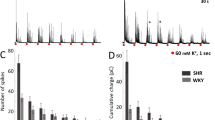
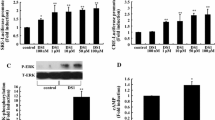
Abstract
Pituitary adenylyl cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) augment the biosynthesis of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). We tested whether secretin belonging to the glucagon/PACAP/VIP superfamily would increase transcription of the tyrosine hydroxylase (Th) gene and modulate catecholamine secretion. Secretin activated transcription of the endogenous Th gene and its transfected promoter (EC50 ∼4.6 nM) in pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. This was abolished by pre-treatment with a secretin receptor (SCTR) antagonist and by inhibition of protein kinase A (PKA), mitogen-activated protein kinase, or CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein). In agreement, secretin increased PKA activity and induced phosphorylation of CREB and binding to Th CRE, suggesting secretin signaling to transcription via a PKA-CREB pathway. Secretin stimulated catecholamine secretion (EC50 ∼3.5 μM) from PC12 cells, but this was inhibited by pre-treatment with VIP-preferring receptor (VPAC1)/PACAP-preferring receptor (PAC1) antagonists. Secretin-evoked secretion occurred without extracellular Ca2+ and was abolished by intracellular Ca2+ chelation. Secretin augmented phospholipase C (PLC) activity and increased inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) levels in PC12 cells; PLC-β inhibition blocked secretin-induced catecholamine secretion, indicating the participation of intracellular Ca2+ from a phospholipase pathway in secretion. Like PACAP, secretin evoked long-lasting catecholamine secretion, even after only a transient exposure. Thus, transcription is triggered by nanomolar concentrations of the peptide through SCTR, with signaling along the cAMP-PKA and extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathways and through CREB. By contrast, secretion is triggered only by micromolar concentrations of peptide through PAC1/VPAC receptors and by utilizing a PLC/intracellular Ca2+ pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Chga :
-
Chromogranin A gene
- CRE:
-
cAMP response element
- ERK:
-
Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase
- GPCR:
-
G-protein-coupled receptor
- IP3 :
-
Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate
- PAC1:
-
PACAP-preferring receptor
- PACAP:
-
Pituitary adenylyl cyclase activating polypeptide
- PHI:
-
Peptide histidine isoleucine
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- PLC:
-
Phospholipase C
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription followed by polymerase Chain reaction
- SCTR:
-
Secretin receptor
- Sctr :
-
Secretin receptor gene
- TH:
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase enzyme
- Th :
-
TH gene
- VIP:
-
Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide
- VPAC1:
-
VIP-preferring receptor
References
Anderova M, Duchene AD, Barbara JG, Takeda K (1998) Vasoactive intestinal peptide potentiates and directly stimulates catecholamine secretion from rat adrenal chromaffin cells. Brain Res 809:97–106
Aragon V, Rossier O, Cianciotto NP (2002) Legionella pneumophila genes that encode lipase and phospholipase C activities. Microbiology 148:2223–2231
Babu GN, Vijayan E (1983) Plasma gonadotropin, prolactin levels and hypothalamic tyrosine hydroxylase activity following intraventricular bombesin and secretin in ovariectomized conscious rats. Brain Res Bull 11:25–29
Bayliss HP, Starling EH (1902) Mechanism of pancreatic secretion. J Physiol (Lond) 28:325–353
Berridge MJ (1998) Neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron 21:13–26
Chatelain P, Gillet L, Waelbroeck M, Camus JC, Robberecht P, Christophe J (1983) Selective alteration of secretin-stimulated cardiac adenylate cyclase activity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Horm Metab Res 15:620–622
Chey WY, Chang TM (2003) Secretin, 100 years later. J Gastroenterol 38:1025–1035
Choi HJ, Park SY, Hwang O (1999) Differential involvement of PKA and PKC in regulation of catecholamine enzyme genes by PACAP. Peptides 20:817–822
