Abstract
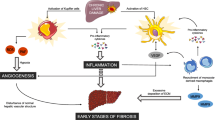
Liver fibrogenesis is a dynamic process including quantitative and qualitative changes of the extracellular matrix, of which the most prominent is the deposition of type I collagen. These changes progressively disrupt normal liver architecture and result in cirrhosis formation. In the fibrotic liver, as in all other fibrotic tissues, the extracellular matrix is produced by cells usually characterized by the de novo expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin and known as myofibroblasts. Portal myofibroblasts (PMFs) appear to be critical in pathological angiogenesis, which constantly occurs in advanced liver fibrosis. Whereas the association between angiogenesis and fibrosis during the progression of liver diseases remains to be elucidated, we suggest that collagen-type-XV-alpha1-producing PMFs could provide an important link both by stabilizing newly formed vessels and by forming a scaffold for the deposition of interstitial collagen.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α-SMA:
-
Alpha-smooth muscle actin
- BDL:
-
Bile duct ligation
- COL15A1:
-
Collagen type XV alpha1
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- HSC:
-
Hepatic stellate cell
- HSC-MF:
-
Hepatic-stellate-cell-derived myofibroblast
- MCD:
-
Methionine-choline-deficient
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- NAFLD:
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PDGF-BB:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor-BB
- PDGFR-β:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta
- PlGF:
-
Placental growth factor
- PMF:
-
Portal myofibroblast
- TAA:
-
Thioacetamide
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-beta
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
References
Beaussier M, Wendum D, Schiffer E, Dumont S, Rey C, Lienhart A, Housset C (2007) Prominent contribution of portal mesenchymal cells to liver fibrosis in ischemic and obstructive cholestatic injuries. Lab Invest 87:292–303
Corpechot C, Barbu V, Wendum D, Kinnman N, Rey C, Poupon R, Housset C, Rosmorduc O (2002) Hypoxia-induced VEGF and collagen I expressions are associated with angiogenesis and fibrogenesis in experimental cirrhosis. Hepatology 35:1010–1021
Ehling J, Bartneck M, Wei X, Gremse F, Fech V, Mockel D, Baeck C, Hittatiya K, Eulberg D, Luedde T, Kiessling F, Trautwein C, Lammers T, Tacke F (2014) CCL2-dependent infiltrating macrophages promote angiogenesis in progressive liver fibrosis. Gut 63:1960–1971
Elpek GO (2015) Angiogenesis and liver fibrosis. World J Hepatol 7:377–391
Eyden B (2008) The myofibroblast: phenotypic characterization as a prerequisite to understanding its functions in translational medicine. J Cell Mol Med 12:22–37
Gao JH, Wen SL, Yang WJ, Lu YY, Tong H, Huang ZY, Liu ZX, Tang CW (2013) Celecoxib ameliorates portal hypertension of the cirrhotic rats through the dual inhibitory effects on the intrahepatic fibrosis and angiogenesis. PloS one 8:e69309
Hennenberg M, Trebicka J, Kohistani Z, Stark C, Nischalke HD, Kramer B, Korner C, Klein S, Granzow M, Fischer HP, Heller J, Sauerbruch T (2011) Hepatic and HSC-specific sorafenib effects in rats with established secondary biliary cirrhosis. Lab Invest 91:241–251
Huang Y, Feng H, Kan T, Huang B, Zhang M, Li Y, Shi C, Wu M, Luo Y, Yang J, Xu F (2013) Bevacizumab attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats by inhibiting activation of hepatic stellate cells. PloS one 8:e73492
