Abstract
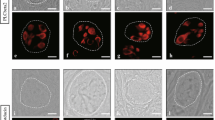
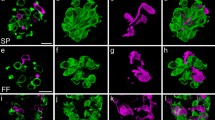
Mammalian taste bud cells are composed of several distinct cell types and differentiated from surrounding tongue epithelial cells. However, the detailed mechanisms underlying their differentiation have yet to be elucidated. In the present study, we examined an Ascl1-expressing cell lineage using circumvallate papillae (CVP) of newborn mice and taste organoids (three-dimensional self-organized tissue cultures), which allow studying the differentiation of taste bud cells in fine detail ex vivo. Using lineage-tracing analysis, we observed that Ascl1 lineage cells expressed type II and III taste cell markers both CVP of newborn mice and taste organoids. However, the coexpression rate in type II cells was lower than that in type III cells. Furthermore, we found that the generation of the cells which express type II and III cell markers was suppressed in taste organoids lacking Ascl1-expressing cells. These findings suggest that Ascl1-expressing precursor cells can differentiate into both type III and a subset of type II taste cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the relevant data is provided in this manuscript and associated figures.
References
Barlow LA (2021) The sense of taste: development, regeneration, and dysfunction. Wires Mech Dis 14:e1547
Barlow LA (2015) Progress and renewal in gustation: new insights into taste bud development. Development 142:3620–3629
Barlow LA, Klein OD (2015) Developing and regenerating a sense of taste. In: Current Topics in Developmental Biology. Elsevier, pp 401–419
Beidler LM, Smallman RL (1965) Renewal of cells within taste buds. J Cell Biol 27:263–272
Castillo-Azofeifa D, Losacco JT, Salcedo E, Golden EJ, Finger TE, Barlow LA (2017) Sonic hedgehog from both nerves and epithelium is a key trophic factor for taste bud maintenance. Development 144:3054–3065
Chandrashekar J, Yarmolinsky D, von Buchholtz L, Oka Y, Sly W, Ryba NJ, Zucker CS (2009) The taste of carbonation. Science 326:443–445
Chaudhari N, Roper SD (2010) The cell biology of taste. J Cell Biol 190:285–296
Clapp TR, Yang R, Stoick CL, Kinnamon SC, Kinnamon JC (2004) Morphologic characterization of rat taste receptor cells that express components of the phospholipase C signaling pathway. J Comp Neurol 468:311–321
DeFazio RA, Dvoryanchikov G, Maruyama Y, KimJW PE, Roper SD, Chaudhari N (2006) Separate populations of receptor cells and presynaptic cells in mouse taste buds. J Neurosci 26:3971–3980
Delay RJ, Kinnamon JC, Roper SD (1986) Ultrastructure of mouse vallate taste buds: II. Cell types and cell lineage. J Comp Neurol 253:242–252
Farbman AI (1980) Renewal of taste bud cells in rat circumvallate papillae. Cell Tissue Kinet 13:349–357
Finger TE, Simon SA (2000) Cell biology of taste epithelium. In: Finger TE, Silver WL, Restrepo D (eds) The Neurobiology of Taste and Smell. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 287–314
Gaillard D, Xu M, Liu F, Millar SE, Barlow LA (2015) β-catenin signaling biases multipotent lingual epithelial progenitors to differentiate and acquire specific taste cell fates. PLOS Genet 11:e1005208
Golden EJ, Larson ED, Shechtman LA, Trahan GD, Gaillard D, Fellin TJ, Scott JK, Jones KL, Barlow LA (2021) Onset of taste bud cell renewal starts at birth and coincides with a shift in SHH function. eLife 10:e64013
Guillemot F, Joyner AL (1993) Dynamic expression of the murine Achaete-Scute homologue Mash-1 in the developing nervous system. Mech Dev 42:171–185
Guillemot F, Lo LC, Johnson JE, Auerbach A, Anderson DJ, Joyner AL (1993) Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is required for the early development of olfactory and autonomic neurons. Cell 75:463–476
