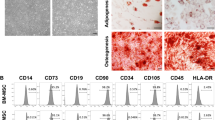
Abstract
In recent years, human umbilical cord blood has emerged as a rich source of stem, stromal and immune cells for cell-based therapy. Among the stem cells from umbilical cord blood, CD45+ multipotent stem cells and CD90+ mesenchymal stem cells have the potential to treat type I diabetes mellitus (T1DM), to correct autoimmune dysfunction and replenish β-cell numbers and function. In this review, we compare the general characteristics of umbilical cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells (UCB-SCs) and umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCB-MSCs) and introduce their applications in T1DM. Although there are some differences in surface marker expression between UCB-SCs and UCB-MSCs, the two cell types display similar functions such as suppressing function of stimulated lymphocytes and imparting differentiation potential to insulin-producing cells (IPCs) in the setting of low immunogenicity, thereby providing a promising and safe approach for T1DM therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi R, Moore R, Sakai S, Donnelly CB, Mounayar M, Sackstein R (2015) Hcell expression on murine MSC licenses pancreatotropism and confers durable reversal of autoimmune diabetes in nod mice. Stem Cells 33:1523–1531
Almici C, Carlo-Stella C, Wagner JE, Rizzoli V (1995) Umbilical cord blood as a source of hematopoietic stem cells: from research to clinical application. Haematologica 80:473–479
Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS, Michels AW (2014) Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 383:69–82
Barachini S, Trombi L, Danti S, D’Alessandro D, Battolla B, Legitimo A, Nesti C, Mucci I, D’Acunto M, Cascone MG, Lazzeri L, Mattii L, Consolini R, Petrini M (2009) Morpho-functional characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood for potential uses in regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Dev 18:293–305
Bhandari DR, Seo K-W, Sun B, Seo M-S, Kim H-S, Seo Y-J, Marcin J, Forraz N, Roy HL, Larry D, Colin M, Kang K-S (2011) The simplest method for in vitro β-cell production from human adult stem cells. Differentiation 82:144–152
Bieback K, Kern S, Klüter H, Eichler H (2004) Critical parameters for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells 22:625–634
Bluestone JA, Herold K, Eisenbarth G (2010) Genetics, pathogenesis and clinical interventions in type 1 diabetes. Nature 464:1293–1300
Broxmeyer HE, Douglas GW, Hangoc G, Cooper S, Bard J, English D, Arny M, Thomas L, Boyse EA (1989) Human umbilical cord blood as a potential source of transplantable hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:3828–3832
Bruni A, Gala-Lopez B, Pepper AR, Abualhassan NS, Shapiro AJ (2014) Islet cell transplantation for the treatment of type 1 diabetes: recent advances and future challenges. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 7:211–223
Cai J, Wu Z, Xu X, Liao L, Chen J, Huang L, Wu W, Luo F, Wu C, Pugliese A, Pileggi A, Ricordi C, Tan J (2016) Umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell with autologous bone marrow cell transplantation in established type 1 diabetes: a pilot randomized controlled open-label clinical study to assess safety and impact on insulin secretion. Diabetes Care 39:149–157
Cappellesso-Fleury S, Puissant-Lubrano B, Apoil P-A, Titeux M, Winterton P, Casteilla L, Bourin P, Blancher A (2010) Human fibroblasts share immunosuppressive properties with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Clin Immunol 30:607–619
Chang J-W, Hung S-P, Wu H-H, Wu W-M, Yang A-H, Tsai H-L, Yang L-Y, Lee OK (2011) Therapeutic effects of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in experimental lupus nephritis. Cell Transplant 20:245–257
Chatenoud L, Warncke K, Ziegler A-G (2012) Clinical immunologic interventions for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2
Davies JE, Walker JT, Keating A (2017) Concise review: Wharton’s jelly: the rich, but enigmatic, source of mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells Transl Med 6:1620–1630
