Abstract
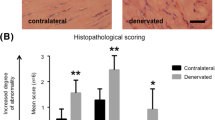
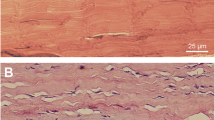
Limited information is available concerning the existence of a cholinergic system in the human Achilles tendon. We have studied pain-free normal Achilles tendons and chronically painful Achilles tendinosis tendons with regard to immunohistochemical expression patterns of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (M2R), choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), and vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT). M2R immunoreactivity was detected in the walls of blood vessels. As evidenced via parallel staining for CD31 and alpha-smooth muscle actin, most M2R immunoreactivity was present in the endothelium. M2R immunoreactivity also occured in tenocytes, which regularly immunoreact for vimentin. The degree of M2R immunoreactivity was highly variable, tendinosis tendons that exhibit hypercellularity and hypervascularity showing the highest levels of immunostaining. Immunoreaction for ChAT and VAChT was detected in tenocytes in tendinosis specimens, particularly in aberrant cells. In situ hybridization revealed that mRNA for ChAT is present in tenocytes in tendinosis specimens. Our results suggest that autocrine/paracrine effects occur concerning the tenocytes in tendinosis. Up-regulation/down-regulation in the levels of M2R immunoreactivity possibly take place in tenocytes and blood vessel cells during the various stages of tendinosis. The presumed local production of acetylcholine (ACh), as evidenced by immunoreactivity for ChAT and VAChT and the detection of ChAT mRNA, appears to evolve in response to tendinosis. These observations are of importance because of the well-known vasoactive, trophic, and pain-modulating effects that ACh is known to have and do unexpectedly establish the presence of a non-neuronal cholinergic system in the Achilles tendon.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfredson H, Lorentzon R (2002) Chronic tendon pain: no signs of chemical inflammation but high concentrations of the neurotransmitter glutamate. Implications for treatment? A review. Curr Drug Targets 3:43–54
Alfredson H, Öhberg L (2005) Sclerosing injections to areas of neo-vascularisation reduce pain in Achilles tendinopathy: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13:338–344
Alfredson H, Forsgren S, Thorsen K, Fahlström M, Johansson H, Lorentzon R (2001) Glutamate NMDAR1 receptors localized to nerves in human Achilles tendons. Implications for treatment? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 9:123–126
Alfredson H, Öhberg L, Forsgren S (2003) Is vasculo-neural ingrowth the cause of pain in chronic Achilles tendinosis? An investigation using ultrasonography and colour Doppler, immunohistochemistry, and diagnostic injections. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 11:334–338
Åström M (1995) Chronic Achilles tendinopathy. A survey of surgical and histopathologic findings. Clin Orthop 316:51–164
Badaut J, Moro V, Seylaz J, Lasbennes F (1997) Distribution of muscarinic receptors on the endothelium of cortical vessels in the brain. Brain Res 778:25–33
Bjur D, Alfredson H, Forsgren S (2005) The innervation pattern of the human Achilles tendon: studies of the normal and tendinosis tendon with markers for general and sensory innervation. Cell Tissue Res 320:201–206
Burnstock G, Ralevic V (1994) New insights into the local regulation of blood flow by perivascular nerves and endothelium. Br J Plast Surg 47:527–543
Cassiman D, Denef C, Desmet VJ, Roskams T (2001) Human and rat hepatic stellate cells express neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors. Hepatology 33:148–158
Caulfield MP, Birdsall NJ (1998) International Union of Pharmacology. XVII. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 50:279–290
Chapple CR, Yamanishi T, Chess-Williams R (2002) Muscarinic receptor subtypes and management of the overactive bladder. Urology 60:82–88
Danielson P, Alfredson H, Forsgren S (2006) Immunohistochemical and histochemical findings favoring the occurrence of autocrine/paracrine as well as nerve-related cholinergic effects in chronic painful patellar tendon tendinosis. Microsc Res Tech 69:808–819
Delaney K, Murph M, Brown L, Radhakrishna H (2002) Transfer of M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors to clathrin-derived early endosomes following clathrin-independent endocytosis. J Biol Chem 277:33439–33446
Dussor GO, Helesic G, Hargreaves KM, Flores CM (2004) Cholinergic modulation of nociceptive responses in vivo and neuropeptide release in vitro at the level of the primary sensory neuron. Pain 107:22–32
