Abstract
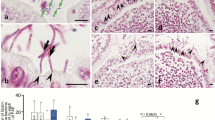
The composition of fecal bacteria is reported to change throughout the day, whereas the circadian rhythmicity of indigenous bacteria that settle on the epithelium is mostly unknown. The present study aimed to clarify the diurnal changes in the settlement of indigenous bacteria in the rat alimentary tract using histological analysis. The settlement of indigenous bacteria on the mucosal epithelium throughout the day and the diurnal changes in settlement levels were observed in the esophagus, the nonglandular area of the stomach, and the ileum. The peak of zeitgeber time (ZT) in the settlement level differed by segment: ZT 12 in the esophagus, ZT 6 in the nonglandular area of the stomach, and ZT 0 in the ileum. Moreover, 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing using tissue sections revealed that the compositions of the indigenous bacteria in the ileum differed among ZT. In the intervillous spaces of the ileum, the formation level of the mucus layer, one of the most fundamental host defenses against bacteria, was lowest at ZT 0. Bacteria were preferentially adjacent to the villous epithelium in the area without coverage by the mucus layer at ZT 0. These findings collectively suggest that the settlement level and possibly the composition of the indigenous bacteria changed diurnally in various segments of the alimentary tract, and the formation of the mucus layer might be the most likely to lead to such diurnal changes in indigenous bacteria, at least in the ileum.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano K, Hayashi H, Araki Y, Ito E (1977) The action of lysozyme on peptidoglycan with N-unsubstituted glucosamine residues. Isolation of glycan fragments and their susceptibility to lysozyme. Eur J Biochem 76:299–307
Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Ando M, Kamada N, Nagano Y, Narushima S, Suda W, Imaoka A, Setoyama H, Nagamori T, Ishikawa E, Shima T, Hara T, Kado S, Jinnohara T, Ohno H, Kondo T, Toyooka K, Watanabe E, Yokoyama S, Tokoro S, Mori H, Noguchi Y, Morita H, Ivanov II, Sugiyama T, Nuñez G, Camp JG, Hattori M, Umesaki Y, Honda K (2015) Th17 cell induction by adhesion of microbes to intestinal epithelial cells. Cell 163:367–380
Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Oshima K, Suda W, Nagano Y, Nishikawa H, Fukuda S, Saito T, Narushima S, Hase K, Kim S, Fritz JV, Wilmes P, Ueha S, Matsushima K, Ohno H, Olle B, Sakaguchi S, Taniguchi T, Morita H, Hattori M, Honda K (2013) Treg induction by a rationally selected mixture of Clostridia strains from the human microbiota. Nature 500:232–236
Bergstrom K, Shan X, Casero D, Batushansky A, Lagishetty V, Jacobs JP, Hoover C, Kondo Y, Shao B, Gao L, Zandberg W, Noyovitz B, McDaniel JM, Gibson DL, Pakpour S, Kazemian N, McGee S, Houchen CW, Rao CV, Griffin TM, Sonnenburg JL, McEver RP, Braun J, Xia L (2020) Proximal colon-derived O-glycosylated mucus encapsulates and modulates the microbiota. Science 370:467–472
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT, Callahan BJ, Caraballo-Rodríguez AM, Chase J, Cope EK, Da Silva R, Diener C, Dorrestein PC, Douglas GM, Durall DM, Duvallet C, Edwardson CF, Ernst M, Estaki M, Fouquier J, Gauglitz JM, Gibbons SM, Gibson DL, Gonzalez A, Gorlick K, Guo J, Hillmann B, Holmes S, Holste H, Huttenhower C, Huttley GA, Janssen S, Jarmusch AK, Jiang L, Kaehler BD, Kang KB, Keefe CR, Keim P, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koester I, Kosciolek T, Kreps J, Langille MGI, Lee J, Ley R, Liu YX, Loftfield E, Lozupone C, Maher M, Marotz C, Martin BD, McDonald D, McIver LJ, Melnik AV, Metcalf JL, Morgan SC, Morton JT, Naimey AT, Navas-Molina JA, Nothias LF, Orchanian SB, Pearson T, Peoples SL, Petras D, Preuss ML, Pruesse E, Rasmussen LB, Rivers A, Robeson MS 2nd, Rosenthal P, Segata N, Shaffer M, Shiffer A, Sinha R, Song SJ, Spear JR, Swafford AD, Thompson LR, Torres PJ, Trinh P, Tripathi A, Turnbaugh PJ, Ul-Hasan S, van der Hooft JJJ, Vargas F, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Vogtmann E, von Hippel M, Walters W, Wan Y, Wang M, Warren J, Weber KC, Williamson CHD, Willis AD, Xu ZZ, Zaneveld JR, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, Knight R, Caporaso JG (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857