Delgado E, Perez-Basterrechea M, Suarez-Alvarez B, Zhou H, Revuelta EM, Garcia-Gala JM, Perez S, Alvarez-Viejo M, Menendez E, Lopez-Larrea C, Tang R, Zhu Z, Hu W, Moss T, Guindi E, Otero J, Zhao Y (2015) Modulation of autoimmune t-cell memory by stem cell educator therapy: phase 1/2 clinical trial. EBioMedicine 2:2024–2036
Denner L, Bodenburg Y, Zhao JG, Howe M, Cappo J, Tilton RG, Copland JA, Forraz N, McGuckin C, Urban R (2007) Directed engineering of umbilical cord blood stem cells to produce C-peptide and insulin. Cell Prolif 40:367–380
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A, Prockop D, Horwitz E (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The international society for cellular therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317
Erices AA, Allers CI, Conget PA, Rojas CV, Minguell JJ (2003) Human cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells home and survive in the marrow of immunodeficient mice after systemic infusion. Cell Transplant 12:555–561
Gao F, Wu D, Hu Y, Jin G (2008a) Extracellular matrix gel is necessary for in vitro cultivation of insulin producing cells from human umbilical cord blood derived mesenchymal stem cells. Chin Med J 121:811–818
Gao F, Wu D-Q, Hu Y-H, Jin G-X, Li G-D, Sun T-W, Li F-J (2008b) In vitro cultivation of islet-like cell clusters from human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Transl Res 151:293–302
Gluckman E, Broxmeyer HA, Auerbach AD, Friedman HS, Douglas GW, Devergie A, Esperou H, Thierry D, Socie G, Lehn P (1989) Hematopoietic reconstitution in a patient with Fanconi’s anemia by means of umbilical-cord blood from an HLA-identical sibling. N Engl J Med 321:1174–1178
Goodwin HS, Bicknese AR, Chien SN, Bogucki BD, Quinn CO, Wall DA (2001) Multilineage differentiation activity by cells isolated from umbilical cord blood: expression of bone, fat, and neural markers. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 7:581–588
Haller MJ, Viener H-L, Wasserfall C, Brusko T, Atkinson MA, Schatz DA (2008) Autologous umbilical cord blood infusion for type 1 diabetes. Exp Hematol 36:710–715
Haller MJ, Wasserfall CH, Hulme MA, Cintron M, Brusko TM, McGrail KM, Sumrall TM, Wingard JR, Theriaque DW, Shuster JJ, Atkinson MA, Schatz DA (2011) Autologous umbilical cord blood transfusion in young children with type 1 diabetes fails to preserve C-peptide. Diabetes Care 34:2567–2569
He Y, Li H, Zhang F, Zhang G, Tang X, Zhu T, Huang N, Li X (2016) Immunotherapeutic effects of lymphocytes co-cultured with human cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells transplantation on APP/PS1 mice. Behav Brain Res 315:94–102
Hematti P, Kim J, Stein AP, Kaufman D (2013) Potential role of mesenchymal stromal cells in pancreatic islet transplantation. Transplant Rev (Orlando) 27:21–29
Hisanaga E, Park K-Y, Yamada S, Hashimoto H, Takeuchi T, Mori M, Seno M, Umezawa K, Takei I, Kojima I (2008) A simple method to induce differentiation of murine bone marrow mesenchymal cells to insulin-producing cells using conophylline and betacellulin-delta4. Endocr J 55:535–543
Hu Y-H, Wu D-Q, Gao F, Li G-D, Yao L, Zhang X-C (2009) A secretory function of human insulin-producing cells in vivo. HBPD Int 8:255–260
Hu J, Yu X, Wang Z, Wang F, Wang L, Gao H, Chen Y, Zhao W, Jia Z, Yan S, Wang Y (2013) Long term effects of the implantation of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells from the umbilical cord for newly-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocr J 60:347–357
Hu J, Wang Y, Wang F, Wang L, Yu X, Sun R, Wang Z, Wang L, Gao H, Fu Z, Zhao W, Yan S (2015) Effect and mechanisms of human Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells on type 1 diabetes in NOD model. Endocrine 48:124–134
Jaing T-H (2014) Umbilical cord blood: a trustworthy source of multipotent stem cells for regenerative medicine. Cell Transplant 23:493–496
Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, Schwartz RE, Keene CD, Ortiz-Gonzalez XR, Reyes M, Lenvik T, Lund T, Blackstad M, Du J, Aldrich S, Lisberg A, Low WC, Largaespada DA, Verfaillie CM (2002) Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature 418:41–49
Jin HJ, Bae YK, Kim M, Kwon S-J, Jeon HB, Choi SJ, Kim SW, Yang YS, Oh W, Chang JW (2013) Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood as sources of cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci 14:17986–18001
