Abstract
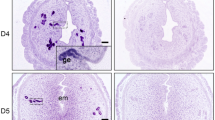
Ovarian steroid hormones, progesterone (P4), and estradiol (E2) strictly regulate the endometrial tissue remodeling required for successful embryo implantation. Indian hedgehog (Ihh) is up-regulated by P4 and critically mediates uterine receptivity in the mouse. However, the regulation of Ihh expression during the implantation period still remains unclear. The present study was conducted to elucidate the mechanism of the steroidal regulation in the expression of Ihh and Gli1, the mediator of the Ihh pathway. Ihh mRNA was expressed in the rat uterus on 3.5–5.5 days post-coitus (dpc), while Gli1 expression transiently increased at 3.5 dpc but decreased significantly on 5.5 dpc (P < 0.001). In delayed implantation, the expression of Ihh was induced by the implantation-induced E2 treatment in the primed rat uterus. In contrast, expression of Gli1 was significantly decreased by E2 treatment (P = 0.016). In the case of ICI182.780 (ICI) treatment, Ihh expression was eliminated by ICI, whilst Gli1 expression increased. These results suggest that Ihh expression is maintained at a high level until the initiation of implantation, while the expression of Gli1 is decreased just prior to the initiation of implantation depending on the E2 action. This observation aids in the understanding of the Ihh signaling pathway mediating uterine remodeling for implantation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellusci S, Furuta Y, Rush MG, Henderson R, Winnier G, Hogan BL (1997) Involvement of sonic hedgehog (Shh) in mouse embryonic lung growth and morphogenesis. Development 124:53–63
Bitgood MJ, Shen L, McMahon AP (1996) Sertoli cell signaling by desert hedgehog regulates the male germline. Curr Biol 6:298–304
Brayman M, Thathiah A, Carson DD (2004) MUC1: a multifunctional cell surface component of reproductive tissue epithelia. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2:4
Carson DD, DeSouza MM, Kardon R, Zhou X, Lagow E, Julian J (1998) Mucin expression and function in the female reproductive tract. Hum Reprod Updat 4:459–464
Carson DD, Bagchi I, Dey SK, Enders AC, Fazleabas AT, Lessey BA, Yoshinaga K (2000) Embryo implantation. Dev Biol 223:217–237
Chuang PT, McMahon AP (1999) Vertebrate hedgehog signalling modulated by induction of a Hedgehog-binding protein. Nature 397:617–621
de Kok JB, Roelofs RW, Giesendorf BA, Pennings JL, Waas ET, Feuth T, Swinkels DW, Span PN (2005) Normalization of gene expression measurements in tumor tissues: comparison of 13 endogenous control genes. Lab Invest 85:154–159
Feng YZ, Shiozawa T, Miyamoto T, Kashima H, Kurai M, Suzuki A, Ying-Song J, Konishi I (2007) Overexpression of hedgehog signaling molecules and its involvement in the proliferation of endometrial carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 13:1389–1398
Guo Y, Wang H, Okamoto Y, Ueda N, Kingsley PJ, Marnett LJ, Schmid HH, Das SK, Dey SK (2005) N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D is an important determinant of uterine anandamide levels during implantation. J Biol Chem 280:23429–23432
Ingham PW, McMahon AP (2001) Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev 15:3059–3087
Katayama S, Ashizawa K, Gohma H, Fukuhara T, Narumi K, Tsuzuki Y, Tatemoto H, Nakada T, Nagai K (2006) The expression of Hedgehog genes (Ihh, Dhh) and Hedgehog target genes (Ptc1, Gli1, Coup-TfII) is affected by estrogenic stimuli in the uterus of immature female rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 217:375–383
Katoh Y, Katoh M (2008) Hedgehog signaling, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and miRNA (review). Int J Mol Med 22:271–275
Kennedy TG, Gillio-Meina C, Phang SH (2007) Prostaglandins and the initiation of blastocyst implantation and decidualization. Reproduction 134:635–643