Collins J, Borojevic R, Verdu EF, Huizinga JD, Ratcliffe EM (2014) Intestinal microbiota influence the early postnatal development of the enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil 26:98–107
Crowley M, Bovet J (1980) Social synchronization of circadian rhythms in deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 7:99–105
Davis CP, Savage DC (1974) Habitat, succession, attachment, and morphology of segmented, filamentous microbes indigenous to the murine gastrointestinal tract. Infect Immun 10:948–956
Del-Pozo J, Turnbull J, Ferguson H, Crumlish M (2010) A comparative molecular study of the presence of “Candidatus arthromitus” in the digestive system of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), healthy and affected with rainbow trout gastroenteritis. J Fish Dis 33:241–250
Duncan K, Carey-Ewend K, Vaishnava S (2021) Spatial analysis of gut microbiome reveals a distinct ecological niche associated with the mucus layer. Gut Microbes 13:e1874815
Goodrich JK, Waters JL, Poole AC, Sutter JL, Koren O, Blekhman R, Beaumont M, Van Treuren W, Knight R, Bell JT, Spector TD, Clark AG, Ley RE (2014) Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 159:789–799
Hastings MH, Maywood ES, Brancaccio M (2018) Generation of circadian rhythms in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Nat Rev Neurosci 19:453–469
Hattori T, Arizono N (1988) Cell kinetics and secretion of mucus in the gastrointestinal mucosa, and their diurnal rhythm. J Clin Gastroenterol 1:S1–S6
Hoogerwerf WA, Hellmich HL, Cornélissen G, Halberg F, Shahinian VB, Bostwick J, Savidge TC, Cassone VM (2007) Clock gene expression in the murine gastrointestinal tract: endogenous rhythmicity and effects of a feeding regimen. Gastroenterology 133:1250–1260
Inamoto T, Namba M, Qi WM, Yamamoto K, Yokoo Y, Miyata H, Kawano J, Yokoyama T, Hoshi N, Kitagawa H (2008) An immunohistochemical detection of actin and myosin in the indigenous bacteria-adhering sites of microvillous columnar epithelial cells in Peyer’s patches and intestinal villi in the rat jejunoileum. J Vet Med Sci 70:1153–1158
Kabouridis PS, Lasrado R, McCallum S, Chng SH, Snippert HJ, Clevers H, Pettersson S, Pachnis V (2015) Microbiota controls the homeostasis of glial cells in the gut lamina propria. Neuron 85:289–295
Karlsson FH, Tremaroli V, Nookaew I, Bergström G, Behre CJ, Fagerberg B, Nielsen J, Bäckhed F (2013) Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature 498:99–103
Klaasen HL, Van der Heijden PJ, Stok W, Poelma FG, Koopman JP, Van den Brink ME, Bakker MH, Eling WM, Beynen AC (1993) Apathogenic, intestinal, segmented, filamentous bacteria stimulate the mucosal immune system of mice. Infect Immun 61:303–306
Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa JA, Org E, Sheehy BT, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Li L, Smith JD, DiDonato JA, Chen J, Li H, Wu GD, Lewis JD, Warrier M, Brown JM, Krauss RM, Tang WH, Bushman FD, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL (2013) Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med 19:576–585
Leone V, Gibbons SM, Martinez K, Hutchison AL, Huang EY, Cham CM, Pierre JF, Heneghan AF, Nadimpalli A, Hubert N, Zale E, Wang Y, Huang Y, Theriault B, Dinner AR, Musch MW, Kudsk KA, Prendergast BJ, Gilbert JA, Chang EB (2015) Effects of diurnal variation of gut microbes and high-fat feeding on host circadian clock function and metabolism. Cell Host Microbe 17:681–689