Jung J-A, Yoon Y-D, Lee H-W, Kang S-R, Han S-K (2018) Comparison of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells with healthy fibroblasts on wound-healing activity of diabetic fibroblasts. Int Wound J 15:133–139
Kang S-Y, Park D-E, Song W-J, Bae B-R, Lee J-W, Sohn K-H, Lee H-S, Kang H-R, Park H-W, Chang Y-S, Choi S-J, Oh W-I, Min K-U, Cho S-H (2017) Immunologic regulatory effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a murine ovalbumin asthma model. Clin Exp Allergy 47:937–945
Kebriaei P, Isola L, Bahceci E, Holland K, Rowley S, McGuirk J, Devetten M, Jansen J, Herzig R, Schuster M, Monroy R, Uberti J (2009) Adult human mesenchymal stem cells added to corticosteroid therapy for the treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 15:804–811
Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, Klüter H, Bieback K (2006) Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells 24:1294–1301
Kim J-Y, Jeon HB, Yang YS, Oh W, Chang JW (2010) Application of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in disease models. World J Stem Cells 2:34–38
Kim H-S, Shin T-H, Lee B-C, Yu K-R, Seo Y, Lee S, Seo M-S, Hong I-S, Choi SW, Seo K-W, Núñez G, Park J-H, Kang K-S (2013) Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells reduce colitis in mice by activating NOD2 signaling to COX2. Gastroenterology 145:1392–1403.e1–8
Kim H-S, Yun J-W, Shin T-H, Lee S-H, Lee B-C, Yu K-R, Seo Y, Lee S, Kang T-W, Choi SW, Seo K-W, Kang K-S (2015) Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell-derived PGE2 and TGF-β1 alleviate atopic dermatitis by reducing mast cell degranulation. Stem Cells 33:1254–1266
Koblas T, Harman SM, Saudek F (2005) The application of umbilical cord blood cells in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Rev Diabet Stud 2:228–234
Koblas T, Zacharovová K, Berková Z, Leontovic I, Dovolilová E, Zámecník L, Saudek F (2009) In vivo differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived cells into insulin-producing beta cells. Folia Biol (Praha) 55:224–232
Kögler G, Sensken S, Wernet P (2006) Comparative generation and characterization of pluripotent unrestricted somatic stem cells with mesenchymal stem cells from human cord blood. Exp Hematol 34:1589–1595
Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, Locatelli F, Roelofs H, Lewis I, Lanino E, Sundberg B, Bernardo ME, Remberger M, Dini G, Egeler RM, Bacigalupo A, Fibbe W, Ringdén O (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet 371:1579–1586
Lee C, Shim S, Jang H, Myung H, Lee J, Bae C-H, Myung JK, Kim M-J, Lee SB, Jang W-S, Lee S-J, Kim H-Y, Lee S-S, Park S (2017a) Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and small intestinal submucosa hydrogel composite promotes combined radiation-wound healing of mice. Cytotherapy 19:1048–1059
Lee YS, Sah SK, Lee JH, Seo K-W, Kang K-S, Kim T-Y (2017b) Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. Biochem Biophys Rep 9:281–288
Li X, Li H, Bi J, Chen Y, Jain S, Zhao Y (2012) Human cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells (CB-SCs) treated with all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) give rise to dopamine neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 419:110–116
Li X-Y, Zheng Z-H, Li X-Y, Guo J, Zhang Y, Li H, Wang Y-W, Ren J, Wu Z-B (2013) Treatment of foot disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells: response and correction of immunological anomalies. Curr Pharm Des 19:4893–4899
Li Y, Yan B, Wang H, Li H, Li Q, Zhao D, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Li W, Zhang J, Wang S, Shen J, Li Y, Guindi E, Zhao Y (2015) Hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients following stem cell educator therapy. BMC Med 13:87
Li L, Hui H, Jia X, Zhang J, Liu Y, Xu Q, Zhu D (2016) Infusion with human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves β-cell function in patients and non-obese mice with severe diabetes. Sci Rep 6:37894
Mabed M (2011) The potential utility of bone marrow or umbilical cord blood transplantation for the treatment of type I diabetes mellitus. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 17:455–464