Eiden LE (1998) The cholinergic gene locus. J Neurochem 70:2227–2240
Falk-Variant J, Israel M, Bruner J, Stinnakre J, Meunier FM, Gaultier P, Meunier FA, Lesbats B, Synguelakis M, Correges P, Dunant Y (1996) Enhancement of quantal transmitter release and mediatophore expression by cyclic AMP in fibroblasts loaded with acetylcholine. Neuroscience 75:353–360
Fisher LJ, Schinstine M, Salvaterra P, Dekker AJ, Thal L, Gage FH (1993) In vivo production and release of acetylcholine from primary fibroblasts genetically modified to express choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem 61:1323–1332
Forsgren S, Danielson P, Alfredson H (2005) Vascular NK-1 receptor occurrence in normal and chronic painful Achilles and patellar tendons: studies on chemically unfixed as well as fixed specimens. Regul Pept 126:173–181
Fritz S, Wessler I, Breitling R, Rossmanith W, Ojeda SR, Dissen GA, Amsterdam A, Mayerhofer A (2001) Expression of muscarinic receptor types in the primate ovary and evidence for nonneural acetylcholine synthesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:349–354
Fu WM, Liou HC, Chen YH, Wang SM (1998) Release of acetylcholine from embryonic myocytes in Xenopus cell cultures. J Physiol (Lond) 509:497–506
Haberberger RV, Bodenbenner M (2000) Immunohistochemical localization of muscarinic receptors (M2) in the rat skin. Cell Tissue Res 300:389–396
Haberberger RV, Bodenbenner M, Kummer W (2000) Expression of the cholinergic gene locus in pulmonary arterial endothelial cells. Histochem Cell Biol 113:379–387
Haberberger RV, Pfeil U, Lips KS, Kummer W (2002) Expression of the high-affinity choline transporter, CHT1, in the neuronal and non-neuronal cholinergic system of human and rat skin. J Invest Dermatol 119:943–948
Hansson M, Forsgren S (1995) Immunoreactive atrial and brain natriuretic peptides are co-localized in Purkinje fibres but not in the innervation of the bovine heart conduction system. Histochem J 27:222–230
Hasegawa T, Hirose T, Kudo E, Abe J, Hizawa K (1990) Cytoskeletal characteristics of myofibroblasts in benign neoplastic and reactive fibroblastic lesions. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 416:375–382
Höckerfelt U, Franzén L, Norrgård Ö, Forsgren S (2002) Early increase and later decrease in VIP and substance P nerve fiber densities following abdominal radiotherapy-a study on the human colon. Int J Radiat Biol 78:1045–1053
Ikeda C, Morita I, Mori A, Fujimoto K, Suzuki T, Kawashima K, Murota S (1994) Phorbol ester stimulates acetylcholine synthesis in cultured endothelial cells isolated from porcine cerebral microvessels. Brain Res 655:147–152
Jacobi J, Jang JJ, Sundram U, Dayoub H, Fajardo LF, Cooke JP (2002) Nicotine accelerates angiogenesis and wound healing in genetically diabetic mice. Am J Pathol 161:97–104
Jozsa L, Kannus P (1997) Human tendons: anatomy, physiology, pathology. Human Kinetics, Champaign, Ill., USA
Khan KM, Cook JL, Bonar F, Harcourt P, Åström M (1999) Histopathology of common tendinopathies. Update and implications for clinical management. Sports Med 27:393–408
Kirkpatrick CJ, Bittinger F, Unger RE, Kriegsmann J, Kilbinger H, Wessler I (2001) The non-neuronal cholinergic system in the endothelium: evidence and possible pathobiological significance. Jpn J Pharmacol 85:24–28
Kirkpatrick J, Bittinger F, Nozadze K, Wessler I (2003) Expression and function of the non-neuronal cholinergic system in endothelial cells. Life Sci 72:2111–2116
Koenig JA, Edwardson JM (1996) Intracellular trafficking of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor: importance of subtype and cell type. Mol Pharmacol 49:351–359
Li M, Yasuda RP, Wall SJ, Wellstein A, Wolfe BB (1991) Distribution of m2 muscarinic receptors in rat brain using antisera selective for m2 receptors. Mol Pharmacol 40:28–35
Liste I, Bernard V, Bloch B (2002) Acute and chronic acetylcholinesterase inhibition regulates in vivo the localization and abundance of muscarinic receptors m2 and m4 at the cell surface and in the cytoplasm of striatal neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 20:244–256
Maffulli N, Testa V, Capasso G, Ewen SW, Sullo A, Benazzo F, King JB (2004) Similar histopathological picture in males with Achilles and patellar tendinopathy. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:1470–1475
Movin T, Gad A, Reinholt FP (1997) Tendon pathology in long-standing achillodynia. Biopsy findings in 40 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 68:170–175