Liang X, Bushman FD, FitzGerald GA (2015) Rhythmicity of the intestinal microbiota is regulated by gender and the host circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:10479–10484
Lipinski JH, Zhou X, Gurczynski SJ, Erb-Downward JR, Dickson RP, Huffnagle GB, Moore BB, O’Dwyer DN (2021) Cage environment regulates gut microbiota independent of Toll-like receptors. Infect Immun 89:e0018721
Mantani Y, Nishida M, Yamamoto K, Miyamoto K, Yuasa H, Masuda N, Omotehara T, Tsuruta H, Yokoyama T, Hoshi KH (2018) Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study on the lamina propria cells beneath Paneth cells in the rat ileum. Anat Rec 301:1074–1085
McVey Neufeld KA, Mao YK, Bienenstock J, Foster JA, Kunze WA (2013) The microbiome is essential for normal gut intrinsic primary afferent neuron excitability in the mouse. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:183-e88
Mukherji A, Kobiita A, Ye T, Chambon P (2013) Homeostasis in intestinal epithelium is orchestrated by the circadian clock and microbiota cues transduced by TLRs. Cell 153:812–827
Nagara Y, Takada T, Nagata Y, Kado S, Kushiro A (2017) Microscale spatial analysis provides evidence for adhesive monopolization of dietary nutrients by specific intestinal bacteria. PLoS ONE 12:e0175497
Pansu D, Berard A, Dechelette MA, Lambert R (1974) Influence of secretin and pentagastrin on the circadian rhythm of cell proliferation in the intestinal mucosa in rats. Digestion 11:266–274
Pelaseyed T, Bergström JH, Gustafsson JK, Ermund A, Birchenough GM, Schütte A, van der Post S, Svensson F, Rodríguez-Piñeiro AM, Nyström EE, Wising C, Johansson ME, Hansson GC (2014) The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol Rev 260:8–20
Qi WM, Yamamoto K, Yokoo Y, Miyata H, Inamoto T, Udayanga KGS, Kawano J, Yokoyama T, Hoshi N, Kitagawa H (2009) Histoplanimetrical study on the relationship between the cell kinetics of villous columnar epithelial cells and the proliferation of indigenous bacteria in rat small intestine. J Vet Med Sci 71:463–470
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D, Peng Y, Zhang D, Jie Z, Wu W, Qin Y, Xue W, Li J, Han L, Lu D, Wu P, Dai Y, Sun X, Li Z, Tang A, Zhong S, Li X, Chen W, Xu R, Wang M, Feng Q, Gong M, Yu J, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Hansen T, Sanchez G, Raes J, Falony G, Okuda S, Almeida M, LeChatelier E, Renault P, Pons N, Batto JM, Zhang Z, Chen H, Yang R, Zheng W, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Nielsen R, Pedersen O, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2012) A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 490:55–60
Riba A, Olier M, Lacroix-Lamandé S, Lencina C, Bacquié V, Harkat C, Gillet M, Baron M, Sommer C, Mallet V, Salvador-Cartier C, Laurent F, Théodorou V, Ménard S (2017) Paneth cell defects induce microbiota dysbiosis in mice and promote visceral hypersensitivity. Gastroenterology 153:1594–1606
Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Cheng J, Duncan AE, Kau AL, Griffin NW, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Ilkayeva O, Semenkovich CF, Funai K, Hayashi DK, Lyle BJ, Martini MC, Ursell LK, Clemente JC, Van Treuren W, Walters WA, Knight R, Newgard CB, Heath AC, Gordon JI (2013) Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 341:1241214
Sigdestad CP, Lesher S (1971) Photo-reversal of the circadian rhythm in the proliferative activity of the mouse small intestine. J Cell Physiol 78:121–126
Sjögren YM, Jenmalm MC, Böttcher MF, Björkstén B, Sverremark-Ekström E (2009) Altered early infant gut microbiota in children developing allergy up to 5 years of age. Clin Exp Allergy 39:518–526
Snel J, Heinen PP, Blok HJ, Carman RJ, Duncan AJ, Allen PC, Collins MD (1995) Comparison of 16S rRNA sequences of segmented filamentous bacteria isolated from mice, rats, and chickens and proposal of “Candidatus Arthromitus.” Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:780–782
