter quality on microbial respiration and biomass in a forest stream. Freshwater Biol 48:1925–1937
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Strickland MS, Rousk J (2010) Considering fungal:bacterial dominance in soils—methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1385–1395
Suberkropp K, Chauvet E (1995) Regulation of leaf breakdown by fungi in streams: influences of water chemistry. Ecology 76:1433–1445
Talbot JM, Treseder KK (2012) Interactions among lignin, cellulose, and nitrogen drive litter chemistry-decay relationships. Ecology 93:345–354
Tank JL, Meyer JL, Sanzone DM, Mulholland PJ, Webster JR, Peterson BJ, Wolheim WM, Leonard NE (2000) Analysis of nitrogen cycling in a forest stream during autumn using a 15N-tracer addition. Limnol Oceanogr 45:1013–1029
Tank JL, Rosi-Marshall EJ, Griffiths NA, Entrekin SA, Stephen ML (2010) A review of allochthonous organic matter dynamics and metabolism in streams. J North Am Benthol Soc 29:118–146
Taylor BR, Parkinson D, Parsons WFJ (1989) Nitrogen and lignin content as predictors of litter decay rates: a microcosm test. Ecology 70:97–104
Tranvik LJ, Downing JA, Cotner JB, Loiselle SA, Striegl RG, Ballatore TJ, Dillon P, Finlay K, Fortino K, Knoll LB, Kortelainen PL, Kutser T, Larsen S, Laurion I, Leech DM, McCallister SL, McKnight DM, Melack JM, Overholt E, Porter JA, Prairie Y, Renwick WH, Roland F, Sherman BS, Schindler DW, Sobek S, Tremblay A, Vanni MJ, Verschoor AM, von Wachenfeldt E, Weyhenmeyer GA (2009) Lakes and reservoirs as regulators of carbon cycling and climate. Limnol Oceanogr 54:2298–2314
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Vannote RL, Minshall GW, Cummins KW, Sedell JR, Cushing CE (1980) The river continuum concept. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 37:130–137
Wallace JB, Eggert SL, Meyer JL, Webster JR (1997) Multiple trophic levels of a forest stream linked to terrestrial litter inputs. Science 277(80):102–104
Webster JR, Benfield EF (1986) Vascular plant breakdown in freshwater ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 17:567–594
Whitham TG, Bailey JK, Schweitzer JA, Shuster SM, Bangert RK, LeRoy CJ, Lonsdorf EV, Allan GJ, DiFazio SP, Potts BM, Fischer DG, Gehring CA, Lindroth RL, Marks JC, Hart SC, Wimp GM, Wooley SC (2006) A framework for community and ecosystem genetics: from genes to ecosystems. Nat Rev Genet 7:510–523
Wiegner TN, Kaplan LA, Newbold JD (2005) Contribution of dissolved organic C to stream metabolism: a mesocosm study using 13C-enriched tree-tissue leachate. J North Am Benthol Soc 24:48–67
Woodward G, Gessner MO, Giller PS, Gulis V, Hladyz S, Lecerf A, Malmqvist B, McKie BG, Tiegs SD, Cariss H, Dobson M, Elosegi A, Ferreira V, Graça MAS, Fleituch T, Lacoursière JO, Nistorescu M, Pozo J, Risnoveanu G, Schindler M, Vadineanu A, Vought LB-M, Chauvet E (2012) Continental-scale effects of nutrient pollution on stream ecosystem functioning. Science 336:1438–1440
Wymore AS, Compson ZG, Liu CM, Price LB, Whitham TG, Keim P, Marks JC (2013) Contrasting rRNA gene abundance patterns for aquatic fungi and bacteria in response to leaf-litter chemistry. Freshwater Sci 32:663–672
Acknowledgments
We thank the Marks, Sabater and Martí labs for their support and feedback on this study. Dr Susana Bernal, Dr Bob Hall and two anonymous reviewers provided helpful comments on an early draft of this manuscript. The Coconino Forest Service provided us with access to sites near Oak Creek. The National Science Foundation provided funding through the Frontiers in Integrative Biological Research (DEB-0425908), Integrative Graduate Education and Research Traineeship (DGE-0549505), and Ecosystem Studies (DEB-1120343) research programs. Funding was also provided by the MED-FORESTSTREAMS (CGL2011-30590-C02-01) project. A. P. was supported by a Formación de Personal Investigador Ph.D. fellowship from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation within the context of ISONEF (CGL2008-05504-C02-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Robert O. Hall.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pastor, A., Compson, Z.G., Dijkstra, P. et al. Stream carbon and nitrogen supplements during leaf litter decomposition: contrasting patterns for two foundation species. Oecologia 176, 1111–1121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-014-3063-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-014-3063-y