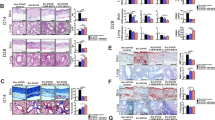
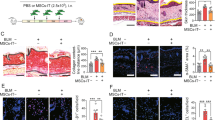
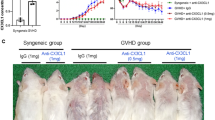
Abstract
Systemic sclerosis associated with lung interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) is the most common cause of death among patients with SSc. Mesenchymal stem cell (MSCs) transplantations had been treated by SSc patients that showed in the previous case report. The therapeutic mechanisms and effects of MSCs on SSc-ILD are still obscure. In this study, we investigated the therapeutic effects and mechanisms of treatment of BM-MSC derived from C57BL/6 on the topoisomerase I (TOPO I) induced SSc-ILD-like mice model. The mice were immunized with a mixture of recombinant human TOPO I in PBS solution (500 U/mL) and completed Freund’s adjuvant [CFA; 1:1 (volume/volume)] twice per week for 9 weeks. On week 10, the mice were sacrificed to analyze the related pathological parameters. Lung and skin pathologies were analyzed using histochemical staining. CD4 T-helper (TH) cell differentiation in lung and skin-draining lymph nodes was detected using flow cytometry. Our results revealed that allogeneic and syngeneic MSCs exhibited similar repressive effects on TOPO I-induced IgG1 and IgG2a in the SSc group. After intravascular (IV) treatment with syngeneic or allogeneic MSCs, the dermal thickness and fibrosis dramatically condensed and significantly reduced airway hyperresponsiveness. These findings showed that both allogeneic and syngeneic MSCs have therapeutic potential for SSc-ILD.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boonstra M, Bakker JA, Grummels A, Ninaber MK, Marsan NA, Wortel CM, Huizinga TWJ, Jordan S, Hoffman-Vold AM, Distler O, Toes REM, Scherer HU, de Vries-Bouwstra JK (2020) Association of anti-topoisomerase I antibodies of the IgM isotype with disease progression in anti-topoisomerase I-positive systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 72:1897–1904
Brembilla NC, Montanari E, Truchetet ME, Raschi E, Meroni P, Chizzolini C (2013) Th17 cells favor inflammatory responses while inhibiting type I collagen deposition by dermal fibroblasts: differential effects in healthy and systemic sclerosis fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 15(5)
Chang YD, Li CH, Tsai CH, Cheng YW, Kang JJ, Lee CC (2020) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficiency enhanced airway inflammation and remodeling in a murine chronic asthma model. Faseb J 34:15300–15313
Chizzolini C, Parel Y, Scheja A, Dayer JM (2006) Polarized subsets of human T-helper cells induce distinct patterns of chemokine production by normal and systemic sclerosis dermal fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R10
Cipriani P, Di Benedetto P, Liakouli V, Del Papa B, Di Padova M, Di Ianni M, Marrelli A, Alesse E, Giacomelli R (2013) Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from scleroderma patients (SSc) preserve their immunomodulatory properties although senescent and normally induce T regulatory cells (Tregs) with a functional phenotype: implications for cellular-based therapy. Clin Exp Immunol 173:195–206
Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, Milanesi M, Longoni PD, Matteucci P, Grisanti S, Gianni AM (2002) Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood 99:3838–3843
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini FC, Krause DS, Deans RJ, Keating A, Prockop DJ, Horwitz EM (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317
Fan Y, Bender S, Shi W, Zoz D (2020) Incidence and prevalence of systemic sclerosis and systemic sclerosis with interstitial lung disease in the United States. J Manag Care Spec Pharm 26:1539–1547
Fuschiotti P (2016) Current perspectives on the immunopathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Immunotargets Ther 5:21–35
Goh NS, Desai SR, Veeraraghavan S, Hansell DM, Copley SJ, Maher TM, Corte TJ, Sander CR, Ratoff J, Devaraj A, Bozovic G, Denton CP, Black CM, du Bois RM, Wells AU (2008) Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: a simple staging system. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:1248–1254
Hamelmann E, Schwarze J, Takeda K, Oshiba A, Larsen GL, Irvin CG, Gelfand EW (1997) Noninvasive measurement of airway responsiveness in allergic mice using barometric plethysmography. Am J Resp Crit Care 156:766–775
Hénault J, Tremblay M, Clément I, Raymond Y, Senécal JL (2004) Direct binding of anti-DNA topoisomerase I autoantibodies to the cell surface of fibroblasts in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 50:3265–3274
Jacobs SA, Roobrouck VD, Verfaillie CM, Van Gool SW (2013) Immunological characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells and multipotent adult progenitor cells. Immunol Cell Biol 91:32–39