Takayasu L, Suda W, Takanashi K, Iioka E, Kurokawa R, Shindo C, Hattori Y, Yamashita N, Nishijima S, Oshima K, Hattori M (2017) Circadian oscillations of microbial and functional composition in the human salivary microbiome. DNA Res 24:261–270
Thaiss CA, Levy M, Korem T, Dohnalová L, Shapiro H, Jaitin DA, David E, Winter DR, Gury-BenAri M, Tatirovsky E, Tuganbaev T, Federici S, Zmora N, Zeevi D, Dori-Bachash M, Pevsner-Fischer M, Kartvelishvily E, Brandis A, Harmelin A, Shibolet O, Halpern Z, Honda K, Amit I, Segal E, Elinav E (2016) Microbiota diurnal rhythmicity programs host transcriptome oscillations. Cell 167:1495–1510
Thaiss CA, Zeevi D, Levy M, Zilberman-Schapira G, Suez J, Tengeler AC, Abramson L, Katz MN, Korem T, Zmora N, Kuperman Y, Biton I, Gilad S, Harmelin A, Shapiro H, Halpern Z, Segal E, Elinav E (2014) Transkingdom control of microbiota diurnal oscillations promotes metabolic homeostasis. Cell 159:514–529
Wada M, Orihara K, Kamagata M, Hama K, Sasaki H, Haraguchi A, Miyakawa H, Nakao A, Shibata S (2017) Circadian clock-dependent increase in salivary IgA secretion modulated by sympathetic receptor activation in mice. Sci Rep 7:8802
Wilhelm MJ, Sheffield JB, Sharifian GhM, Wu Y, Spahr C, Gonella G, Xu B, Dai HL (2015) Gram’s stain does not cross the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. ACS Chem Biol 10:1711–1717
Wu G, Tang W, He Y, Hu J, Gong S, He Z, Wei G, Lv L, Jiang Y, Zhou H, Chen P (2018) Light exposure influences the diurnal oscillation of gut microbiota in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 501:16–23
Yamamoto K, Qi WM, Yokoo Y, Miyata H, Udayanga KGS, Kawano J, Yokoyama T, Hoshi N, Kitagawa H (2009) Histoplanimetrical study on the spatial relationship of distribution of indigenous bacteria with mucosal lymphatic follicles in alimentary tract of rat. J Vet Med Sci 71:621–630
Yokoo Y, Miyata H, Udayanga KGS, Qi WM, Takahara E, Mantani Y, Kawano J, Yokoyama T, Hoshi N, Kitagawa H (2011) Immunohistochemical and histoplanimetrical study on the spatial relationship between the settlement of indigenous bacteria and the secretion of bactericidal peptides in rat alimentary tract. J Vet Med Sci 73:1043–1050
Yu S, Balasubramanian I, Laubitz D, Tong K, Bandyopadhyay S, Lin X, Flores J, Singh R, Liu Y, Macazana C, Zhao Y, Béguet-Crespel F, Patil K, Midura-Kiela MT, Wang D, Yap GS, Ferraris RP, Wei Z, Bonder EM, Häggblom MM, Zhang L, Douard V, Verzi MP, Cadwell K, Kiela PR, Gao N (2020) Paneth cell-derived lysozyme defines the composition of mucolytic microbiota and the inflammatory tone of the intestine. Immunity 53:398–416
Zarrinpar A, Chaix A, Yooseph S, Panda S (2014) Diet and feeding pattern affect the diurnal dynamics of the gut microbiome. Cell Metab 20:1006–1017
Acknowledgements
Gram-positive Staphylococcus epidermidis and Gram-negative Escherichia coli for evaluating the quantity of Gram-positive bacteria were kindly provided by Dr. Eiko Matsuo (Kobe University).
Funding
This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant numbers: 16K18813 and 20K15902) and by the Foundation of Kinoshita Memorial Enterprise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (permission number 30–05-01). All procedures in studies involving animals were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution (the Kobe University Animal Experimentation Regulations) or at the practice at which the studies were conducted.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakata, N., Mantani, Y., Nakanishi, S. et al. Histological study of diurnal changes in bacterial settlement in the rat alimentary tract. Cell Tissue Res 389, 71–83 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03626-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03626-9