Hsu CC, Seta Y, Matsuyama K, Kataoka S, Nakatomi M, Toyono T, Gunjigake KK, Kuroishi KN, Kawamoto T (2021) Mash1-expressing cells may be relevant to type III cells and a subset of PLCβ2-positive cell differentiation in adult mouse taste buds. Cell Tissue Res 383:667–675
Huang AL, Chen X, Hoon MA, Chandrashekar J, Guo W, Tränkner D, Ryba NJP, Zuker CS (2006) The cells and logic for mammalian sour taste detection. Nature 442:934–938
Huang YA, Maruyama Y, Stimac R, Roper SD (2008) Presynaptic (type III) cells in mouse taste buds sense sour (acid) taste: sour taste mechanisms in mouse taste buds. J Physiol 586:2903–2912
Kim MR, Kusakabe Y, Miura H, Shindo Y, Ninomiya Y, Hino A (2003) Regional expression patterns of taste receptors and gustducin in the mouse tongue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312:500–506
Kito-Shingaki A, Seta Y, Toyono T, Kataoka S, Kakinoki Y, Yanagawa Y, Toyoshima K (2014) Expression of GAD67 and Dlx5 in the taste buds of mice genetically lacking Mash1. Chem Senses 39:403–414
Lindeman B (1996) Taste reception. Physiol Rev 76:719–766
Lin X, Lu C, Ohmoto M, Choma K, Margolskee RF, Matsumoto I, Jiang P (2021) R-spondin substitutes for neuronal input for taste cell regeneration in adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 118:e2001833118
Lo LC, Johnson JE, Wuenschell CW, Saito T, Anderson DJ (1991) Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is transiently expressed by spatially restricted subsets of early neuroepithelial and neural crest cells. Genes Dev 5:1524–1537
Matsumoto I, Ohmoto M, Narukawa M, Yoshihara Y, Abe K (2011) Skn-1a (Pou2f3) specifies taste receptor cell lineage. Nat Neurosci 14:685–687
Matsumura H, Hasuwa H, Inoue N, Ikawa M, Okabe M (2004) Lineage-specific cell disruption in living mice by Cre-mediated expression of diphtheria toxin A chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321:275–279
Mistretta CM, Bosma JF (1972) Topographical and histological study of the developing rat tongue, palate and taste buds. Third Symp Oral Sensat Percept Mouth Infant Springf I1:163–187
Miura H, Kato H, Kusakabe Y, Ninomiya Y, Hino A (2005) Temporal changes in NCAM immunoreactivity during taste cell differentiation and cell lineage relationships in taste buds. Chem Senses 30:367–375
Miura H, Kusakabe Y, Harada S (2006) Cell lineage and differentiation in taste buds. Arch Histol Cytol 69:209–225
Miura H, Scott JK, Harada S, Barlow LA (2014) Sonic hedgehog-expressing basal cells are general post-mitotic precursors of functional taste receptor cells. Dev Dyn 243:1286–1297
Murray R (1973) The ultrastructure of taste buds. In: Friedmann I (ed) The Ultrastructure of Sensory Organs. North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 1–81
Nakayama A, Miura H, Shindo Y, Kusakabe Y, Tomonari H, Harada S (2008) Expression of the basal cell markers of taste buds in the anterior tongue and soft palate of the mouse embryo. J Comp Neurol 509:211–224
Nguyen HM, Barlow LA (2010) Differential expression of a BMP4 reporter allele in anterior fungiform versus posterior circumvallate taste buds of mice. BMC Neurosci 11:129
Ohmoto M, Kitamoto S, Hirota J (2021) Expression of Eya1 in mouse taste buds. Cell Tissue Res 383:979–986
Perea-Martinez I, Nagai T, Chaudhari N (2013) Functional cell types in taste buds have distinct longevities. PLoS ONE 8:e53399
Qin Y, Sukumaran SK, Jyotaki M et al (2018) Gli3 is a negative regulator of Tas1r3-expressing taste cells. PLOS Genet 14:e1007058
Ren W, Aihara E, Lei W, Gheewala N, Uchiyama H, Margolskee RF, Iwatsuki K, Jiang P (2017) Transcriptome analyses of taste organoids reveal multiple pathways involved in taste cell generation. Sci Rep 7:4004
