Abstract
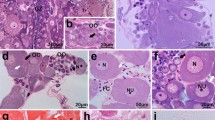
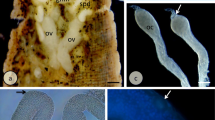
We describe the ultrastructural organization of the vitellogenic follicle stages in two caecilian species. Monthly samples of slices of ovary of Ichthyophis tricolor and Gegeneophis ramaswamii from the Western Ghats of India were subjected to transmission electron-microscopic analysis, with special attention to the follicle cell/oocyte interface. In order to maintain uniformity of the stages among the amphibians, all the stages in the caecilian follicles were assigned to stages I–VI, the vitellogenic and post-vitellogenic follicles being assigned to stages III–VI. Stage III commences with the appearance of precursors of vitelline envelope material in the perivitelline space. Stages IV and V have been assigned appropriate substages. During the transition of stage III to stage VI oocytes, a sequential change occurs in the manifestations of follicle cells, perivitelline space, vitelline envelope and oocyte cortex. The vitelline envelope becomes a tough coat through the tunnels of which the macrovilli pass to interdigitate between the microvilli. The oocyte surface forms pinocytic vesicles that develop into coated pits and, later, coated vesicles. Contributions of the oocyte cortex to the vitelline envelope and of the follicle cells to yolk material via synthesis within them are indicated. The follicle cell/oocyte interface of vitellogenic follicles of these two caecilians resembles that in anurans and urodeles, with certain features being unique to caecilians. Thus, this paper throws light on the possible relationships of caecilians to anurans and urodeles with special reference to ovarian follicles.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anjubault E, Exbrayat JM (2004) Contribution à la connaissance de l’appareil génital de Typhlonectes compressicauda (Duméril et Bibron, 1841), Amphibien Gymnophione. I. Gonadogenèse. Bull Mens Soc Linn Lyon 73:379–392
Begovac PC, Wallace RA (1988) Stages of oocyte development in the pipe fish, Syngnathus scovelli. J Morphol 197:353–369
Beyo RS, Sreejith P, Divya L, Oommen OV, Akbarsha MA (2007a) Ultrastructural observations of previtellogenic ovarian follicles of the caecilians Ichthyophis tricolor and Gegeneophis ramaswamii. J Morphol 268:329–342
Beyo RS, Sreejith P, Divya L, Oommen OV, Akbarsha MA (2007b) Assembly of ovarian follicles in the caecilians Ichthyophis tricolor and Gegeneophis ramaswamii: light and transmission electron microscopic study. Zygote 15:199–213
Berois N, Sa R de (1988) Histology of the ovaries and fat bodies of Chthonerpeton indistinctum. J Herpetol 22:146–151
Brummett AR, Dumont JN (1977) Intracellular transport of vitellogenin in Xenopus laevis oocytes: an autoradiographic study. Dev Biol 60:482–486
Cabada MO, Sanchez Riera AN, Genta HD, Sanchez SS, Barisone GA (1996) Vitelline envelope formation during oogenesis in Bufo arenarum. Biocell 20:77–86
Carotenuto R, Vaccaro MC, Capriglione T, Petrucci TC, Campanella C (2000) α-Spectrin has a stage-specific asymmetrical localization during Xenopus oogenesis. Mol Reprod Dev 55:229–239
Davidson EH (1994) Molecular biology of embryonic development: how far have we come in the last ten years? Bioessays 16:603–615
Del Pino EM (1989) Modifications of oogenesis and development in marsupial frogs. Development 107:169–187
Del Pino EM, Humphries AA Jr (1978) Multiple nuclei during early oogenesis in Flectonotus pygmaeus and other marsupial frogs. Biol Bull 154:198–212
Del Pino EM, Steibeisser H, Hofmann A, Dreyer C, Campos M, Trendelenburg MF (1986) Oogenesis in the egg-brooding frog Gastrotheca riobambae produces large oocytes with fewer nucleoli and low RNA content in comparison to Xenopus laevis. Differentiation 32:24–33
Dumont JN (1972) Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory-maintained animals. J Morphol 136:153–179
Dumont JN (1978) Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). VI. The route of injected tracer transport in the follicle and developing oocyte. J Exp Zool 204:193–217
Dumont JN, Brummet AR (1978) Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). V. Relationships between developing oocytes and their developing follicular tissues. J Morphol 155:73–98
