Abstract
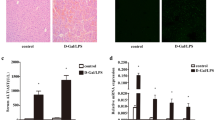
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α exists in two bioactive forms, a 26-kDa transmembrane form (tmTNF-α) and a 17-kDa soluble form (sTNF-α). sTNF-α has been recognized as a key regulator of hepatitis; however, serum sTNF-α disappears in mice during the development of severe liver injury, and high levels of serum sTNF-α do not necessarily result in liver damage. Interestingly, in a mouse model of acute hepatitis, we have found that tmTNF-α expression on Kupffer cells (KCs) significantly increases when mice develop severe liver injury caused by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/D-galactosamine (D-gal), and the level of tmTNF-α expression is positively related to the activity of serum transaminases. Therefore, we hypothesized that KC-expressed tmTNF-α constitutes a pathomechanism in hepatitis and have explored the role of tmTNF-α in this disease model. Here, we have compared the impact of KCstmTNFlow and KCstmTNFhigh on acute hepatitis in vivo and ex vivo and have further demonstrated that KCstmTNFhigh, rather than KCstmTNFlow, not only exhibit an imbalance in secretion of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, favoring inflammatory response and exacerbating liver injury, but also induce hepatocellular apoptosis via tmTNF-α and the expression of another pro-apoptotic factor, Fas ligand. Our data suggest that KCtmTNFhigh is a major contributor to liver injury in LPS/D-gal-induced hepatitis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniades CG, Berry PA, Wendon JA, Vergani D (2008) The importance of immune dysfunction in determining outcome in acute liver failure. J Hepatol 49:845–861
Ardestani S, Li B, Deskins DL, Wu H, Massion PP, Young PP (2013) Membrane versus soluble isoforms of TNF-alpha exert opposing effects on tumor growth and survival of tumor-associated myeloid cells. Cancer Res 73:3938–3950
Bilzer M, Roggel F, Gerbes AL (2006) Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int 26:1175–1186
Cressman DE, Greenbaum LE, DeAngelis RA, Ciliberto G, Furth EE, Poli V, Taub R (1996) Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science 274:1379–1383
Gantner F, Leist M, Lohse AW, Germann PG, Tiegs G (1995) Concanavalin A-induced T-cell-mediated hepatic injury in mice: the role of tumor necrosis factor. Hepatology 21:190–198
Gonzalez-Teran B, Cortes JR, Manieri E, Matesanz N, Verdugo A, Rodriguez ME, Gonzalez-Rodriguez A, Valverde A, Martin P, Davis RJ, Sabio G (2013) Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 controls TNF-alpha translation in LPS-induced hepatitis. J Clin Invest 123:164–178
Hatano E (2007) Tumor necrosis factor signaling in hepatocyte apoptosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(Suppl 1):S43–S44
Iimuro Y, Yamamoto M, Kohno H, Itakura J, Fujii H, Matsumoto Y (1994) Blockade of liver macrophages by gadolinium chloride reduces lethality in endotoxemic rats—analysis of mechanisms of lethality in endotoxemia. J Leukoc Biol 55:723–728
Jung K, Kang M, Park C, Hyun Choi Y, Jeon Y, Park SH, Seo SK, Jin D, Choi I (2012) Protective role of V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing 4 expressed on Kupffer cells during immune-mediated liver injury by inducing tolerance of liver T- and natural killer T-cells. Hepatology 56:1838–1848
Kresse M, Latta M, Kunstle G, Riehle HM, van Rooijen N, Hentze H, Tiegs G, Biburger M, Lucas R, Wendel A (2005) Kupffer cell-expressed membrane-bound TNF mediates melphalan hepatotoxicity via activation of both TNF receptors. J Immunol 175:4076–4083
Kuboki S, Okaya T, Schuster R, Blanchard J, Denenberg A, Wong HR, Lentsch AB (2007) Hepatocyte NF-kappaB activation is hepatoprotective during ischemia-reperfusion injury and is augmented by ischemic hypothermia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292:G201–G207
Kusters S, Tiegs G, Alexopoulou L, Pasparakis M, Douni E, Kunstle G, Bluethmann H, Wendel A, Pfizenmaier K, Kollias G, Grell M (1997) In vivo evidence for a functional role of both tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors and transmembrane TNF in experimental hepatitis. Eur J Immunol 27:2870–2875
Lehmann V, Freudenberg MA, Galanos C (1987) Lethal toxicity of lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor in normal and D-galactosamine-treated mice. J Exp Med 165:657–663
Leist M, Gantner F, Jilg S, Wendel A (1995) Activation of the 55 kDa TNF receptor is necessary and sufficient for TNF-induced liver failure, hepatocyte apoptosis, and nitrite release. J Immunol 154:1307–1316
