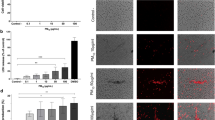
Abstract
Receptors for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell-surface receptors implicated in mechanisms of pulmonary inflammation. In the current study, we test the hypothesis that RAGE mediates inflammation in primary alveolar macrophages (AMs) exposed to diesel particulate matter (DPM). Quantitative RT-PCR and immunoblotting revealed that RAGE was up-regulated in Raw264.7 cells, an immortalized murine macrophage cell line and primary AMs exposed to DPM for 2 h. Because DPM increased RAGE expression, we exposed Raw264.7 cells and primary AMs isolated from RAGE null and wild-type (WT) mice to DPM prior to the assessment of inflammatory signaling intermediates. DPM led to the activation of Rat sarcoma GTPase (Ras), p38 MAPK and NF-κB in WT AMs and, when compared to WT AMs, these intermediates were diminished in DPM-exposed AMs isolated from RAGE null mice. Furthermore, cytokines implicated in inflammation, including IL-4, IL-12, IL-13 and TNFα, were all significantly decreased in DPM-exposed RAGE null AMs compared to similarly exposed WT AMs. These results demonstrate that diesel-induced inflammatory responses by primary AMs are mediated, at least in part, via RAGE signaling mechanisms. Further work may show that RAGE signaling in both alveolar epithelial cells and resident macrophages is a potential target in the treatment of inflammatory lung diseases exacerbated by environmental pollution.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB (2004) Nuclear Factor-kappaB: The Enemy Within. Cancer Cell 6:203–208
Bayram H, Ito K, Issa R, Ito M, Sukkar M, Churg KF (2006) Regulation of Human Lung Epithelial Cell Numbers by Diesel Exhaust Particles. Eur Resp J 27(4):705–713
Becker S, Mundandhara S, Devlin RB, Madden M (2005) Regulation of Cytokine Production in Human Alveolar Macrophages and Airway Epithelial Cells in Response to Ambient air Pollution Particles: Further Mechanistic Studies. J Tox Appl Pharm 207:S269–S275
Buckley ST, Ehrhardt C (2010) The Receptor for Advanced Glycation end-Products (RAGE) and the Lung. J Biomed Biotechnol Epub ahead of print. doi:10.1155/2010/917108
Campo I, Morbini P, Pozzi E, Luisetti M (2008) AGE Receptor: A Novel pro-Inflammatory Pathway for Chronic Respiratory Disorders. Recenti Prog Med 99(5):271–278
Dale DC, Boxer L, Liles WC (2008) The Phagocytes: Neutrophils and Monocytes. Blood 112:935–945
Demling N, Ehrhardt C, Kasper M, Laue M, Knels L, Rieber EP (2006) Promotion of Cell Adherence and Spreading: A Novel Function of RAGE, the Highly Selective Differentiation Marker of Human Alveolar Epithelial Type I Cells. Cell Tissue Res 323:475–488
Dickerson TJ, Janda KD (2002) A Previously Undescribed Chemical Link Between Smoking and Metabolic Disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(23):15084–15088
Diesel B, Hoppstadter J, Hachenthal N, Zarbock R, Cavelius C, Wahl B, Thewes N, Jacobs K, Kraegeloh A, Kiemer AK (2013) Activation of Rac1 GTPase by Nanoparticulate Structures in Human Macrophages. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 84(2):315–324
Dreher KL. 2000. Particulate matter physiochemistry and toxicology: in search of causality-a critical perspective. Inhal Toxicol. 12 (supplement):45–57.
