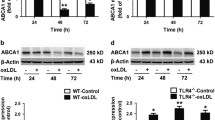
Abstract
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) plays critical roles in vascular inflammation, lipid accumulation and atherosclerosis development. However, the mechanisms underlying these processes are still not well established, especially in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 (ABCG1) is one of the key genes mediating inflammation and cellular lipid accumulation. The function of TLR4 in regulating the expression of ABCG1 and the underlying molecular mechanisms remain to be elucidated. In this study, we cultured VSMCs from the thoracic aortas of mice and treated the cells with 50 μg/ml oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) to activate TLR4 signaling. We observed that activating TLR4 with oxLDL induced inflammatory responses and lipid accumulation in VSMCs. The expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), liver X receptor alpha (LXRα) and ABCG1 was inhibited by TLR4 activation. However, these effects could be reversed by knocking out TLR4. PPARγ activation by rosiglitazone rescued LXRα and ABCG1 expression and reduced TLR4-induced inflammation and lipid accumulation. Silencing PPARγ expression with a specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) inhibited LXRα and ABCG1 expression and, importantly, enhanced TLR4-induced inflammation and lipid accumulation. In conclusion, ABCG1 expression was down-regulated by TLR4, which induces inflammation and lipid accumulation in VSMCs via PPARγ/LXRα signaling. These findings indicate a novel molecular mechanism underlying TLR4-induced inflammation and lipid accumulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABCG1:
-
ATP-binding cassette transporter G1
- LXRα:
-
Liver X receptor alpha
- oxLDL:
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- RSG:
-
Rosiglitazone
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- VSMCs:
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells
References
Akiyama TE, Sakai S, Lambert G, Nicol CJ, Matsusue K, Pimprale S, Lee YH, Ricote M, Glass CK, Brewer HB Jr, Gonzalez FJ (2002) Conditional disruption of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma gene in mice results in lowered expression of ABCA1, ABCG1, and apoE in macrophages and reduced cholesterol efflux. Mol Cell Biol 22:2607–2619
Allahverdian S, Pannu PS, Francis GA (2012) Contribution of monocyte-derived macrophages and smooth muscle cells to arterial foam cell formation. Cardiovasc Res 95:165–172
Bo QL, Chen YH, Yu Z, Fu L, Zhou Y, Zhang GB, Wang H, Zhang ZH, Xu DX (2016) Rosiglitazone pretreatment protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced fetal demise through inhibiting placental inflammation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 423:51–59
Broad A, Kirby JA, Jones DE (2007) Toll-like receptor interactions: tolerance of MyD88-dependent cytokines but enhancement of MyD88-independent interferon-beta production. Immunology 120:103–111
Bujold K, Rhainds D, Jossart C, Febbraio M, Marleau S, Ong H (2009) CD36-mediated cholesterol efflux is associated with PPARgamma activation via a MAPK-dependent COX-2 pathway in macrophages. Cardiovasc Res 83:457–464
Chavez-Sanchez L, Madrid-Miller A, Chavez-Rueda K, Legorreta-Haquet MV, Tesoro-Cruz E, Blanco-Favela F (2010) Activation of TLR2 and TLR4 by minimally modified low-density lipoprotein in human macrophages and monocytes triggers the inflammatory response. Hum Immunol 71:737–744
Chawla A, Barak Y, Nagy L, Liao D, Tontonoz P, Evans RM (2001a) PPAR-gamma dependent and independent effects on macrophage-gene expression in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Nat Med 7:48–52
Chawla A, Boisvert WA, Lee CH, Laffitte BA, Barak Y, Joseph SB, Liao D, Nagy L, Edwards PA, Curtiss LK, Evans RM, Tontonoz P (2001b) A PPAR gamma-LXR-ABCA1 pathway in macrophages is involved in cholesterol efflux and atherogenesis. Mol Cell 7:161–171
Chen W, Lin YJ, Zhou XY, Chen H, Jin Y (2016) Rosiglitazone protects rat liver against acute liver injury associated with the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 94:28–34
Collins T, Read MA, Neish AS, Whitley MZ, Thanos D, Maniatis T (1995) Transcriptional regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules: NF-kappa B and cytokine-inducible enhancers. FASEB J 9:899–909
Dubuquoy L, Jansson EA, Deeb S, Rakotobe S, Karoui M, Colombel JF, Auwerx J, Pettersson S, Desreumaux P (2003) Impaired expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 124:1265–1276