Chowdhury PS, Guo X, Wakade TD, Przywara DA, Wakade AR (1994) Exocytosis from a single rat chromaffin cell by cholinergic and peptidergic neurotransmitters. Neuroscience 59:1–5
Chu JY, Yung WH, Chow BK (2006) Secretin: a pleiotrophic hormone. Ann NY Acad Sci 1070:27–50
Corbitt J, Vivekananda J, Wang SS, Strong R (1998) Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression during persistent stimulation of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptors on PC12 cells: regulation by protein kinase A-dependent and protein kinase A-independent pathways. J Neurochem 71:478–486
Corbitt J, Hagerty T, Fernandez E, Morgan WW, Strong R (2002) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase messenger RNA in PC12 cells during persistent stimulation by VIP and PACAP38: differential regulation by protein kinase A and protein kinase C-dependent pathways. Neuropeptides 36:34–45
Cui J, Zhou X, Chazaro I, DeStefano AL, Manolis AJ, Baldwin CT, Gavras H (2003) Association of polymorphisms in the promoter region of the PNMT gene with essential hypertension in African Americans but not in Whites. Am J Hypertens 16:859–863
Deak M, Clifton AD, Lucocq LM, Alessi DR (1998) Mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1 (MSK1) is directly activated by MAPK and SAPK2/p38, and may mediate activation of CREB. EMBO J 17:4426–4441
Deisseroth K, Bito H, Tsien RW (1996) Signaling from synapse to nucleus: postsynaptic CREB phosphorylation during multiple forms of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Neuron 16:89–101
Douglas WW (1968) Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol 34:453–474
Garcia AG, Garcia-De-Diego AM, Gandia L, Borges R, Garcia-Sancho J (2006) Calcium signaling and exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Physiol Rev 86:1093–1131
Gayen JR, Saberi M, Schenk S, Biswas N, Vaingankar SM, Cheung WW, Najjar SM, O'Connor DT, Bandyopadhyay G, Mahata SK (2009) A novel pathway of insulin sensitivity in chromogranin a null mice: a crucial role for pancreastatin in glucose homeostasis. J Biol Chem 284:28498–28509
Grabner CP, Fox AP (2006) Stimulus-dependent alterations in quantal neurotransmitter release. J Neurophysiol 96:3082–3087
Gunnes P, Rasmussen K (1986) Haemodynamic effects of pharmacological doses of secretin in patients with impaired left ventricular function. Eur Heart J 7:146–149
Gunnes P, Smiseth OA, Lygren I, Jorde R (1985) Effects of secretin infusion on myocardial performance and metabolism in the dog. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 7:1183–1187
Gunnes P, Reikeras O, Lygren I (1986) Secretin infusion in acute ischemic left ventricular failure: effects on myocardial performance and metabolism in a closed-chest dog model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 239:915–918
Guo X, Wakade AR (1994) Differential secretion of catecholamines in response to peptidergic and cholinergic transmitters in rat adrenals. J Physiol (Lond) 475:539–545
Hagiwara M, Brindle P, Harootunian A, Armstrong R, Rivier J, Vale W, Tsien R, Montminy MR (1993) Coupling of hormonal stimulation and transcription via the cyclic AMP-responsive factor CREB is rate limited by nuclear entry of protein kinase A. Mol Cell Biol 13:4852–4859
Hamelink C, Tjurmina O, Damadzic R, Young WS, Weihe E, Lee HW, Eiden LE (2002) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide is a sympathoadrenal neurotransmitter involved in catecholamine regulation and glucohomeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:461–466
Ip NY, Zigmond RE (2000) Synergistic effects of muscarinic agonists and secretin or vasoactive intestinal peptide on the regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase activity in sympathetic neurons. J Neurobiol 42:14–21
