Abstract
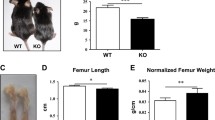
In recent years, several studies have found that the disruption of type IA receptor of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPR1A) could increase bone mass. However, whether disruption of BMPR1A could have an effect on bone quality and bone strength is currently unknown. Osteoblast-targeted conditional knockout (cKO) of BMPRIA by crossing 3.2-kb Col1-CreER™ mice with BMPR1A fx +/+ mice was conducted. Then, in vitro and in vivo studies were employed to examine the effect of BMPR1A knockout on bone quality and bone strength. It was found that the ultimate force and stiffness of the femora decreased significantly in cKO mice when compared to control mice. The content of collagen and mineralization level decreased as the structure of the collagen became disorganized. The morphology of osteocytes in cKO mice was abnormal as well. The expression level of osteocalcin, a marker for the terminal differentiation of osteoblasts, decreased in cKO mice. This data indicated that the differentiation of osteoblasts in cKO mice was impaired. Immunohistochemistry examination revealed deregulated expression of dickkopf 1(DKK1) in osteocytes in cKO mice. Adding DKK1 to the culture medium reversed these effects. In conclusion, even though disruption of BMPR1A could increase bone mass, it also impairs bone quality and bone strength.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandyopadhyay A, Tsuji K, Cox K, Harfe BD, Rosen V, Tabin CJ (2006) Genetic analysis of the roles of BMP2, BMP4, and BMP7 in limb patterning and skeletogenesis. PLoS Genet 2:e216
Bao Q, Chen S, Qin H, Feng J, Liu H, Liu D, Li A, Shen Y, Zhong X, Li J, Zong Z (2017) Constitutive beta-catenin activation in osteoblasts impairs terminal osteoblast differentiation and bone quality. Exp Cell Res 350:123–131
Baud'huin M, Solban N, Cornwall-Brady M, Sako D, Kawamoto Y, Liharska K, Lath D, Bouxsein ML, Underwood KW, Ucran J, Kumar R, Pobre E, Grinberg A, Seehra J, Canalis E, Pearsall RS, Croucher PI (2012) A soluble bone morphogenetic protein type IA receptor increases bone mass and bone strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:12207–12212
Bragdon B, Thinakaran S, Moseychuk O, Gurski L, Bonor J, Price C, Wang L, Beamer WG, Nohe A (2011) Casein kinase 2 regulates in vivo bone formation through its interaction with bone morphogenetic protein receptor type Ia. Bone 49:944–954
Chen S, Feng J, Bao Q, Li A, Zhang B, Shen Y, Zhao Y, Guo Q, Jing J, Lin S, Zong Z (2015) Adverse effects of osteocytic constitutive activation of ss-catenin on bone strength and bone growth. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 30:1184–1194
Danesh SM, Villasenor A, Chong D, Soukup C, Cleaver O (2009) BMP and BMP receptor expression during murine organogenesis. Gene Expression Patterns: GEP 9:255–265
Davison KS, Siminoski K, Adachi JD, Hanley DA, Goltzman D, Hodsman AB, Josse R, Kaiser S, Olszynski WP, Papaioannou A, Ste-Marie LG, Kendler DL, Tenenhouse A, Brown JP (2006) Bone strength: the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. Semin Arthritis Rheum 36:22–31
Feng JQ, Ward LM, Liu S, Lu Y, Xie Y, Yuan B, Yu X, Rauch F, Davis SI, Zhang S, Rios H, Drezner MK, Quarles LD, Bonewald LF, White KE (2006) Loss of DMP1 causes rickets and osteomalacia and identifies a role for osteocytes in mineral metabolism. Nat Genet 38:1310–1315
Glass DA II, Bialek P, Ahn JD, Starbuck M, Patel MS, Clevers H, Taketo MM, Long F, McMahon AP, Lang RA, Karsenty G (2005) Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation. Dev Cell 8:751–764
Holmen SL, Zylstra CR, Mukherjee A, Sigler RE, Faugere MC, Bouxsein ML, Deng L, Clemens TL, Williams BO (2005) Essential role of beta-catenin in postnatal bone acquisition. J Biol Chem 280:21162–21168
Jia M, Chen S, Zhang B, Liang H, Feng J, Zong Z (2013) Effects of constitutive beta-catenin activation on vertebral bone growth and remodeling at different postnatal stages in mice. PLoS One 8:e74093
Jing J, Ren Y, Zong Z, Liu C, Kamiya N, Mishina Y, Liu Y, Zhou X, Feng JQ (2013) BMP receptor 1A determines the cell fate of the postnatal growth plate. Int J Biol Sci 9:895–906
Kamiya N, Ye L, Kobayashi T, Lucas DJ, Mochida Y, Yamauchi M, Kronenberg HM, Feng JQ, Mishina Y (2008a) Disruption of BMP signaling in osteoblasts through type IA receptor (BMPRIA) increases bone mass. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 23:2007–2017
Kamiya N, Ye L, Kobayashi T, Mochida Y, Yamauchi M, Kronenberg HM, Feng JQ, Mishina Y (2008b) BMP signaling negatively regulates bone mass through sclerostin by inhibiting the canonical Wnt pathway. Development 135:3801–3811
Kamiya N, Kobayashi T, Mochida Y, Yu PB, Yamauchi M, Kronenberg HM, Mishina Y (2010) Wnt inhibitors Dkk1 and Sost are downstream targets of BMP signaling through the type IA receptor (BMPRIA) in osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 25:200–210
Kaps C, Hoffmann A, Zilberman Y, Pelled G, Haupl T, Sittinger M, Burmester G, Gazit D, Gross G (2004) Distinct roles of BMP receptors type IA and IB in osteo−/chondrogenic differentiation in mesenchymal progenitors (C3H10T1/2). BioFactors 20:71–84
