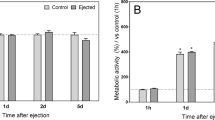
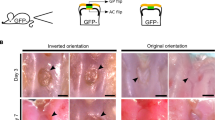
Abstract.
A transgenic rat was used as a transplantation donor to simulate autologous transplantation. The sex-matched transplantation between a female transgenic and a wild-type rat can theoretically be regarded as an autologous transplantation due to the genetic agreement of these rats except for the non-protein-producing transgenes. Transgene-containing synovial cells were tracked in the joint using this autologous transplantation model. The transgenes in the donor synovial cells were detected using in situ hybridization (ISH), while mitotic activities were simultaneously examined by immunodetection of 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU). A defect was generated in the knee joint capsule of a Fischer 344 (wild-type) rat. The synovium of a transgenic rat was sutured to the defect of the wild-type rat in group 1 and was allowed to free float in the joint in group 2. A large number of BrdU-labeled, transgene-containing synovial cells were detected in both groups at 3 days. The number of these cells then decreased, but they could still be identified even at 4 weeks after autologous transplantation. These results indicated that transplanted synovial cells were viable in the joint for at least 4 weeks. Furthermore, the transgenic rat was shown to be an effective animal model for distinguishing the extrinsic from the intrinsic cells in the cellular intermixed tissues in vivo. The combined method of ISH for detecting transgene-containing cells and the immunohistochemistry of BrdU for detecting proliferating cells was also shown to be effective for tracking the viability of extrinsic cells after autologous transplantation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, N., Takai, S., Morita, N. et al. A method of tracking donor cells after simulated autologous transplantation: a study using synovial cells of transgenic rats. Cell Tissue Res 298, 519–525 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004419900095
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004419900095