Iwaisako K, Jiang C, Zhang M, Cong M, Moore-Morris TJ, Park TJ, Liu X, Xu J, Wang P, Paik YH, Meng F, Asagiri M, Murray LA, Hofmann AF, Iida T, Glass CK, Brenner DA, Kisseleva T (2014) Origin of myofibroblasts in the fibrotic liver in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E3297–E3305
Kang DH, Hughes J, Mazzali M, Schreiner GF, Johnson RJ (2001) Impaired angiogenesis in the remnant kidney model. II. Vascular endothelial growth factor administration reduces renal fibrosis and stabilizes renal function. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1448–1457
Kimura K, Nakayama M, Naito I, Komiyama T, Ichimura K, Asano H, Tsukuda K, Ohtsuka A, Oohashi T, Miyoshi S, Ninomiya Y (2016) Human collagen XV is a prominent histopathological component of sinusoidal capillarization in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Int J Clin Oncol 21:302–309
Kinnman N, Francoz C, Barbu V, Wendum D, Rey C, Hultcrantz R, Poupon R, Housset C (2003) The myofibroblastic conversion of peribiliary fibrogenic cells distinct from hepatic stellate cells is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor during liver fibrogenesis. Lab Invest 83:163–173
Lemoinne S, Cadoret A, Rautou PE, El Mourabit H, Ratziu V, Corpechot C, Rey C, Bosselut N, Barbu V, Wendum D, Feldmann G, Boulanger C, Henegar C, Housset C, Thabut D (2015) Portal myofibroblasts promote vascular remodeling underlying cirrhosis formation through the release of microparticles. Hepatology 61:1041–1055
Li Z, Dranoff JA, Chan EP, Uemura M, Sevigny J, Wells RG (2007) Transforming growth factor-beta and substrate stiffness regulate portal fibroblast activation in culture. Hepatology 46:1246–1256
Liu C, Yang Z, Wang L, Lu Y, Tang B, Miao H, Xu Q, Chen X (2015) Combination of sorafenib and gadolinium chloride (GdCl3) attenuates dimethylnitrosamine(DMN)-induced liver fibrosis in rats. BMC Gastroenterol 15:159
Lua I, Li Y, Zagory JA, Wang KS, French SW, Sevigny J, Asahina K (2016) Characterization of hepatic stellate cells, portal fibroblasts, and mesothelial cells in normal and fibrotic livers. J Hepatol 64:1137–1146
May D, Djonov V, Zamir G, Bala M, Safadi R, Sklair-Levy M, Keshet E (2011) A transgenic model for conditional induction and rescue of portal hypertension reveals a role of VEGF-mediated regulation of sinusoidal fenestrations. PloS one 6:e21478
Mederacke I, Hsu CC, Troeger JS, Huebener P, Mu X, Dapito DH, Pradere JP, Schwabe RF (2013) Fate tracing reveals hepatic stellate cells as dominant contributors to liver fibrosis independent of its aetiology. Nat Commun 4:2823
Mejias M, Garcia-Pras E, Tiani C, Miquel R, Bosch J, Fernandez M (2009) Beneficial effects of sorafenib on splanchnic, intrahepatic, and portocollateral circulations in portal hypertensive and cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 49:1245–1256
Novo E, Cannito S, Zamara E, Valfre di Bonzo L, Caligiuri A, Cravanzola C, Compagnone A, Colombatto S, Marra F, Pinzani M, Parola M (2007) Proangiogenic cytokines as hypoxia-dependent factors stimulating migration of human hepatic stellate cells. Am J Pathol 170:1942–1953
Patsenker E, Popov Y, Stickel F, Schneider V, Ledermann M, Sagesser H, Niedobitek G, Goodman SL, Schuppan D (2009) Pharmacological inhibition of integrin alphavbeta3 aggravates experimental liver fibrosis and suppresses hepatic angiogenesis. Hepatology 50:1501–1511
Rappaport AM, MacPhee PJ, Fisher MM, Phillips MJ (1983) The scarring of the liver acini (cirrhosis). Tridimensional and microcirculatory considerations. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 402:107–137