Kawasaki K, Buchanan AV, Weiss KM (2009) Biomineralization in humans: making the hard choices in life. Annu Rev Genet 43:119–142
Kumar J, Swanberg M, McGuigan F, Callreus M, Gerdhem P, Akesson K (2011) LRP4 association to bone properties and fracture and interaction with genes in the Wnt- and BMP signaling pathways. Bone 49:343–348
Lavery K, Swain P, Falb D, Alaoui-Ismaili MH (2008) BMP-2/4 and BMP-6/7 differentially utilize cell surface receptors to induce osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem 283:20948–20958
Li X, Liu P, Liu W, Maye P, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Hurley M, Guo C, Boskey A, Sun L, Harris SE, Rowe DW, Ke HZ, Wu D (2005) Dkk2 has a role in terminal osteoblast differentiation and mineralized matrix formation. Nat Genet 37:945–952
Liu F, Fang F, Yuan H, Yang D, Chen Y, Williams L, Goldstein SA, Krebsbach PH, Guan JL (2013) Suppression of autophagy by FIP200 deletion leads to osteopenia in mice through the inhibition of osteoblast terminal differentiation. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 28:2414–2430
Liu HJ, Yan H, Yan J, Li H, Chen L, Han LR, Yang XF (2016) Substance P promotes the proliferation, but inhibits differentiation and mineralization of osteoblasts from rats with spinal cord injury via RANKL/OPG system. PLoS One 11:e0165063
Martineau, C., Kevorkova, O., Brissette, L., Moreau, R. (2014) Scavenger receptor class B, type I (Scarb1) deficiency promotes osteoblastogenesis but stunts terminal osteocyte differentiation. Physiol Reports 2. 2(10): e12117. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12117
Mishina Y, Starbuck MW, Gentile MA, Fukuda T, Kasparcova V, Seedor JG, Hanks MC, Amling M, Pinero GJ, Harada S, Behringer RR (2004) Bone morphogenetic protein type IA receptor signaling regulates postnatal osteoblast function and bone remodeling. J Biol Chem 279:27560–27566
Miyazono K, Kamiya Y, Morikawa M (2010) Bone morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J Biochem 147:35–51
Nakao Y, Koike T, Ohta Y, Manaka T, Imai Y, Takaoka K (2009) Parathyroid hormone enhances bone morphogenetic protein activity by increasing intracellular 3′, 5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Bone 44:872–877
Nishikawa Y, Akiyama Y, Yamamoto K, Kobayashi M, Watanabe E, Watanabe N, Shimizu N, Mikami Y, Komiyama K (2015) Osteocytes up-regulate the terminal differentiation of pre-osteoblasts via gap junctions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 456:1–6
Okamoto M, Murai J, Yoshikawa H, Tsumaki N (2006) Bone morphogenetic proteins in bone stimulate osteoclasts and osteoblasts during bone development. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 21:1022–1033
Singhatanadgit W, Salih V, Olsen I (2008) RNA interference of the BMPR-IB gene blocks BMP-2-induced osteogenic gene expression in human bone cells. Cell Biol Int 32:1362–1370
Uchihashi K, Aoki S, Matsunobu A, Toda S (2013) Osteoblast migration into type I collagen gel and differentiation to osteocyte-like cells within a self-produced mineralized matrix: a novel system for analyzing differentiation from osteoblast to osteocyte. Bone 52:102–110
van der Horst G, van der Werf SM, Farih-Sips H, van Bezooijen RL, Lowik CW, Karperien M (2005) Downregulation of Wnt signaling by increased expression of Dickkopf-1 and -2 is a prerequisite for late-stage osteoblast differentiation of KS483 cells. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 20:1867–1877
Wu XB, Li Y, Schneider A, Yu W, Rajendren G, Iqbal J, Yamamoto M, Alam M, Brunet LJ, Blair HC, Zaidi M, Abe E (2003) Impaired osteoblastic differentiation, reduced bone formation, and severe osteoporosis in noggin-overexpressing mice. J Clin Invest 112:924–934
Yi SE, Daluiski A, Pederson R, Rosen V, Lyons KM (2000) The type I BMP receptor BMPRIB is required for chondrogenesis in the mouse limb. Development 127:621–630
Yu PB, Deng DY, Lai CS, Hong CC, Cuny GD, Bouxsein ML, Hong DW, McManus PM, Katagiri T, Sachidanandan C, Kamiya N, Fukuda T, Mishina Y, Peterson RT, Bloch KD (2008) BMP type I receptor inhibition reduces heterotopic [corrected] ossification. Nat Med 14:1363–1369
Zeng S, Chen J, Shen H (2010) Controlling of bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Cell Signal 22:888–893
Zhao M, Harris SE, Horn D, Geng Z, Nishimura R, Mundy GR, Chen D (2002) Bone morphogenetic protein receptor signaling is necessary for normal murine postnatal bone formation. J Cell Biol 157:1049–1060
Zuo C, Huang Y, Bajis R, Sahih M, Li YP, Dai K, Zhang X (2012) Osteoblastogenesis regulation signals in bone remodeling. Osteoporos Int 23:1653–1663
Funding
This work was funded by National Science Foundation of China (81271935).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, Q., Li, A., Chen, S. et al. Disruption of bone morphogenetic protein type IA receptor in osteoblasts impairs bone quality and bone strength in mice. Cell Tissue Res 374, 263–273 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2873-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2873-3