Markov V, Kusumi K, Tadesse MG, William DA, Hall DM, Lounev V, Carlton A, Leonard J, Cohen RI, Rappaport EF, Saitta B (2007) Identification of cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cell populations with distinct growth kinetics, differentiation potentials, and gene expression profiles. Stem Cells Dev 16:53–73
Montanucci P, Alunno A, Basta G, Bistoni O, Pescara T, Caterbi S, Pennoni I, Bini V, Gerli R, Calafiore R (2016) Restoration of t cell substes of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus by microencapsulated human umbilical cord Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells: an in vitro study. Clin Immunol 163:34–41
Murohara T, Ikeda H, Duan J, Shintani S, Sasaki K i, Eguchi H, Onitsuka I, Matsui K, Imaizumi T (2000) Transplanted cord blood-derived endothelial precursor cells augment postnatal neovascularization. J Clin Invest 105:1527–1536
Oh W, Kim D-S, Yang YS, Lee JK (2008) Immunological properties of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cell Immunol 251:116–123
Park JH, Hwang I, Hwang SH, Han H, Ha H (2012) Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent diabetic renal injury through paracrine action. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 98:465–473
Phuc PV, Nhung TH, Loan DTT, Chung DC, Ngoc PK (2011) Differentiating of banked human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 47:54–63
Prabakar KR, Domínguez-Bendala J, Molano RD, Pileggi A, Villate S, Ricordi C, Inverardi L (2012) Generation of glucose-responsive, insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant 21:1321–1339
Reddi AS, Kuppasani K, Ende N (2010) Human umbilical cord blood as an emerging stem cell therapy for diabetes mellitus. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 5:356–361
Reddi AS, Kothari N, Kuppasani K, Ende N (2015) Human umbilical cord blood cells and diabetes mellitus: recent advances. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 10:266–270
Sahraneshin Samani F, Ebrahimi M, Zandieh T, Khoshchehreh R, Baghaban Eslaminejad M, Aghdami N, Baharvand H (2015) In vitro differentiation of human umbilical cord blood CD133(+)cells into insulin producing cells in co-culture with rat pancreatic mesenchymal stem cells. Cell J 17:211–220
Salazar KD, Lankford SM, Brody AR (2009) Mesenchymal stem cells produce Wnt isoforms and TGF-beta1 that mediate proliferation and procollagen expression by lung fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 297:L1002–L1011
Sato K, Ozaki K, Oh I, Meguro A, Hatanaka K, Nagai T, Muroi K, Ozawa K (2007) Nitric oxide plays a critical role in suppression of T-cell proliferation by mesenchymal stem cells. Blood 109:228–234
Secco M, Moreira YB, Zucconi E, Vieira NM, Jazedje T, Muotri AR, Okamoto OK, Verjovski-Almeida S, Zatz M (2009) Gene expression profile of mesenchymal stem cells from paired umbilical cord units: cord is different from blood. Stem Cell Rev 5:387–401
Shin T-H, Kim H-S, Kang T-W, Lee B-C, Lee H-Y, Kim Y-J, Shin J-H, Seo Y, Won Choi S, Lee S, Shin K, Seo K-W, Kang K-S (2016) Human umbilical cord blood-stem cells direct macrophage polarization and block inflammasome activation to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis 7:e2524
Sordi V, Pellegrini S, Krampera M, Marchetti P, Pessina A, Ciardelli G, Fadini G, Pintus C, Pantè G, Piemonti L (2017) Stem cells to restore insulin production and cure diabetes. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 27:583–600
Sun L, Wang D, Liang J, Zhang H, Feng X, Wang H, Hua B, Liu B, Ye S, Hu X, Xu W, Zeng X, Hou Y, Gilkeson GS, Silver RM, Lu L, Shi S (2010) Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 62:2467–2475
Sun B, Liu R, Xiao Z-D (2015) Induction of insulin-producing cells from umbilical cord blood-derived stromal cells by activation of the c-met/HGF axis. Develop Growth Differ 57:353–361
Van Pham P, Thi-My Nguyen P, Thai-Quynh Nguyen A, Minh Pham V, Nguyen-Tu Bui A, Thi-Tung Dang L, Gia Nguyen K, Kim Phan N (2014) Improved differentiation of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-producing cells by PDX-1 mRNA transfection. Differentiation 87:200–208