Isobe K, Yukimasa N, Nakai T, Takuwa Y (1996) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide induces gene expression of the catecholamine synthesizing enzymes, tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine beta hydroxylase, through 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate- and protein kinase C-dependent mechanisms in cultured porcine adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. Neuropeptides 30:167–175
Koshimizu H, Cawley NX, Kim T, Yergey AL, Loh YP (2011) Serpinin: a novel chromogranin A-derived, secreted peptide up-regulates protease nexin-1 expression and granule biogenesis in endocrine cells. Mol Endocrinol (in press)
Kurioka S, Matsuda M (1976) Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem 75:281–289
Lazaroff M, Patankar S, Yoon SO, Chikaraishi DM (1995) The cyclic AMP response element directs tyrosine hydroxylase expression in catecholaminergic central and peripheral nervous system cell lines from transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 270:21579–21589
Lewis-Tuffin LJ, Quinn PG, Chikaraishi DM (2004) Tyrosine hydroxylase transcription depends primarily on cAMP response element activity, regardless of the type of inducing stimulus. Mol Cell Neurosci 25:536–547
Mahapatra NR, Mahata M, Datta A, Gerdes H-H, Huttner WB, O’Connor DT, Mahata SK (2000) Neuroendocrine cell type-specific and inducible expression of the chromogranin B gene: crucial role of the proximal promoter. Endocrinology 141:3668–3678
Mahapatra NR, Mahata M, O'Connor DT, Mahata SK (2003) Secretin activation of chromogranin A gene transcription. Identification of the signaling pathways in cis and in trans. J Biol Chem 278:19986–19994
Mahata M, Mahata SK, Parmer RJ, O'Connor DT (1996) Vesicular monoamine transport inhibitors novel action at calcium channels to prevent catecholamine secretion. Hypertension 28:414–420
Mahata SK, Mahata M, Livsey CV, Gerdes H-H, Huttner WB, O'Connor DT (1999) Neuroendocrine cell type-specific and inducible expression of the secretogranin II gene: crucial role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and serum response elements. Endocrinology 140:739–749
Malhotra RK, Wakade TD, Wakade AR (1988) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and muscarine mobilize intracellular Ca2+ through breakdown of phosphoinositides to induce catecholamine secretion. Role of IP3 in exocytosis. J Biol Chem 263:2123–2126
Muller A, Monnier D, Rene F, Larmet Y, Koch B, Loeffler JP (1997) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide triggers dual transduction signaling in CATH.a cells and transcriptionally activates tyrosine hydroxylase and c-fos expression. J Neurochem 68:1696–1704
Mutt V (1980) Chemistry, isolation and purification of gastrointestinal hormones. Biochem Soc Trans 8:11–14
O'Donohue TL, Charlton CG, Miller RL, Boden G, Jacobowitz DM (1981) Identification, characterization, and distribution of secretin immunoreactivity in rat and pig brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:5221–5224
Park SY, Choi HJ, Hwang O (1999) Regulation of basal expression of catecholamine-synthesizing enzyme genes by PACAP. Mol Cells 9:146–151
Przywara DA, Guo X, Angelilli ML, Wakade TD, Wakade AR (1996) A non-cholinergic transmitter, pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide, utilizes a novel mechanism to evoke catecholamine secretion in rat adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem 271:10545–10550
Rao F, Zhang L, Wessel J, Zhang K, Wen G, Kennedy BP, Rana BK, Das M, Rodriguez-Flores JL, Smith DW, Cadman PE, Salem RM, Mahata SK, Schork NJ, Taupenot L, Ziegler MG, O'Connor DT (2007) Tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in catecholamine biosynthesis: discovery of common human genetic variants governing transcription, autonomic activity, and blood pressure in vivo. Circulation 116:993–1006
Roskoski R Jr, White L, Knowlton R, Roskoski LM (1989) Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase activity in rat PC12 cells by neuropeptides of the secretin family. Mol Pharmacol 36:925–931
Schwarzschild MA, Zigmond RE (1989) Secretin and vasoactive intestinal peptide activate tyrosine hydroxylase in sympathetic nerve endings. J Neurosci 9:160–166