Khatua A, Wang X, Ding T, Zhang Q, Reese J, DeMayo FJ, Paria BC (2006) Indian hedgehog, but not histidine decarboxylase or amphiregulin, is a progesterone-regulated uterine gene in hamsters. Endocrinology 147:4079–4092
Kubota K, Yamauchi N, Matsumoto K, Watanabe R, Oozono S, Aramaki S, Wood C, Soh T, Hattori MA (2008) Expression of hedgehog family genes in the rat uterus during early pregnancy. J Reprod Dev 54:340–345
Lee DS, Yanagimoto Ueta Y, Suzuki H (2006a) Expression of amphiregulin during the pre- and post-implantation period in the mouse reproductive tract. J Reprod Dev 52:781–787
Lee K, Jeong J, Kwak I, Yu CT, Lanske B, Soegiarto DW, Toftgard R, Tsai MJ, Tsai S, Lydon JP, DeMayo FJ (2006b) Indian hedgehog is a major mediator of progesterone signaling in the mouse uterus. Nat Genet 38:1204–1209
Lubahn DB, Moyer JS, Golding TS, Couse JF, Korach KS, Smithies O (1993) Alteration of reproductive function but not prenatal sexual development after insertional disruption of the mouse estrogen receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:11162–11166
Matsumoto H, Zhao X, Das SK, Hogan BL, Dey SK (2002) Indian hedgehog as a progesterone-responsive factor mediating epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the mouse uterus. Dev Biol 245:280–290
Paria BC, Song H, Wang X, Schmid PC, Krebsbach RJ, Schmid HH, Bonner TI, Zimmer A, Dey SK (2001) Dysregulated cannabinoid signaling disrupts uterine receptivity for embryo implantation. J Biol Chem 276:20523–20528
Pathi S, Pagan-Westphal S, Baker DP, Garber EA, Rayhorn P, Bumcrot D, Tabin CJ, Blake Pepinsky R, Williams KP (2001) Comparative biological responses to human sonic, Indian, and desert hedgehog. Mech Dev 106:107–117
Sahlin L, Masironi B, Akerberg S, Eriksson H (2006) Tissue- and hormone-dependent progesterone receptor distribution in the rat uterus. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 4:47
Simon L, Spiewak KA, Ekman GC, Kim J, Lydon JP, Bagchi MK, Bagchi IC, DeMayo FJ, Cooke PS (2009) Stromal progesterone receptors mediate induction of Indian hedgehog (IHH) in uterine epithelium and its downstream targets in uterine stroma. Endocrinology 150:3871–3876
Stewart CL, Cullinan EB (1997) Preimplantation development of the mammalian embryo and its regulation by growth factors. Dev Genet 21:91–101
Taipale J, Beachy PA (2001) The hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 411:349–354
Takamoto N, Zhao B, Tsai SY, DeMayo FJ (2002) Identification of Indian hedgehog as a progesterone-responsive gene in the murine uterus. Mol Endocrinol 16:2338–2348
Tan J, Paria BC, Dey SK, Das SK (1999) Differential uterine expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors correlates with uterine preparation for implantation and decidualization in the mouse. Endocrinology 140:5310–5321
Tibbetts TA, Mendoza-Meneses M, O'Malley BW, Conneely OM (1998) Mutual and intercompartmental regulation of estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor expression in the mouse uterus. Biol Reprod 59:1143–1152
Wakitani S, Hondo E, Phichitraslip T, Stewart CL, Kiso Y (2008) Upregulation of Indian hedgehog gene in the uterine epithelium by leukemia inhibitory factor during mouse implantation. J Reprod Dev 54:113–116
Wang H, Dey SK (2006) Roadmap to embryo implantation: clues from mouse models. Nat Rev Genet 7:185–199
Wang H, Matsumoto H, Guo Y, Paria BC, Roberts RL, Dey SK (2003) Differential G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor signaling by anandamide directs blastocyst activation for implantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14914–14919
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS; no. 21580349, to N. Yamauchi).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubota, K., Yamauchi, N., Yamagami, K. et al. Steroidal regulation of Ihh and Gli1 expression in the rat uterus. Cell Tissue Res 340, 389–395 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-0945-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-0945-0