Koenig M, Joyal F, Fritzler MJ, Roussin A, Abrahamowicz M, Boire G, Goulet JR, Rich E, Grodzicky T, Raymond Y, Senécal JL (2008) Autoantibodies and microvascular damage are independent predictive factors for the progression of Raynaud’s phenomenon to systemic sclerosis: a twenty-year prospective study of 586 patients, with validation of proposed criteria for early systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 58:3902–3912
Kumamoto M, Nishiwaki T, Matsuo N, Kimura H, Matsushima K (2009) Minimally cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate fibrotic lung injury. Eur Respir J 34:740–748
Kuwana M, Kaburaki J, Mimori T, Kawakami Y, Tojo T (2000) Longitudinal analysis of autoantibody response to topoisomerase I in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum-Us 43:1074–1084
Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, Locatelli F, Roelofs H, Lewis I, Lanino E, Sundberg B, Bernardo ME, Remberger M, Dini G, Egeler RM, Bacigalupo A, Fibbe W, Ringden O, Developmental Committee of the European Group for B, Marrow T (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet 371:1579–1586
Lee CC, Lin CL, Leu SJ, Lee YL (2018a) Overexpression of Notch ligand Delta-like-1 by dendritic cells enhances their immunoregulatory capacity and exerts antiallergic effects on Th2-mediated allergic asthma in mice. Clin Immunol 187:58–67
Lee K, Park N, Jung H, Rim YA, Nam Y, Lee J, Park SH, Ju H (2018b) Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental arthritis via expression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Plos One 13(2)
Lee SH, Jang AS, Kim YE, Cha JY, Kim TH, Jung S, Park SK, Lee YK, Won JH, Kim YH, Park CS (2010) Modulation of cytokine and nitric oxide by mesenchymal stem cell transfer in lung injury/fibrosis. Resp Res 11
Lee YL, Chang YD, Liu CW, Lee CC (2020) Extract of Pyrus nivalis enhances phagocytosis in lungs after particles matter exposure in BALB/c mice. J Food Biochem e13469
Lei L, Zhao C, Qin F, He ZY, Wang X, Zhong XN (2016) Th17 cells and IL-17 promote the skin and lung inflammation and fibrosis process in a bleomycin-induced murine model of systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 34:S14–S22
Machado CV, Telles PD, Nascimento IL (2013) Immunological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter 35(1):62–67
Maria ATJ, Maumus M, Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C, Noel D, Guilpain P (2017) Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in autoimmune disorders: state of the art and perspectives for systemic sclerosis. Clin Rev Allerg Immu 52:234–259
Maria ATJ, Toupet K, Bony C, Pirot N, Vozenin MC, Petit B, Roger P, Batteux F, Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C, Noel D, Guilpain P (2016) Antifibrotic, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells in HOCl-induced systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:1013–1025
Maria ATJ, Toupet K, Maumus M, Rozier P, Vozenin MC, Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C, Noel D, Guilpain P (2018) Fibrosis development in HOCl-induced systemic sclerosis: a multistage process hampered by mesenchymal stem cells. Front Immunol 9:2571
Martinet L, Fleury-Cappellesso S, Gadelorge M, Dietrich G, Bourin P, Fournié JJ, Poupot R (2009) A regulatory cross-talk between Vgamma9Vdelta2 T lymphocytes and mesenchymal stem cells. Eur J Immunol 39:752–762
Maumus M, Guerit D, Toupet K, Jorgensen C, Noel D (2011) Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies in regenerative medicine: applications in rheumatology. Stem Cell Res Ther 2:14
Mehta H, Goulet PO, Nguyen V, Perez G, Koenig M, Senecal JL, Sarfati M (2016) Topoisomerase I peptide-loaded dendritic cells induce autoantibody response as well as skin and lung fibrosis. Autoimmunity 49:503–513
Meyer KC (2018) Scleroderma with fibrosing interstitial lung disease: where do we stand? Ann Am Thorac Soc 15:1273–1275
Nemeth K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PST, Mayer B, Parmelee A, Doi K, Robey PG, Leelahavanichkul K, Koller BH, Brown JM, Hu XZ, Jelinek I, Star RA, Mezey E (2009) Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E-2-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nature Medicine 15:42–49
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, Gaupp D, Baddoo M, Kaminski N, Phinney DG (2003) Mesenchymal stem cell engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin exposure and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. P Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8407–8411
Reveille JD, Solomon DH (2003) Evidence-based guidelines for the use of immunologic tests: anticentromere, Scl-70, and nucleolar antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 49:399–412