Schwarzschild MA, Zigmond RE (1991) Effects of peptides of the secretin-glucagon family and cyclic nucleotides on tyrosine hydroxylase activity in sympathetic nerve endings. J Neurochem 56:400–406
Shaywitz AJ, Greenberg ME (1999) CREB: a stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu Rev Biochem 68:821–861
Sitniewska EM, Wisniewska RJ, Wisniewski K (2002) Diabetes-induced changes of nitric oxide influence on the cardiovascular action of secretin. Regul Pept 105:163–172
Sun P, Enslen H, Myung PS, Maurer RA (1994) Differential activation of CREB by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases type II and type IV involves phosphorylation of a site that negatively regulates activity. Genes Dev 8:2527–2539
Taupenot L, Mahata SK, Wu H, O'Connor DT (1998) Peptidergic activation of transcription and secretion in chromaffin cells. Cis and trans signaling determinants of pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP). J Clin Invest 101:863–876
Taupenot L, Mahata M, Mahata SK, O'Connor DT (1999) Time-dependent effects of the neuropeptide PACAP on catecholamine secretion: stimulation and desensitization. Hypertension 34:1152–1162
Tinti C, Yang C, Seo H, Conti B, Kim C, Joh TH, Kim KS (1997) Structure/function relationship of the cAMP response element in tyrosine hydroxylase gene transcription. J Biol Chem 272:19158–19164
Tonshoff C, Hemmick L, Evinger MJ (1997) Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) regulates expression of catecholamine biosynthetic enzyme genes in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Mol Neurosci 9:127–140
Trimble ER, Buchanan KD, Hadden DR, Montgomery DA (1977) Secretin: high plasma levels in diabetes mellitus. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 85:799–805
Ulrich CD 2nd, Holtmann M, Miller LJ (1998) Secretin and vasoactive intestinal peptide receptors: members of a unique family of G protein-coupled receptors. Gastroenterology 114:382–397
Wakade AR (1988) Noncholinergic transmitter(s) maintains secretion of catecholamines from rat adrenal medulla for several hours of continuous stimulation of splanchnic neurons. J Neurochem 50:1302–1308
Wakade TD, Blank MA, Malhotra RK, Pourcho R, Wakade AR (1991) The peptide VIP is a neurotransmitter in rat adrenal medulla: physiological role in controlling catecholamine secretion. J Physiol (Lond) 444:349–362
Wessels-Reiker M, Basiboina R, Howlett AC, Strong R (1993) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-related peptides modulate tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in PC12 cells through multiple adenylate cyclase-coupled receptors. J Neurochem 60:1018–1029
Wu H, Mahata SK, Mahata M, Webster NJ, Parmer RJ, O'Connor DT (1995) A functional cyclic AMP response element plays a crucial role in neuroendocrine cell type-specific expression of the secretory granule protein chromogranin A. J Clin Invest 96:568–578
Xing J, Ginty DD, Greenberg ME (1996) Coupling of the RAS-MAPK pathway to gene activation by RSK2, a growth factor-regulated CREB kinase. Science 273:959–963
Yang B, Goulet M, Boismenu R, Ferguson AV (2004) Secretin depolarizes nucleus tractus solitarius neurons through activation of a nonselective cationic conductance. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 286:R927–R934
Yukimasa N, Isobe K, Nagai H, Takuwa Y, Nakai T (1999) Successive occupancy by immediate early transcriptional factors of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene TRE and CRE sites in PACAP-stimulated PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Neuropeptides 33:475–482
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the Department of Veterans Affairs (to S.K.M. and D.T.O’C.) and the National Institutes of Health (R01 DA011311 to S.K.M.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahata, M., Zhang, K., Gayen, J.R. et al. Catecholamine biosynthesis and secretion: physiological and pharmacological effects of secretin. Cell Tissue Res 345, 87–102 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1177-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1177-7