Abstract
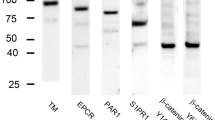
The immunolocalization of protease-activated receptors (PARs) and related proteins in splenic sinus endothelial cells was examined using immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. Immunofluorescence microscopy showed that PAR1 colocalized with PAR2, PAR3, and PAR4. PAR4 colocalized with PAR3 and P2Y12. Myosin heavy chain IIA localized to the outer shape and at the base of cells, but did not colocalize with α-catenin. The localization of di-phosphorylated myosin regulatory light chains (ppMLC) was partially detected on the outer circumference and conspicuously at the base of cells. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) also localized in cells. Immunogold electron microscopy revealed the localization of PAR1 on the caveolar membrane, plasma membrane, and junctional membrane of cells. PAR2 and PAR3 localized to the plasma membrane of cells. PAR4 localized to the plasma membrane, depressions in the plasma membrane, and cytoplasmic vesicles. PpMLC was detected in stress fibers, but rarely near the adherens junctions of neighboring cells. MIF localized in vesicles on the apical and basal sides of the Golgi apparatus. Electron microscopy of endothelial cells with saponin extraction showed the depression of many coated pits formed by clathrin from the plasma membrane. Stress fibers developed at the base of cells; however, few actin filaments were observed near adherens junctions. These results indicate that PARs play important roles in splenic sinus endothelial cells, such as in endothelial barrier protection and the maintenance of firm adhesion to ring fibers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arachiche A, Mumaw MM, de la Fuente M, Nieman MT (2013) Protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) and PAR4 heterodimers are required for PAR1-enhanced cleavage of PAR4 by α-thrombin. J Biol Chem 288:32553–32562
Burnier L, Mosnier LO (2013) Novel mechanisms for activated protein C cytoprotective activities involving noncanonical activation of protease-activated receptor 3. Blood 122:807–816
Cheng Q, McKeown SJ, Santos L, Santiago FS, Khachigian LM, Morand EF, Hickey MJ (2010) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor increases leukocyte-endothelial interactions in human endothelial cells via promotion of expression of adhesion molecules. J Immunol 185:1238–1247
Duluc L, Wojciak-Stothard B (2014) Rho GTPases in the regulation of pulmonary vascular barrier function. Cell Tissue Res 355:675–685
Gloushankova NA, Rubtsova SN, Zhitnyak IY (2017) Cadherin-mediated cell-cell interactions in normal and cancer cells. Tissue Barr 5:e1356900
Golomb E, Ma X, Jana SS, Preston YA, Kawamoto S, Shoham NG, Goldin E, Conti MA, Sellers JR, Adelstein RS (2004) Identification and characterization of nonmuscle myosin II-C, a new member of the myosin II family. J Biol Chem 279:2800–2808
Hirano M, Hirano K (2016) Myosin di-phosphorylation and peripheral actin bundle formation as initial events during endothelial barrier disruption. Sci Rep 6:20989
Hong S, Troyanovsky RB, Troyanovsky SM (2013) Binding to F-actin guides cadherin cluster assembly, stability, and movement. J Cell Biol 201:131–143
Kawabata A, Kuroda R, Nakaya Y, Kawai K, Nishikawa H, Kawao N (2001) Factor Xa-evoked relaxation in rat aorta: involvement of PAR-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 282:432–435
Li D, D’Angelo L, Chavez M, Woulfe DS (2011) Arrestin-2 differentially regulates PAR4 and ADP receptor signaling in platelets. J Biol Chem 286:3805–3814
McLaughlin JN, Patterson MM, Malik AB (2007) Protease-activated receptor-3 (PAR3) regulates PAR1 signaling by receptor dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:5662–5667
Nakanishi-Matsui M, Zheng YW, Sulciner DJ, Weiss EJ, Ludeman MJ, Coughlin SR (2000) PAR3 is a cofactor for PAR4 activation by thrombin. Nature 404:609–613
Nieman MT (2016) Protease-activated receptors in hemostasis. Blood 128:169–177
O’Brien PJ, Prevost N, Molino M, Hollinger MK, Woolkalis MJ, Woulfe DS, Brass LF (2000) Thrombin responses in human endothelial cells. Contributions from receptors other than PAR1 include the transactivation of PAR2 by thrombin-cleaved PAR1. J Biol Chem 275:13502–13509
Rezaie AR (2014) Protease-activated receptor signalling by coagulation proteases in endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 112:876–882
Saitoh T, Takemura S, Ueda K, Hosoya H, Nagayama M, Haga H, Kawabata K, Yamagishi A, Takahashi M (2001) Differential localization of non-muscle myosin II isoforms and phosphorylated regulatory light chains in human MRC-5 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett 509:365–369
Shikata Y, Birukov KG, Birukova AA, Verin A, Garcia JG (2003) Involvement of site-specific FAK phosphorylation in sphingosine-1 phosphate- and thrombin-induced focal adhesion remodeling: role of Src and GIT. Faseb j 17:2240–2249
Shimizu T, Nishihira J, Watanabe H, Abe R, Honda A, Ishibashi T, Shimizu H (2004) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is induced by thrombin and factor Xa in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 279:13729–13737
Smith TH, Li JG, Dores MR, Trejo J (2017) Protease-activated receptor-4 and purinergic receptor P2Y12 dimerize, co-internalize, and activate Akt signaling via endosomal recruitment of β-arrestin. J Biol Chem 292:13867–13878
Steiniger BS (2015) Human spleen microanatomy: why mice do not suffice. Immunology 145:334–346
Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M, Etzrodt M, Wildgruber M, Cortez-Retamozo V, Panizzi P, Figueiredo JL, Kohler RH, Chudnovskiy A, Waterman P, Aikawa E, Mempel TR, Libby P, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2009) Identification of splenic reservoir monocytes and their deployment to inflammatory sites. Science 325:612–616
Taylor PR, Martinez-Pomares L, Stacey M, Lin HH, Brown GD, Gordon S (2005) Macrophage receptors and immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 23:901–944
Uehara K, Miyoshi M (1999) Stress fiber networks in sinus endothelial cells in the rat spleen. Anat Rec 254:22–27
Uehara K, Uehara A (2010) Vimentin intermediate filaments: the central base in sinus endothelial cells of the rat spleen. Anat Rec (hoboken) 293:2034–2043
Uehara K, Uehara A (2014) Integrin alphavbeta5 in endothelial cells of rat splenic sinus: an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res 356:183–193
Uehara K, Uehara A (2016) Differentiated localizations of phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase in endothelial cells of rat splenic sinus. Cell Tissue Res 364:611–622
Uehara K, Uehara A (2021) Immunohistochemical study of dissociation and association of adherens junctions in splenic sinus endothelial cells. Cell Tissue Res 384:25–33
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All animals used in the present study were processed according to the animal welfare regulations of Japan. All processes were approved by the Committee of Experimental Animals of Fukuoka University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uehara, K., Uehara, A. Immunolocalization of protease-activated receptors in endothelial cells of splenic sinuses. Cell Tissue Res 386, 605–615 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-021-03535-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-021-03535-3