Nakaya M, Yuasa T, Usui N (2002) Immunohistochemical localization of subtypes of muscarinic receptors in human inferior turbinate mucosa. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 111:593–597
Oben JA, Yang S, Lin H, Ono M, Diehl AM (2003) Acetylcholine promotes the proliferation and collagen gene expression of myofibroblastic hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 300:172–177
Olsson C, Costa M, Brookes SJ (2004) Neurochemical characterization of extrinsic innervation of the guinea pig rectum. J Comp Neurol 470:357–371
Osborn M, Debus E, Weber K (1984) Monoclonal antibodies specific for vimentin. Eur J Cell Biol 34:137–143
Pals-Rylaarsdam R, Hosey MM (1997) Two homologous phosphorylation domains differentially contribute to desensitization and internalization of the m2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem 272:14152–14158
Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Bucy RP (1995) In situ hybridization with digoxigenin-labeled RNA probes: facts and artifacts. Biotechniques 18:300–307
Pesic S, Grbovic L, Jovanovic A, Radenkovic M, Stojic D, Cvetkovic Z, Ilic I (2003) Endothelium-dependent relaxation of canine uterine artery in response to acetylcholine: the possible involvement of alternative pathways. J Vet Med 50:391–396
Phillips J, Hickey H, Hill C (2000) Heterogeneity in mechanisms underlying vasodilatory responses in small arteries of the rat hepatic mesentery. Auton Neurosci 83:159–170
Riley G (2005) Chronic tendon pathology: molecular basis and therapeutic implications. Expert Rev Mol Med 7:1–25
Rufai A, Benjamin M, Ralphs JR (1992) Development and ageing of phenotypically distinct fibrocartilages associated with the rat Achilles tendon. Anat Embryol 186:611–618
Schlador M, Grubbs R, Nathanson N (2000) Multiple topological domains mediate subtype-specific internalization of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem 275:23295–23302
Sekhon HS, Keller JA, Proskocil BJ, Martin EL, Spindel ER (2002) Maternal nicotine exposure upregulates collagen gene expression in fetal monkey lung. Association with alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 26:31–41
Shalabi A (2004) Magnetic resonance imaging in chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Thesis, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm
Skalli O, Ropraz P, Trzeciak A, Benzonana G, Gillessen D, Gabbiani G (1986) A monoclonal antibody against alfa-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol 103:2787–2796
Tsuga H, Kameyama K, Haga T, Honma T, Lameh J, Sadée W (1998) Internalization and down-regulation of human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor m2 subtypes. J Biol Chem 273:5323–5330
Uchiyama T, Chess-Williams R (2004) Muscarinic receptor subtypes of the bladder and gastrointestinal tract. J Smooth Muscle Res 40:237–247
van Koppen C, Kaiser B (2003) Regulation of acetylcholine receptor signaling. Pharmacol Ther 98:197–220
Vane JR, Angerred EE, Botting RM (1990) Regulatory functions of the vascular endothelium. N Engl J Med 323:27–36
Vogelsang H, Meyer G, Homstein OP (1995) Acetylcholine induces different cutaneous sensations in atopic and non-atopic subjects. Acta Derm Venereol 75:434–436
Wehrwein E, Thompson SA, Coulibaly SF, Linn DM, Linn CL (2004) Acetylcholine protection of adult pig retinal ganglion cells from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:1531–1543
Wessler I, Kilbinger H, Bittinger F, Unger R, Kirkpatrick J (2003) The non-neuronal cholinergic system in humans: expression, function and pathophysiology. Life Sci 72:2055–2061
Yung KK, Lo YL (1997) Immunocytochemical localization of muscarinic m2 receptor in the rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 27:81–84
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Ulla Hedlund and Lena Jonsson for excellent technical services and to Professor L.-E. Thornell for generous gifts of antibodies against human vimentin and alpha-smooth muscle actin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Financial support was provided by the Faculty of Medicine at Umeå University, the Swedish National Centre for Research in Sports, and the County Council of Västerbotten.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bjur, D., Danielson, P., Alfredson, H. et al. Presence of a non-neuronal cholinergic system and occurrence of up- and down-regulation in expression of M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: new aspects of importance regarding Achilles tendon tendinosis (tendinopathy). Cell Tissue Res 331, 385–400 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0524-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0524-1