Abstract
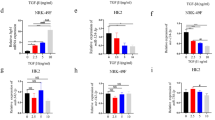
Although growing advances have been made in the regulation of lupus nephritis recently, lupus nephritis is still one of the major causes of death in SLE patients and the pathogenesis remains largely unknown. Therefore, exploring the pathological mechanisms is urgently needed for designing and developing novel therapeutic strategies for lupus nephritis. Human renal mesangial cells (HRMCs) were transfected with sh-NEAT1, miR-146b mimic, pcDNA-NEAT1, miR-146b inhibitor, or sh-TRAF6 to modify their expression. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used to induce inflammatory injury. Cell viability was examined with CCK8. Apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry and Hoechst staining. qRT-PCR and western blot were used to analyze gene expression. The secretion of inflammatory cytokines was examined with ELISA. The bindings of NEAT1 with miR-146b and miR-146b with TRAF6 were tested by dual-luciferase reporter assay. NEAT1 was upregulated in LPS-treated HRMCs. Both the knockdown of NEAT1 and TRAF6 suppressed the LPS-induced inflammatory injury in HRMCs. NEAT1 directly targeted miR-146b to control miR-146b-mediated regulation of TRAF6 expression in HRMCs. NEAT1 promoted the expression of TRAF6 via targeting miR-146b to accelerate the LPS-mediated renal mesangial cell injury in HRMCs. Moreover, TRAF6 activated the NF-κB signaling in HRMCs. NEAT1 accelerated renal mesangial cell injury via directly targeting miR-146b, promoting the expression of TRAF6, and activating the NF-κB signaling in lupus nephritis. Our investigation elucidated novel pathological mechanisms and provided potential therapeutic targets for lupus nephritis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almaani S, Meara A, Rovin BH (2017) Update on lupus nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 12:825–835
Bao Z, Yang Z, Huang Z, Zhou Y, Cui Q, Dong D (2019) LncRNADisease 2.0: an updated database of long non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D1034–D1037
Butler AA, Johnston DR, Kaur S, Lubin FD (2019) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 mediates neuronal histone methylation and age-related memory impairment. Sci Signal 12
Cesana M, Daley GQ (2013) Deciphering the rules of ceRNA networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:7112–7113
Choi Y (2005) Role of TRAF6 in the immune system. Adv Exp Med Biol 560:77–82
Ding YH, Song YD, Wu YX, He HQ, Yu TH, Hu YD, Zhang DP, Jiang HC, Yu KK, Li XZ, Sun L, Qian F (2019) Isoalantolactone suppresses LPS-induced inflammation by inhibiting TRAF6 ubiquitination and alleviates acute lung injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40:64–74
Geng H, Tan XD (2016) Functional diversity of long non-coding RNAs in immune regulation. Genes Dis 3:72–81
Heward JA, Lindsay MA (2014) Long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of the immune response. Trends Immunol 35:408–419
Huang X, Zhong R, He X, Deng Q, Peng X, Li J, Luo X (2019) Investigations on the mechanism of progesterone in inhibiting endometrial cancer cell cycle and viability via regulation of long noncoding RNA NEAT1/microRNA-146b-5p mediated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. IUBMB Life 71:223–234
Ji S, Wang S, Zhao X, Lv L (2019) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 regulates the development of osteosarcoma through sponging miR-34a-5p to mediate HOXA13 expression as a competitive endogenous RNA. Mol Genet Genomic Med 7:e673
Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow MK, Touma Z, Urowitz MB, van Vollenhoven R, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Hughes G (2016) Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16039
Liao Z, Ye Z, Xue Z, Wu L, Ouyang Y, Yao C, Cui C, Xu N, Ma J, Hou G, Wang J, Meng Y, Yin Z, Liu Y, Qian J, Zhang C, Ding H, Guo Q, Qu B, Shen N (2019) Identification of renal long non-coding RNA RP11-2B6.2 as a positive regulator of type I interferon signaling pathway in lupus nephritis. Front Immunol 10:975
Lisnevskaia L, Murphy G, Isenberg D (2014) Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 384:1878–1888
Liu B, Sun L, Liu Q, Gong C, Yao Y, Lv X, Lin L, Yao H, Su F, Li D, Zeng M, Song E (2015a) A cytoplasmic NF-kappaB interacting long noncoding RNA blocks IkappaB phosphorylation and suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell 27:370–381
Liu J, Xu J, Li H, Sun C, Yu L, Li Y, Shi C, Zhou X, Bian X, Ping Y, Wen Y, Zhao S, Xu H, Ren L, An T, Wang Q, Yu S (2015b) miR-146b-5p functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting TRAF6 and predicts the prognosis of human gliomas. Oncotarget 6:29129–29142
Liu K, Chen K, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Yan Y, Guo C, Qi J, Yang K, Wang F, Huang P, Guo L, Deng L, Li C (2019) TRAF6 neddylation drives inflammatory arthritis by increasing NF-kappaB activation. Lab Invest 99:528–538