Ferhani N, Letuve S, Kozhich A, Thibaudeau O, Grandsaigne M, Maret M et al (2010) Expression of High-Mobility Group box 1 and of Receptor for Advanced Glycation end Products in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 181(9):917–927
Fritz G (2011) RAGE: A Single Receptor Fits Multiple Ligands. Trends Biochem Sci 36:625–632
Gualtieri M, Øvrevik J, Holme JA, Perrone MG, Bolzacchini E, Schwarze PE, Camatini M (2010) Differences in Cytotoxicity Versus pro-Inflammatory Potency of Different PM Fractions in Human Epithelial Lung Cells. Toxicol In Vitro 24(1):29–39
Hales S, Salmond C, Town GI, Kjellstrom T, Woodward A (2000) Daily Mortality in Relation to Weather and air Pollution in Christchurch, New Zealand. 2000. Aust NZ J Public Health 24:89–91
Hashimoto, Matsumoto, Gon, Maruoka, Kujime, Hayashi, Takeshita (2000) p38 MAP Kinase Regulates TNFα-, IL-1α- and PAF-Induced RANTES and GM-CSF Production by Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Clin Exp Allergy 30(W Horie):48–55
Ho SM, Johnson A, Tarapore P, Janakiram V, Zhang X, Leung YK (2012) Environmental Epigenetics and its Implication on Disease Risk and Health Outcomes. ILAR J 53(3–4):289–305
Hofmann MA, Drury S, Fu C, Qu W, Taguchi A, Lu Y et al (1999) RAGE Mediates a Novel Proinflammatory Axis: A Central Cell Surface Receptor for S100/Calgranulin Polypeptides. Cell 97:889–901
Huang W, Tang Y, Li L (2010) HMGB1, a Potent Proinflammatory Cytokine in Sepsis. Cytokine 51:119–126
Huttunen HJ, Fages C, Rauvala H (1999) Receptor for Advanced Glycation end Products (RAGE)-Mediated Neurite Outgrowth and Activation of NF-kappaB Require the Cytoplasmic Domain of the Receptor but Different Downstream Signaling Pathways. J Biol Chem 274:19919–19924
Inoue K, Koike E, Yanagisawa R, Takano H (2008) Impact of Diesel Exhaust Particles on th2 Response in the Lung in Asthmatic Mice. J Clin Biochem Nutr 43(3):199–200
Inoue K, Koike E, Takano H, Yanagisawa R, Ichinose T, Yoshikawa T (2009) Effects of Diesel Exhaust Particles on Antigen-Presenting Cells and Antigen-Specific Th Immunity in Mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 234(2):200–9
Kafoury RM, Madden MC (2005) Diesel Exhaust Particles Induce the Over Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-Alpha) Gene in Alveolar Macrophages and Failed to Induce Apoptosis Through Activation of Nuclear Factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB). Int J Environ Res Public Health 2(1):107–13
Kokkola R, Andersson A, Mullins G, Ostberg T, Treutiger CJ, Arnold B, Nawroth P, Andersson U, Harris RA, Harris HE (2005) RAGE is the Major Receptor for the Proinflammatory Activity of HMGB1 in Rodent Macrophages. Scand J Immunol 61:1–9
Laskin DL (2009) Macrophages and Inflammatory Mediators in Chemical Toxicity: A Battle of Forces. Chem Res Toxicol 22:1376–1385
Laskin DL, Sunil VR, Fakhrzadeh L, Groves A, Gow AJ, Laskin JD (2010a) Macrophages, Reactive Nitrogen Species, and Lung Injury. Ann NY Acad Sci 1203:60–65
Laskin DL, Mainelis G, Turpin BJ, Patel KJ, Sunil VR; HEI Health Review Committee (2010b) Pulmonary effects of inhaled diesel exhaust in young and old mice: a pilot project. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 151:3–31
Lee YL, Chen W, Tsai WK, Lee JC, Chiou HL, Shih CM, Wang YC (2006) Polymorphisms of p53 and p21 Genes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J Lab Clin Med 147:228–233
Li N, Sioutas C, Cho A, Schmitz D, Misra C, Sempf J et al (2003) Ultrafine Particulate Pollutants Induce Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Damage. Environ Health Perspect 111:445–450
Ling SH, van Eden SF (2009) Particulate Matter air Pollution Exposure: Role in the Development and Exacerbation of COPD. Int J COPD 4:233–243