Exbrayat JM (1986) Quelques observations sur la reproduction en élevage de Typhlonectes compressicauda, Amphibien Apode vivipare. Possibilité de rythmes endogèns. Bull Soc Herpetol Fr 40:52–62
Exbrayat JM (2006) Oogenesis and folliculogenesis. In: Exbrayat JM (ed) Reproductive biology and phylogeny of Gymnophiona, vol 5. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire, pp 275–290
Exbrayat JM, Collenot G (1983) Quelques aspects de l’évolution de l’ovaire de Typhlonectes compressicauda (Duméril et Bibron, 1841), Batracien Apode vivipare. Étude quantitative et histochimique des corps jaunes. Reprod Nutr Dev 23:889–898
Exbrayat JM, Laurent MT (1983) Quelques observations concernant le maintien en élevage de deux Amphibiens Apodes: Typhlonectes compressicauda et un Ichthyophis. Reproduction de Typhlonectes compressicauda. Bull Soc Herpetol Fr 26:25–26
Guraya SS (1976) Recent advances in the morphology, histochemistry and biochemistry of steroid synthesizing cellular sites in non-mammalian vertebrate ovary. Int Rev Cytol 44:365–409
Guraya SS (1979) Recent advances in the morphology, cytochemistry and function of Balbiani vitelline body in animal oocytes. Int Rev Cytol 59:249–321
Holland CA, Dumont JN (1975) Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). IV. Effects of gonadotropin, estrogen and starvation on endocytosis in developing oocytes. Cell Tissue Res 162:177–184
Hope J, Humphries AA Jr, Bourne GH (1963) Ultrastructural studies on the developing oocytes of the salamander Notophthalmus viridescens. I. The relationship between follicle cells and developing oocytes. J Ultrastruct Res 9:302–324
Hope J, Humphries AA Jr, Bourne GH (1964) Ultrastructural studies on the developing oocytes of the salamander Notophthalmus viridescens. II. The formation of the yolk. J Ultrastruct Res 10:547–556
Inoue S, Inoue Y (1986) Fertilization (activation)-induced 200- to 9-kDa depolymerization of polysialoglycoprotein, a distinct component of cortical alveoli of rainbow trout eggs. J Biol Chem 261:5256–5261
Kanamadai RD, Saidapur SK (1982) Pattern of ovarian activity in the Indian toad Bufo melanostictus (Schn). Proc Natl Sci Acad India B48:307–316
Kessel RG, Ganion LR (1980) Electron microscopic and autoradiographic studies on vitellogenesis in Necturus maculosus. J Morphol 164:215–233
Kitajima K, Inoue Y, Inoue S (1986) Polysialoglycoproteins of salmonidae fish eggs. Complete structure of 200-kDa polysialoglycoprotein from the unfertilized eggs of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Biol Chem 261:5262–5269
Masood-Parveez U, Nadkarni VB (1993a) The ovarian cycle in an oviparous gymnophione amphibian, Ichthyophis beddomei (Peters). J Herpetol 27:59–63
Masood-Parveez U, Nadkarni VB (1993b) Morphological, histological and histochemical studies on the ovary of an oviparous caecilian, Ichthyophis beddomei (Peters). J Herpetol 27:63–69
Oommen OV, Measey GJ, Gower DJ, Wilkinson M (2000) Distribution and abundance of the caecilian Gegeneophis ramaswamii (Amphibia: Gymnophiona) in Southern Kerala. Curr Sci 79:1386–1389
Prisco M, Romano M, Ricchiari L, Limatola E, Andreuccetti P (2002) An ultrastructural study on the vitellogenesis in the spotted ray Torpedo marmorata. Gen Comp Endocrinol 128:171–179
Sanchez S, Villecco EI (2003) Oogenesis. In: Jamieson BGM (ed) Reproductive biology and phylogeny of Anura, vol 2. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire, pp 27–71
Selman K, Wallace RA, Barr V (1986) Oogenesis in Fundulus heteroclitus. IV. Yolk-vesicle formation. J Exp Zool 239:277–288
Selman K, Wallace RA, Barr V (1988) Oogenesis in Fundulus heteroclitus. V. The relationship of yolk vesicle and cortical alveoli. J Exp Zool 246:42–56
Skinner MK (2005) Regulation of primordial follicle assembly and development. Human Reprod 11:461–471
Sretarugsa P, Weerachatyanukul W, Chavadej J, Kruatrachue M, Sobhon P (2001) Classification of developing oocytes, ovarian development and seasonal variation in Rana tigrina. Sci Asia 27:1–14
Uribe MCA (2001) Reproductive systems of caudate amphibians. In: Dutta HM, Datta Munshi JS (eds) Vertebrate functional morphology. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire, pp 267–294
Uribe MCA (2003) Ovary and oogenesis. In: Sever DM (ed) Reproductive biology and phylogeny of Urodela, vol 1. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire, pp 135–150