Louis H, Le Moine O, Goldman M, Deviere J (2003) Modulation of liver injury by interleukin-10. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 66:7–14
Mizuhara H, O’Neill E, Seki N, Ogawa T, Kusunoki C, Otsuka K, Satoh S, Niwa M, Senoh H, Fujiwara H (1994) T cell activation-associated hepatic injury: mediation by tumor necrosis factors and protection by interleukin 6. J Exp Med 179:1529–1537
Mohler KM, Sleath PR, Fitzner JN, Cerretti DP, Alderson M, Kerwar SS, Torrance DS, Otten-Evans C, Greenstreet T, Weerawarna K et al (1994) Protection against a lethal dose of endotoxin by an inhibitor of tumour necrosis factor processing. Nature 370:218–220
Nakashima H, Kinoshita M, Nakashima M, Habu Y, Shono S, Uchida T, Shinomiya N, Seki S (2008) Superoxide produced by Kupffer cells is an essential effector in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice. Hepatology 48:1979–1988
Olleros ML, Vesin D, Fotio AL, Santiago-Raber ML, Tauzin S, Szymkowski DE, Garcia I (2010) Soluble TNF, but not membrane TNF, is critical in LPS-induced hepatitis. J Hepatol 53:1059–1068
Pfeffer K, Matsuyama T, Kundig TM, Wakeham A, Kishihara K, Shahinian A, Wiegmann K, Ohashi PS, Kronke M, Mak TW (1993) Mice deficient for the 55 kD tumor necrosis factor receptor are resistant to endotoxic shock, yet succumb to L. monocytogenes infection. Cell 73:457–467
Pinkoski MJ, Brunner T, Green DR, Lin T (2000) Fas and Fas ligand in gut and liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 278:G354–G366
Roland CR, Walp L, Stack RM, Flye MW (1994) Outcome of Kupffer cell antigen presentation to a cloned murine Th1 lymphocyte depends on the inducibility of nitric oxide synthase by IFN-gamma. J Immunol 153:5453–5464
Rolando N, Wade J, Davalos M, Wendon J, Philpott-Howard J, Williams R (2000) The systemic inflammatory response syndrome in acute liver failure. Hepatology 32:734–739
Rudiger HA, Clavien PA (2002) Tumor necrosis factor alpha, but not Fas, mediates hepatocellular apoptosis in the murine ischemic liver. Gastroenterology 122:202–210
Sun R, Tian Z, Kulkarni S, Gao B (2004) IL-6 prevents T cell-mediated hepatitis via inhibition of NKT cells in CD4+ T cell- and STAT3-dependent manners. J Immunol 172:5648–5655
Ware CF, Crowe PD, Grayson MH, Androlewicz MJ, Browning JL (1992) Expression of surface lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor on activated T, B, and natural killer cells. J Immunol 149:3881–3888
Wright HL, Chikura B, Bucknall RC, Moots RJ, Edwards SW (2011) Changes in expression of membrane TNF, NF-{kappa}B activation and neutrophil apoptosis during active and resolved inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis 70:537–543
Yamano T, DeCicco LA, Rikans LE (2000) Attenuation of cadmium-induced liver injury in senescent male Fischer 344 rats: role of Kupffer cells and inflammatory cytokines. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 162:68–75
Yoshida T, Abe K, Ikeda T, Matsushita T, Wake K, Sato T, Inoue H (2007) Inhibitory effect of glycyrrhizin on lipopolysaccharide and D-galactosamine-induced mouse liver injury. Eur J Pharmacol 576:136–142
You Q, Cheng L, Kedl RM, Ju C (2008) Mechanism of T cell tolerance induction by murine hepatic Kupffer cells. Hepatology 48:978–990
Yu M, Shi W, Zhang J, Niu L, Chen Q, Yan D, Liu T, Jing W, Jiang X, Wei F, Yin B, Zhang W, Li Q, Li Z (2009) Influence of reverse signaling via membrane TNF-alpha on cytotoxicity of NK92 cells. Eur J Cell Biol 88:181–191
Yu M, Zhou X, Niu L, Lin G, Huang J, Zhou W, Gan H, Wang J, Jiang X, Yin B, Li Z (2013) Targeting transmembrane TNF-alpha suppresses breast cancer growth. Cancer Res 73:4061–4074
Zhang M, Xu S, Han Y, Cao X (2011) Apoptotic cells attenuate fulminant hepatitis by priming Kupffer cells to produce interleukin-10 through membrane-bound TGF-beta. Hepatology 53:306–316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Peng Yang and Wenjing Zhou contributed equally to this work.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272520), National Program on Key Basic Research Project (973 Program, 2013CB530505), and Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91029709).
The authors declare that they do not have any conflicting financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, P., Zhou, W., Li, C. et al. Kupffer-cell-expressed transmembrane TNF-α is a major contributor to lipopolysaccharide and D-galactosamine-induced liver injury. Cell Tissue Res 363, 371–383 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2252-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2252-2