Mendez R, Zheng Z, Fan Z, Rajagopalan S, Sun Q, Zhang K (2013) Exposure to Fine Airborne Particualte Matter Induces Macrophage Infiltration, Unfolded Protein Response, and Lipid Deposition in White Adipose Tissue. Am J Transl Res 5(2):224–234
Miller MR, McLean SG, Duffin R, Lawal AO, Araujo JA, Shaw CA, Mills NL, Donaldson K, Newby DE, Hadoke PW (2013) Diesel Exhaust Particulate Increases the Size and Complexity of Lesions in Atherosclerotic Mice. Part Fibre Toxicol 10:61
Morbini P, Villa C, Campo I, Zorzetto M, Inghilleri S, Luisetti M (2006) The Receptor for Advanced Glycation end Products and its Ligands: A new Inflammatory Pathway in Lung Disease? Mod Pathol 19:1437–1445
Nicholl ID, Bacala R (1998) Advanced Glycation Endproducts and Cigarette Smoking. Cell Mol Biol 44(7):1025–1033
Pendino KJ, Shuler RL, Laskin JD, Laskin DL (1994) Enhanced Production of Interleukin-1, Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha, and Fibronectin by rat Lung Phagocytes Following Inhalation of a Pulmonary Irritant. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 11:279–286
Pope CA III, Thun MJ, Namboodiri MM, Dochery DW, Evans JS, Speizer FE et al (1995) Particulate air Pollution as a Predictor of Mortality in a Prospective Study of US Adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:669–674
Pourazar J, Frew AJ, Blomberg A, Helleday R, Kelly FJ, Wilson S, Sandström T (2004) Diesel Exhaust Exposure Enhances the Expression of IL-13 in the Bronchial Epithelium of Healthy Subjects. Respir Med 98(9):821–5
Riedl MA, Diaz-Sanchez D, Linn WS, Gong H Jr, Clark KW, Efforts RM, Miller JW, Cocker DR, Berhane KT; HEI Health Review Committee. 2012. Allergic inflammation in the human lower respiratory tract affected by exposure to diesel exhaust. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. (165):5–43; discussion 45–64.
Reuter CW, Morgan MA, Bergmann L (2000) Targeting the Ras Signaling Pathway: A Rational, Mechanism-Based Treatment for Hematologic Malignancies? Blood 96:1655–1669
Reynolds PR, Mucenski ML, Le Cras TD, Nichols WC, Whitsett JA (2004) Midkine is Regulated by Hypoxia and Causes Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling. J Biol Chem 279(35):37124–37132
Reynolds PR, Kasteller S, Cosio MG, Sturrock A, Huecksteadt TP, Hoidal JR (2008) RAGE: Developmental Expression and Positive Feedback Regulation by Egr-1 During Cigarette Smoke Exposure in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294(6):L1094–1101
Reynolds PR, Wasley KM, Allison CH (2010) Diesel Particulate Matter Induces RAGE Expression in Pulmonary Epithelium and RAGE Signaling Influences NF-κB-Mediated Inflammation. Environ Health Per 119(3):332–9
Reynolds PR, Stogsdill JA, Stogsdill MP, Heimann NB (2011a) Up-Regulation of RAGE by Alveolar Epithelium Influences Cytodifferentiation and Causes Severe Lung Hypoplasia. Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 45(6):1195–202
Reynolds PR, Kasteler SD, Schmitt RE, Hoidal JR (2011b) Receptor for Advanced Glycation end-Products Signals Through Ras During Tobacco Smoke-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 45:411–418
Ristovski ZD, Miljevic B, Surawski NC, Morawska L, Fong KM, Goh F, Yang IA (2012) Respiratory Health Effects of Diesel Particulate Matter. Respirology 17(2):201–12
Robinson AB, Stogsdill JA, Lewis JP, Wood TA, Reynolds PR (2012a) RAGE and Tobacco Smoke: Insights into Modeling Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front Resp Physiol 3:301. doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00301
Robinson AB, Dickson KD, Bennion BG, Reynolds PR (2012b) RAGE Signaling by Alveolar Macrophages Influences Tobacco Smoke-Induced Inflammation, AJP. Lung Cell Mol Physiol 302(11):L1192–9