Edfeldt K, Swedenborg J, Hansson GK, Yan ZQ (2002) Expression of toll-like receptors in human atherosclerotic lesions: a possible pathway for plaque activation. Circulation 105:1158–1161
Higashimori M, Tatro JB, Moore KJ, Mendelsohn ME, Galper JB, Beasley D (2011) Role of toll-like receptor 4 in intimal foam cell accumulation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:50–57
Huang Q, Pope RM (2010) Toll-like receptor signaling: a potential link among rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus, and atherosclerosis. J Leukoc Biol 88:253–262
Ji Y, Wang Z, Li Z, Liu J (2010) Modulation of LPS-mediated inflammation by fenofibrate via the TRIF-dependent TLR4 signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 25:631–640
Jia SJ, Niu PP, Cong JZ, Zhang BK, Zhao M (2014) TLR4 signaling: a potential therapeutic target in ischemic coronary artery disease. Int Immunopharmacol 23:54–59
Jiang C, Ting AT, Seed B (1998) PPAR-gamma agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines. Nature 391:82–86
Johnson JL (2014) Emerging regulators of vascular smooth muscle cell function in the development and progression of atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 103:452–460
Kennedy MA, Barrera GC, Nakamura K, Baldan A, Tarr P, Fishbein MC, Frank J, Francone OL, Edwards PA (2005) ABCG1 has a critical role in mediating cholesterol efflux to HDL and preventing cellular lipid accumulation. Cell Metab 1:121–131
Kuo MY, Ou HC, Lee WJ, Kuo WW, Hwang LL, Song TY, Huang CY, Chiu TH, Tsai KL, Tsai CS, Sheu WH (2011) Ellagic acid inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL)-induced metalloproteinase (MMP) expression by modulating the protein kinase C-alpha/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma/nuclear factor-kappaB (PKC-alpha/ERK/PPAR-gamma/NF-kappaB) signaling pathway in endothelial cells. J Agric Food Chem 59:5100–5108
Li AC, Binder CJ, Gutierrez A, Brown KK, Plotkin CR, Pattison JW, Valledor AF, Davis RA, Willson TM, Witztum JL, Palinski W, Glass CK (2004) Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARalpha, beta/delta, and gamma. J Clin Invest 114:1564–1576
McMurray HF, Parrott DP, Bowyer DE (1991) A standardised method of culturing aortic explants, suitable for the study of factors affecting the phenotypic modulation, migration and proliferation of aortic smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis 86:227–237
Michelsen KS, Wong MH, Shah PK, Zhang W, Yano J, Doherty TM, Akira S, Rajavashisth TB, Arditi M (2004) Lack of Toll-like receptor 4 or myeloid differentiation factor 88 reduces atherosclerosis and alters plaque phenotype in mice deficient in apolipoprotein E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:10679–10684
Moghimpour Bijani F, Vallejo JG, Rezaei N (2012) Toll-like receptor signaling pathways in cardiovascular diseases: challenges and opportunities. Int Rev Immunol 31:379–395
Necela BM, Su W, Thompson EA (2008) Toll-like receptor 4 mediates cross-talk between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and nuclear factor-kappaB in macrophages. Immunology 125:344–358
Park Y, Pham TX, Lee J (2012) Lipopolysaccharide represses the expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 and scavenger receptor class B, type I in murine macrophages. Inflamm Res 61:465–472
Raines EW, Ferri N (2005) Thematic review series: the immune system and atherogenesis. Cytokines affecting endothelial and smooth muscle cells in vascular disease. J Lipid Res 46:1081–1092
Rong JX, Shapiro M, Trogan E, Fisher EA (2003) Transdifferentiation of mouse aortic smooth muscle cells to a macrophage-like state after cholesterol loading. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:13531–13536
Sabol SL, Brewer HB Jr, Santamarina-Fojo S (2005) The human ABCG1 gene: identification of LXR response elements that modulate expression in macrophages and liver. J Lipid Res 46:2151–2167
Sasu S, LaVerda D, Qureshi N, Golenbock DT, Beasley D (2001) Chlamydia pneumoniae and chlamydial heat shock protein 60 stimulate proliferation of human vascular smooth muscle cells via toll-like receptor 4 and p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Circ Res 89:244–250
Thieringer R, Fenyk-Melody JE, Le Grand CB, Shelton BA, Detmers PA, Somers EP, Carbin L, Moller DE, Wright SD, Berger J (2000) Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma does not inhibit IL-6 or TNF-alpha responses of macrophages to lipopolysaccharide in vitro or in vivo. J Immunol 164:1046–1054