Rojas M, Xu JG, Woods CR, Mora AL, Spears W, Roman J, Brigham KL (2005) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in repair of the injured lung. Am J Resp Cell Mol 33:145–152
Rozier P, Maria A, Goulabchand R, Jorgensen C, Guilpain P, Noel D (2018) Mesenchymal stem cells in systemic sclerosis: allogenic or autologous approaches for Therapeutic ase? Front Immunol 9:2938
Senécal JL, Hénault J, Raymond Y (2005) The pathogenic role of autoantibodies to nuclear autoantigens in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). J Rheumatol 32:1643–1649
Shackelford C, Long G, Wolf J, Okerberg C, Herbert R (2002) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of nonneoplastic lesions in toxicology studies. Toxicol Pathol 30:93–96
Sotiropoulou PA, Perez SA, Gritzapis AD, Baxevanis CN, Papamichail M (2006) Interactions between human mesenchymal stem cells and natural killer cells. Stem Cells 24:74–85
Taki ZGE, Thilly W, Yaseen B, Lopez H, Mirza M, Hassuji Z, Vigneswaran S, Ahmed Abdi B, Hart A, Arumalla N, Thomas G, Denton CP, Suleman Y, Liu H, Venturini C, O’Reilly S, Xu S, Stratton R (2020) Pathogenic activation of mesenchymal stem cells is induced by the disease microenvironment in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 72:1361–1374
Truchetet ME, Brembilla NC, Montanari E, Allanore Y, Chizzolini C (2011) Increased frequency of circulating Th22 in addition to Th17 and Th2 lymphocytes in systemic sclerosis: association with interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Res Therapy 13(5)
Valenzi E, Bulik M, Tabib T, Morse C, Sembrat J, Trejo Bittar H, Rojas M, Lafyatis R (2019) Single-cell analysis reveals fibroblast heterogeneity and myofibroblasts in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis 78:1379–1387
Wang CN, Lin YC, Chang BC, Chen CH, Wu R, Lee CC (2019) Targeting the phosphorylation site of myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate alleviates symptoms in a murine model of steroid-resistant asthma. Brit J Pharmacol 176:1122–1134
Wang JL, Ren HZ, Yuan XW, Ma HC, Shi XL, Ding YT (2018) Interleukin-10 secreted by mesenchymal stem cells attenuates acute liver failure through inhibiting pyroptosis. Hepatol Res 48:E194–E202
Wolf D, Wolf AM (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells as cellular immunosuppressants. Lancet 371:1553–1554
Wynn TA (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol 214:199–210
Yew TL, Chang MC, Hsu YT, He FY, Weng WH, Tsai CC, Chiu FY, Hung SC (2013) Efficient expansion of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone marrow under hypoxic conditions. J Tissue Eng Regen M 7:984–993
Yim J, Koh J, Kim S, Song SG, Ahn HK, Kim YA, Jeon YK, Chung DH (2020) Effects of B7–H3 expression on tumour-infiltrating immune cells and clinicopathological characteristics in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer 133:74–85
Yoshizaki A, Yanaba K, Ogawa A, Asano Y, Kadono T, Sato S (2011) Immunization with DNA topoisomerase I and Freund’s complete adjuvant induces skin and lung fibrosis and autoimmunity via interleukin-6 signaling. Arthritis Rheum-Us 63:3575–3585
Zhao F, Zhang YF, Liu YG, Zhou JJ, Li ZK, Wu CG, Qi HW (2008) Therapeutic effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells engraftment on bleomycin-induced lung injury in rats. Transpl P 40:1700–1705
Funding
This work was supported by China Medical University (CMU108-S-28, CMU108-MF-78, CMU109-MF-84, and CMU110-MF-12). Financial support was provided by the Drug Development Center, China Medical University, from the Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan. Experiments and data analysis were performed in part using the Medical Research Core Facilities, Office of Research and Development at China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This study was designed, directed, and coordinated by C.-C.L. In addition, C.-C.L. provided conceptual and manuscript editing, performed the experiments, modulated the animal models, analyzed the data, and wrote and edited the manuscript. N.G, Y-D.C, S-C.H, J-L L, J-W L, and S-T. F conducted experiments and the data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The Animal Care and Use Committee of the China Medical University approved protocols for animal experiments (Protocol No. 2020–264).
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ganesan, N., Chang, YD., Hung, SC. et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppressed skin and lung inflammation and fibrosis in topoisomerase I-induced systemic sclerosis associated with lung disease mouse model. Cell Tissue Res 391, 323–337 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03716-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03716-8