Rouhiainen A, Kuja-Panula J, Tumova S, Rauvala H (2013) RAGE-Mediated Cell Signaling. Methods Mol Biol 963:239–63
Salvi SS, Nordenhall C, Blomberg A, Rudell B, Pourazar J, Kelly FJ et al (2000) Acute Exposure to Diesel Exhaust Increases IL-8 and Grow-a Production in Healthy Human Airways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161:550–557
Schmidt AM, Vianna M, Gerlach M, Brett J, Ryan J, Kao J et al (1992) Isolation and Characterization of two Binding Proteins for Advanced Glycosylation end Products from Bovine Lung Which are Present on the Endothelial Cell Surface. J Biol Chem 267:14987–14997
Schmidt AM, Yan SD, Yan SF, Stern DM (2001) The Multiligand Receptor RAGE as a Progression Factor Amplifying Immune and Inflammatory Responses. J Clin Invest 108:949–955
Shinyashiki M, Eiguren-Fernandez A, Schmitz DA, Di Stephano E, Li N, Emak WP et al (2009) Electrophilic and Redox Properties of Diesel Exhaust Particles. Environ Res 109:239–244
Taguchi A, Blood DC, del Toro G, Canet A, Lee DC, Qu W et al (2000) Blockade of Amphoterin/RAGE Signalling Suppresses Tumor Growth and Metastases. Nature 405:354–360
Takizawa H, Ohtoshi T, Kawasaki S, Kohyama T, Desaki M, Kosama T et al (1999) Diesel Exhaust Particles Induce NF-Kappa B Activation in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells in Vitro: Importance in Cytokine Transcription. J Immunol 162:4705–4711
Terzano C, Di Stefano F, Conti V, Graziani E, Petroianni A (2010) Air Pollution Ultrafine Particles: Toxicity Beyond the Lung. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 14(10):809–21
Wendt TM, Tanji N, Guo J, Kislinger TR, Qu W, Lu Y, Bucciarelli LG, Rong LL, Moser B, Markowitz GS, Stein G, Bierhaus A, Liliensiek B, Arnold B, Nawroth PP, Stern DM, D’Agati VD, Schmidt AM (2003) RAGE Drives the Development of Glomerulosclerosis and Implicates Podocyte Activation in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Neuropathy. Am J Pathol 162(4):1123–37
Wesselborg S, Bauer MKA, Vogt M, Schmitz ML, Schulze-Osthoff K (1997) Activation of Transcription Factor NF-κB and p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Is Mediated by Distinct and Separate Stress Effector Pathways. J Biol Chem 272:12422–12429
Wichmann HE. 2007. Diesel exhaust particles. Inhal Toxicol. 19 (supplement 1):241–244.
Wright ME, Klein AD, Stesniak EJ. 1991. A diesel exhaust filter system for industrial forklifts. SAE Technical Paper Series 911852: Warrendale, PA.
Wu X, Mi Y, Yang H, Hu A, Zhang Q, Shang C (2013) The Activation of HMGB1 as a Progression Factor on Inflammation Response in Normal Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Through RAGE/JNK/NF-κB Pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 380(1–2):249–57
Yamamoto Y, Harashima A, Saito H, Tsuneyama K, Munesue S, Motoyoshi S, Han D, Watanabe T, Asano M, Takasawa S, Okamoto H, Shimura S, Karasawa T, Yonekura H, Yamamoto H (2011) Septic Shock is Associated With Receptor for Advanced Glycation end Products Ligation of LPS. J Immunol 186:3248–3257
Yan SD, Chen X, Fu J, Chen M, Zhu H, Roher A et al (1996) RAGE and Amyloid Beta Peptide Neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 382:685–691
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Flight Attendant’s Medical Research Institute (FAMRI; P.R.R.) and a BYU Mentoring Environment Grant (P.R.R.). The other authors declare that they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barton, D.B., Betteridge, B.C., Earley, T.D. et al. Primary alveolar macrophages exposed to diesel particulate matter increase RAGE expression and activate RAGE signaling. Cell Tissue Res 358, 229–238 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1905-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1905-x