Abstract
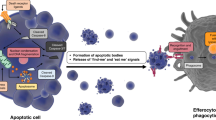
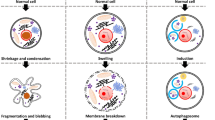
The concept of apoptotic cell death as an essential part of the development and life of complex organisms has been devised in different situations and tested from various angles. This review article discusses the morphological changes during death by apoptosis. In cells undergoing apoptosis, an intracellular signalling pathway operates cell autonomously to implement the death and disposal of the cell. The similarity of the biochemical events during apoptosis in different situations is reflected by a high uniformity of morphological changes in many situations of naturally occurring or experimentally induced cell death. The unifying concept of apoptosis has been derived from the observation of this morphological consistency of dying cells almost 30 years ago. Since then, we have learned much about the intracellular signalling in the apoptotic process and the molecular background has been delineated which guides the initiation of the morphological changes. Here, an attempt is made to present the current knowledge about the molecular events in the development of these morphological alterations and to place these changes in the context of apoptotic cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Häcker, G. The morphology of apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res 301, 5–17 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410000193
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410000193