Sahin H, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Kuppe C, Zaldivar MM, Grouls C, Al-samman M, Nellen A, Schmitz P, Heinrichs D, Berres ML, Doleschel D, Scholten D, Weiskirchen R, Moeller MJ, Kiessling F, Trautwein C, Wasmuth HE (2012) Chemokine Cxcl9 attenuates liver fibrosis-associated angiogenesis in mice. Hepatology 55:1610–1619
Semela D, Das A, Langer D, Kang N, Leof E, Shah V (2008) Platelet-derived growth factor signaling through ephrin-b2 regulates hepatic vascular structure and function. Gastroenterology 135:671–679
Sun K, Wernstedt Asterholm I, Kusminski CM, Bueno AC, Wang ZV, Pollard JW, Brekken RA, Scherer PE (2012) Dichotomous effects of VEGF-A on adipose tissue dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:5874–5879
Taura K, De Minicis S, Seki E, Hatano E, Iwaisako K, Osterreicher CH, Kodama Y, Miura K, Ikai I, Uemoto S, Brenner DA (2008) Hepatic stellate cells secrete angiopoietin 1 that induces angiogenesis in liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135:1729–1738
Thabut D, Routray C, Lomberk G, Shergill U, Glaser K, Huebert R, Patel L, Masyuk T, Blechacz B, Vercnocke A, Ritman E, Ehman R, Urrutia R, Shah V (2011) Complementary vascular and matrix regulatory pathways underlie the beneficial mechanism of action of sorafenib in liver fibrosis. Hepatology 54:573–585
Tugues S, Fernandez-Varo G, Munoz-Luque J, Ros J, Arroyo V, Rodes J, Friedman SL, Carmeliet P, Jimenez W, Morales-Ruiz M (2007) Antiangiogenic treatment with sunitinib ameliorates inflammatory infiltrate, fibrosis, and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 46:1919–1926
Van Steenkiste C, Ribera J, Geerts A, Pauta M, Tugues S, Casteleyn C, Libbrecht L, Olievier K, Schroyen B, Reynaert H, Grunsven LA van, Blomme B, Coulon S, Heindryckx F, De Vos M, Stassen JM, Vinckier S, Altamirano J, Bataller R, Carmeliet P, Van Vlierberghe H, Colle I, Morales-Ruiz M (2011) Inhibition of placental growth factor activity reduces the severity of fibrosis, inflammation, and portal hypertension in cirrhotic mice. Hepatology 53:1629–1640
Wang B, Dolinski BM, Kikuchi N, Leone DR, Peters MG, Weinreb PH, Violette SM, Bissell DM (2007) Role of alphavbeta6 integrin in acute biliary fibrosis. Hepatology 46:1404–1412
Yan Z, Qu K, Zhang J, Huang Q, Qu P, Xu X, Yuan P, Huang X, Shao Y, Liu C, Zhang H, Xing J (2015) CD147 promotes liver fibrosis progression via VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signalling-mediated cross-talk between hepatocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells. Clin Sci (Lond) 129:699–710
Yang L, Kwon J, Popov Y, Gajdos GB, Ordog T, Brekken RA, Mukhopadhyay D, Schuppan D, Bi Y, Simonetto D, Shah VH (2014) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes fibrosis resolution and repair in mice. Gastroenterology 146:1339-1350
Yang YY, Liu RS, Lee PC, Yeh YC, Huang YT, Lee WP, Lee KC, Hsieh YC, Lee FY, Tan TW, Lin HC (2014) Anti-VEGFR agents ameliorate hepatic venous dysregulation/microcirculatory dysfunction, splanchnic venous pooling and ascites of NASH-cirrhotic rat. Liver Int 34:521–534
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Ikenaka Y, Noguchi R, Hicklin DJ, Wu Y, Yanase K, Namisaki T, Yamazaki M, Tsujinoue H, Imazu H, Masaki T, Fukui H (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor and receptor interaction is a prerequisite for murine hepatic fibrogenesis. Gut 52:1347–1354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lemoinne, S., Thabut, D. & Housset, C. Portal myofibroblasts connect angiogenesis and fibrosis in liver. Cell Tissue Res 365, 583–589 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2443-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2443-5