Ren W, Lewandowski BC, Watson J, Aihara E, Iwatsuki K, Bachmanov AA, Margolskee RF, Jiang P (2014) Single Lgr5- or Lgr6-expressing taste stem/progenitor cells generate taste bud cells ex vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:16401–16406
Schuurmans C, Guillemot F (2002) Molecular mechanisms underlying cell fate specification in the developing telencephalon. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:26–34
Seta Y, Kataoka S, Toyono T, Toyoshima K (2007) Immunohistochemical localization of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase in mouse taste buds and developing taste papillae. Histochem Cell Biol 127:415–422
Seta Y, Oda M, Kataoka S, Toyono T, Toyoshima K (2011) Mash1 is required for the differentiation of AADC-positive type III cells in mouse taste buds. Dev Dyn 240:775–784
Seta Y, Seta C, Barlow LA (2003) Notch-associated gene expression in embryonic and adult taste papillae and taste buds suggests a role in taste cell lineage decisions. J Comp Neurol 464:49–61
Seta Y, Stoick-Cooper CL, Toyono T, Kataoka S, Toyoshima K, Barlow LA (2006) The bHLH transcription factors, Hes6 and Mash1, are expressed in distinct subsets of cells within adult mouse taste buds. Arch Histol Cytol 69:189–198
Stone LM, Finger TE, Tam PP, Tan SS (1995) Taste receptor cells arise from local epithelium, not neurogenic ectoderm. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92:1916–1920
Takagi H, Seta Y, Kataoka S, Nakatomi M, Toyono T, Kawamoto T (2018) Mash1-expressing cells could differentiate to type III cells in adult mouse taste buds. Anat Sci Int 93:422–429
Takai S, Watanabe Y, Sanematsu K, Yoshida R, Margolskee RF, Jiang P, Atsuta I, Koyano K, Ninomiya Y, Shigemura N (2019) Effects of insulin signaling on mouse taste cell proliferation. PLoS ONE 14:e0225190
Tomita K, Nakanishi S, Guillemot F, Kageyama R (1996) Mash1 promotes neuronal differentiation in the retina. Genes Cells 1:765–774
Yang R, Stoick CL, Kinnamon JC (2004) Synaptobrevin-2-like immunoreactivity is associated with vesicles at synapses in rat circumvallate taste buds. J Comp Neurol 471:59–71
Yee KK, Li Y, Redding KM, Iwatsuki K, Margolskee RF, Jiang P (2013) Lgr5-EGFP marks taste bud stem/progenitor cells in posterior tongue. Stem Cells Dayt Ohio 31:992–1000
Zhou Y, Liu H-X, Mistretta CM (2006) Bone morphogenetic proteins and noggin: inhibiting and inducing fungiform taste papilla development. Dev Biol 297:198–213
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Jeffrey Whitsett (University of Cincinnati) for the R-spondin2 stable cell line, Dr. Hans Clevers (Hubrecht Institute) and Dr. Toshiro Sato (Keio University) for the Wnt3a stable cell line, and Dr. Peihua Jiang (Monell Chemical Senses Center) for the Noggin stable cell line. We thank Ms. M. Ishikawa for secretarial assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI grant JP20K18461.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.S., conceptualization and study design; K.M., S.T., N.S., T.T., and Y.S., methodology; K.M., S.K., and T.T., investigation; K.M., T.T., and Y.S., project administration; K.M., M.N., and S.K., visualization; K.M., writing—original draft; Y.S., T.K., and M.N., writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were approved by Kyushu Dental University Animal Care (approval No: 20–03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuyama, K., Takai, S., Shigemura, N. et al. Ascl1-expressing cell differentiation in initially developed taste buds and taste organoids. Cell Tissue Res 392, 631–641 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-023-03756-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-023-03756-8