Valdez Toledo CL, Pisanó A (1980) Fases ovogenéticas en Bufo arenarum. Studies of oogenesis in Bufo arenarum. Reproducción 4:315–330
Van Voorhis BJ (1999) Follicular development. In: Knobil E, Nill JD (eds) Encyclopedia of reproduction, vol 2. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 376–389
Villecco EI, Aybar MJ, Sánchez SS, Sánchez Riera AN (1996) Heterologous gap junctions between oocyte and follicle cells in Bufo arenarum: hormonal effects on their permeability and potential role in meiotic arrest. J Exp Zool 276:76–85
Villecco EI, Aybar MJ, Sánchez Riera AN, Sánchez SS (1999) Comparative study of vitellogenesis in the anuran amphibians Ceratophyrs cranwelli (Leptodactylidae) and Bufo arenarum (Bufonidae). Zygote 7:11–19
Villecco EI, Aybar MJ, Genta SB, Sánchez SS, Sánchez Riera AN (2000) Effect of gap junction uncoupling in full Bufo arenarum ovarian follicles: participation of cAMP in meiotic arrest. Zygote 8:171–179
Villecco EI, Genta SB, Sánchez Riera, AN Sánchez SS (2002) Ultrastructural characteristics of the follicle cell-oocyte interface in the oogenesis of Ceratophrys cranwelli. Zygote 10:163–173
Wake MH (1968) Evolutionary morphology of the caecilian urogenital system. Part I. The gonads and fat bodies. J Morphol 126:291–332
Wake MH (1970a) Evolutionary morphology of the caecilian urogenital system. Part II. The kidneys and urogenital ducts. Acta Anat 75:321–358
Wake MH (1970b) Evolutionary morphology of the caecilian urogenital system. Part III. The bladder. J Herpetol 26:120–128
Wake MH (1972) Evolutionary morphology of the caecilian urogenital system. Part IV. The cloaca. J Morphol 136:353–366
Wake MH (1977) The reproductive biology of caecilians. In: Taylor DH, Guttman SI (eds) The reproductive biology of amphibians, an evolutionary perspective. Plenum, New York, pp 73–101
Wake MH (1980) Reproduction, growth and population structure of the Central American caecilian Dermophis mexicanus. J Herpetol 36:244–256
Wake MH (1993) The evolution of oviductal gestation in amphibians. J Exp Zool 266:394–413
Wake MH, Dickie R (1998) Oviduct structure and function and reproductive modes in amphibians. J Exp Zool 282:477–506
Wallace RA (1985) Vitellogenesis and oocyte growth in non-mammalian vertebrates. In: Browder LW (ed) Developmental biology, vol I. Plenum, New York, pp 127–177
Wallace RA, Bergink EW (1974) Amphibian vitellogenin: properties, hormonal regulation of hepatic synthesis and ovarian uptake, and conversion to yolk proteins. Am Zool 14:1159–1175
Wallace RA, Jared DW (1976) Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. V. Specificity for vitellogenin incorporation. J Cell Biol 69:345–351
Wallace RA, Selman K (1990) Ultrastructural aspects of oogenesis and oocyte growth in fish and amphibians. J Electron Microsc Tech 16:175–201
Ward RT (1962) The origin of protein and fatty yolk in Rana pipiens. II. Electron microscopical and cytochemical observations of young and mature oocytes. J Cell Biol 14:309–341
Wartenberg H, Gusek W (1960) Electron microscopic research on the fine structure of the ovarian ovum and the follicular epithelium of amphibian. Exp Cell Res 19:199–209
Yamaguchi S, Hedrick JL, Katagiri C (1989) The synthesis and localization of envelope glycoprotein in oocytes of Xenopus laevis using immuno-cytochemical methods. Dev Growth Differ 31:85–94
Acknowledgements
The TEM facility of the Welcome Trust Research Laboratory, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore 632002, India, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by funds from the Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment (KSCSTE), through the SARD facility, and by the FIST scheme of Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi, to the Department of Zoology, University of Kerala, Thiruvananthapuram, and to the Department of Animal Science, Bharathidasan University, Thiruchirapalli (SR/FST/LSI-233/2002).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beyo, R.S., Divya, L., Smita, M. et al. Stages in follicle cell/oocyte interface during vitellogenesis in caecilians Ichthyophis tricolor and Gegeneophis ramaswamii: a transmission electron-microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res 331, 519–528 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0523-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0523-2