von Bonin M, Stölzel F, Goedecke A, Richter K, Wuschek N, Hölig K, Platzbecker U, Illmer T, Schaich M, Schetelig J, Kiani A, Ordemann R, Ehninger G, Schmitz M, Bornhäuser M (2009) Treatment of refractory acute GVHD with third-party MSC expanded in platelet lysate-containing medium. Bone Marrow Transplant 43:245–251
Wang M, Yang Y, Yang D, Luo F, Liang W, Guo S, Xu J (2009) The immunomodulatory activity of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Immunology 126:220–232
Wang L, Wang L, Cong X, Liu G, Zhou J, Bai B, Li Y, Bai W, Li M, Ji H, Zhu D, Wu M, Liu Y (2013) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell therapy for patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: safety and efficacy. Stem Cells Dev 22:3192–3202
Wang D, Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Chen J, Li X, Hu X, Jiang S, Shi S, Sun L (2014) Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in active and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicenter clinical study. Arthritis Res Ther 16:R79
Willcox A, Gillespie KM (2016) Histology of type 1 diabetes pancreas. Methods Mol Biol 1433:105–117
Wu K-H, Chan C-K, Tsai C, Chang Y-H, Sieber M, Chiu T-H, Ho M, Peng C-T, Wu H-P, Huang J-L (2011) Effective treatment of severe steroid-resistant acute graft-versus-host disease with umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Transplantation 91:1412–1416
Xv J, Ming Q, Wang X, Zhang W, Li Z, Wang S, Li Y, Li L (2017) Mesenchymal stem cells moderate immune response of type 1 diabetes. Cell Tissue Res 368:239–248
Yoshida S, Ishikawa F, Kawano N, Shimoda K, Nagafuchi S, Shimoda S, Yasukawa M, Kanemaru T, Ishibashi H, Shultz LD, Harada M (2005) Human cord blood-derived cells generate insulin-producing cells in vivo. Stem Cells 23:1409–1416
Zhao Y (2012) Stem cell educator therapy and induction of immune balance. Curr Diab Rep 12:517–523
Zhao Y, Mazzone T (2010) Human cord blood stem cells and the journey to a cure for type 1 diabetes. Autoimmun Rev 10:103–107
Zhao Y, Wang H, Mazzone T (2006) Identification of stem cells from human umbilical cord blood with embryonic and hematopoietic characteristics. Exp Cell Res 312:2454–2464
Zhao Y, Huang Z, Qi M, Lazzarini P, Mazzone T (2007) Immune regulation of T lymphocyte by a newly characterized human umbilical cord blood stem cell. Immunol Lett 108:78–87
Zhao Y, Lin B, Darflinger R, Zhang Y, Holterman MJ, Skidgel RA (2009) Human cord blood stem cell-modulated regulatory T lymphocytes reverse the autoimmune-caused type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. PLoS One 4:e4226
Zhao Y, Lin B, Dingeldein M, Guo C, Hwang D, Holterman MJ (2010) New type of human blood stem cell: a double-edged sword for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Transl Res 155:211–216
Zhao Y, Jiang Z, Zhao T, Ye M, Hu C, Yin Z, Li H, Zhang Y, Diao Y, Li Y, Chen Y, Sun X, Fisk MB, Skidgel R, Holterman M, Prabhakar B, Mazzone T (2012) Reversal of type 1 diabetes via islet β cell regeneration following immune modulation by cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells. BMC Med 10(3)
Zhao Q-S, Xia N, Zhao N, Li M, Bi C-L, Zhu Q, Qiao G-F, Cheng Z-F (2013a) Localization of human mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood and their role in repair of diabetic foot ulcers in rats. Int J Biol Sci 10:80–89
Zhao Y, Jiang Z, Zhao T, Ye M, Hu C, Zhou H, Yin Z, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Wang S, Shen J, Thaker H, Jain S, Li Y, Diao Y, Chen Y, Sun X, Fisk MB, Li H (2013b) Targeting insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes via immune modulation of cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells (CB-SCs) in stem cell educator therapy: phase I/II clinical trial. BMC Med 11:160
Funding
This research was supported by the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (Grant No. 17-2013-288), NIH (Grant No. 1DP2CA195763-01) and Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (Grant No. 17-2013-491).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stiner, R., Alexander, M., Liu, G. et al. Transplantation of stem cells from umbilical cord blood as therapy for type I diabetes. Cell Tissue Res 378, 155–162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03046-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03046-2