Magilnick N, Reyes EY, Wang WL, Vonderfecht SL, Gohda J, Inoue JI, Boldin MP (2017) miR-146a-Traf6 regulatory axis controls autoimmunity and myelopoiesis, but is dispensable for hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis and tumor suppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E7140–E7149
Maroz N, Segal MS (2013) Lupus nephritis and end-stage kidney disease. Am J Med Sci 346:319–323
Matsumoto R, Dainichi T, Tsuchiya S, Nomura T, Kitoh A, Hayden MS, Ishii KJ, Tanaka M, Honda T, Egawa G, Otsuka A, Nakajima S, Sakurai K, Nakano Y, Kobayashi T, Sugimoto Y, Kabashima K (2018) Epithelial TRAF6 drives IL-17-mediated psoriatic inflammation. JCI Insight 3
Mello SS, Sinow C, Raj N, Mazur PK, Bieging-Rolett K, Broz DK, Imam JFC, Vogel H, Wood LD, Sage J, Hirose T, Nakagawa S, Rinn J, Attardi LD (2017) Neat1 is a p53-inducible lincRNA essential for transformation suppression. Genes Dev 31:1095–1108
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS (2009) Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 10:155–159
Molino C, Fabbian F, Longhini C (2009) Clinical approach to lupus nephritis: recent advances. Eur J Intern Med 20:447–453
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146:353–358
Sasaki YT, Ideue T, Sano M, Mituyama T, Hirose T (2009) MENepsilon/beta noncoding RNAs are essential for structural integrity of nuclear paraspeckles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2525–2530
Saxena R, Mahajan T, Mohan C (2011) Lupus nephritis: current update. Arthritis Res Ther 13:240
Shen P, Yang X, Jiang J, Wang X, Liang T, He L (2017) Wedelolactone from Eclipta alba inhibits lipopolysaccharide-enhanced cell proliferation of human renal mesangial cells via NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res 9:2132–2142
Walsh MC, Lee J, Choi Y (2015) Tumor necrosis factor receptor- associated factor 6 (TRAF6) regulation of development, function, and homeostasis of the immune system. Immunol Rev 266:72–92
Wu F, Zhang W, Li L, Zheng F, Shao X, Zhou J, Li H (2011) Inhibitory effects of honokiol on lipopolysaccharide-induced cellular responses and signaling events in human renal mesangial cells. Eur J Pharmacol 654:117–121
Wu GC, Pan HF, Leng RX, Wang DG, Li XP, Li XM, Ye DQ (2015a) Emerging role of long noncoding RNAs in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev 14:798–805
Wu Y, Zhang F, Ma J, Zhang X, Wu L, Qu B, Xia S, Chen S, Tang Y, Shen N (2015b) Association of large intergenic noncoding RNA expression with disease activity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 17:131
Wu GC, Li J, Leng RX, Li XP, Li XM, Wang DG, Pan HF, Ye DQ (2017) Identification of long non-coding RNAs GAS5, linc0597 and lnc-DC in plasma as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Oncotarget 8:23650–23663
Xu Y, Deng W, Zhang W (2018) Long non-coding RNA TUG1 protects renal tubular epithelial cells against injury induced by lipopolysaccharide via regulating microRNA-223. Biomed Pharmacother 104:509–519
Yao K, Lee SY, Peng C, Lim DY, Yamamoto H, Ryu J, Lim TG, Chen H, Jin G, Zhao Z, Han Y, Ma WY, Bode AM, Dong Z (2018) RSK2 is required for TRAF6 phosphorylation-mediated colon inflammation. Oncogene 37:3501–3513
Yung RL (1999) Mechanisms of lupus: the role of estrogens. Clin Exp Rheumatol 17:271–275
Zemmour D, Pratama A, Loughhead SM, Mathis D, Benoist C (2017) Flicr, a long noncoding RNA, modulates Foxp3 expression and autoimmunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E3472–E3480
Zhang F, Wu L, Qian J, Qu B, Xia S, La T, Wu Y, Ma J, Zeng J, Guo Q, Cui Y, Yang W, Huang J, Zhu W, Yao Y, Shen N, Tang Y (2016) Identification of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 as a novel inflammatory regulator acting through MAPK pathway in human lupus. J Autoimmun 75:96–104
Zhu LJ, Dai L, Zheng DH, Mo YQ, Ou-Yang X, Wei XN, Shen J, Zhang BY (2012) Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 correlated with synovitis severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 14:R133
Zhu Y, Xue Z, Di L (2017) Regulation of MiR-146a and TRAF6 in the diagnose of lupus nephritis. Med Sci Monit 23:2550–2557
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2018JJ6017), Hunan Provincial Health Planning Commission Research Project (B20180563).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Written informed permission was obtained from the patients and healthy donors. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hunan Provincial People’s Hospital/The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, LH., Xiao, B., Zhong, M. et al. LncRNA NEAT1 accelerates renal mesangial cell injury via modulating the miR-146b/TRAF6/NF-κB axis in lupus nephritis. Cell Tissue Res 382, 627–638 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03248-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03248-z