Thomassen MJ, Barna BP, Malur AG, Bonfield TL, Farver CF, Malur A, Dalrymple H, Kavuru MS, Febbraio M (2007) ABCG1 is deficient in alveolar macrophages of GM-CSF knockout mice and patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. J Lipid Res 48:2762–2768
Torocsik D, Barath M, Benko S, Szeles L, Dezso B, Poliska S, Hegyi Z, Homolya L, Szatmari I, Lanyi A, Nagy L (2010) Activation of liver X receptor sensitizes human dendritic cells to inflammatory stimuli. J Immunol 184:5456–5465
Xu XH, Shah PK, Faure E, Equils O, Thomas L, Fishbein MC, Luthringer D, Xu XP, Rajavashisth TB, Yano J, Kaul S, Arditi M (2001) Toll-like receptor-4 is expressed by macrophages in murine and human lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques and upregulated by oxidized LDL. Circulation 104:3103–3108
Yang X, Coriolan D, Murthy V, Schultz K, Golenbock DT, Beasley D (2005) Proinflammatory phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells: role of efficient Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H1069–H1076
Yang K, Zhang XJ, Cao LJ, Liu XH, Liu ZH, Wang XQ, Chen QJ, Lu L, Shen WF, Liu Y (2014) Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory cytokine secretion in smooth muscle cells induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein. PLoS ONE 9, e95935
Yin YW, Liao SQ, Zhang MJ, Liu Y, Li BH, Zhou Y, Chen L, Gao CY, Li JC, Zhang LL (2015) TLR4-mediated inflammation promotes foam cell formation of vascular smooth muscle cell by upregulating ACAT1 expression. Cell Death Dis 6:1659
Yvan-Charvet L, Wang N, Tall AR (2010) Role of HDL, ABCA1, and ABCG1 transporters in cholesterol efflux and immune responses. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:139–143
Zhang JY, Liu B, Wang YN, Zhang WN, Wang FJ (2014) Effect of rosuvastatin on OX40L and PPAR-gamma expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and atherosclerotic cerebral infarction patients. J Mol Neurosci 52:261–268
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jianhong Mi, Yang Liu and Fangfang Li for their experimental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (number 81271282, 81400967) and the Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ CSTC (CSTC2012JJJQ10003).
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table S1
(DOC 34 kb)
Supplementary Figure 1
Identification of mice and primary VSMCs. a PCR identification of TLR4 KO mice. The 390-bp PCR products represent the WT TLR4 genotype, the 140-bp PCR products represent the mutant TLR4 genotype and both the 390-bp and 140-bp PCR products represent the heterozygous TLR4 genotype. b The first generation of cells came from thoracic aorta pieces cultured for 8 days and observed under an ordinary light microscope. Scale bar 200 μm. c Primary VSMC identification. Immunofluorescence images show the expression of α-SMA (green) and SM-22α (red) in VSMCs. Representative pictures of three independent experiments are shown. Scale bar 50 μm. (GIF 670 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
OxLDL stimulated TLR4 expression and promoted inflammatory responses, reversed by TLR4 deaficiency. a The images show TLR4 mRNA levels, which were normalized to β-actin mRNA levels (n = 3). b Representative immunoblotting and statistics data revealed the TLR4 protein expression in WT VSMCs (n = 3). The mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1 and VCAM-1 were detected via real-time PCR (c, n = 4). The data are represented as the fold change relative to the control and are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the untreated control group. (GIF 134 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
PPARγ-siRNA silencing efficiency. a The images show PPARγ mRNA levels, which were normalized to β-actin mRNA levels (n = 3). b Representative immunoblotting and statistics data revealed PPARγ expression in WT VSMCs (n = 3). The data are represented as the fold change relative to the control and are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the untreated control group. (GIF 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Zhang, L., Chen, C. et al. The critical role of ABCG1 and PPARγ/LXRα signaling in TLR4 mediates inflammatory responses and lipid accumulation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Tissue Res 368, 145–157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2518-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2518-3