Abstract
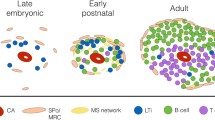
The formation of peripheral lymphoid tissues is indispensable for the efficient recognition and elimination of external antigens by lymphoid and accessory cells of the adaptive immune system. The spleen is structurally arranged around various vascular beds with distinct endothelial phenotypes. Using immunohistochemistry, we investigated the postnatal developmental characteristics of the marginal sinus and its relationship with various red-pulp sinus subsets. We also determined the importance of the lymphotoxin β receptor (LTβR) and the role of the Nkx2.3 transcription factor for the formation of the splenic vasculature. Both the administration of soluble LTβR-Ig fusion protein to neonates and the deletion of LTβR or downstream signaling components (RelB and p52) of the NF-κB family inhibited the phenotypic maturation of marginal sinus but had no effect on the vascular compartmentalization of the red pulp. The integrity of the marginal sinus and the proper vascular segregation of the red pulp appeared to be controlled by Nkx2.3, as Nkx2.3-deficient mice exhibited an abnormal distribution of IBL-7/1hi/IBL-9/2− sinuses and a lack of IBL-7/1lo/IBL-9/2+ vessels. Our data suggest that phenotypic heterogeneity among different vascular elements within distinct anatomical regions of the spleen differentially depends on developmental factors such as lymphotoxin signaling or Nkx2.3, whereas the marginal sinus is controlled by both pathways.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB (2003) Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3:745–756
Balázs M, Grama L, Balogh P (1999) Detection of phenotypic heterogeneity within the murine splenic vasculature using rat monoclonal antibodies IBL-7/1 and IBL-7/22. Hybridoma 18:177–182
Balázs M, Horváth G, Grama L, Balogh P (2001) Phenotypic identification and development of distinct microvascular compartments in the postnatal mouse spleen. Cell Immunol 212:126–137
Balogh P, Petz A (2005) Selective binding of biotinylated albumin to the lymphoid microvasculature. Histochem Cell Biol 123:357–363
Balogh P, Aydar Y, Tew JG, Szakal AK (2001) Ontogeny of the follicular dendritic cell phenotype and function in the postnatal murine spleen. Cell Immunol 214:45–53
Balogh P, Horváth G, Szakal AK (2004) Immunoarchitecture of distinct reticular fibroblastic domains in the white pulp of mouse spleen. J Histochem Cytochem 52:1287–1298
Brendolan A, Ferretti E, Salsi V, Moses K, Quaggin S, Blasi F, Cleary ML, Selleri L (2005) A Pbx1-dependent genetic and transcriptional network regulates spleen ontogeny. Development 132:3113–3126
Browning JL, French LE (2002) Visualization of lymphotoxin-beta and lymphotoxin-beta receptor expression in mouse embryos. J Immunol 168:5079–5087
Crowley MT, Reilly CR, Lo D (1999) Influence of lymphocytes on the presence and organization of dendritic cell subsets in the spleen. J Immunol 163:4894–4900
Cuff CA, Schwartz J, Bergman CM, Russell KS, Bender JR, Ruddle NH (1998) Lymphotoxin alpha3 induces chemokines and adhesion molecules: insight into the role of LT alpha in inflammation and lymphoid organ development. J Immunol 161:6853–6860
Cyster JG (2005) Chemokines, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Annu Rev Immunol 23:127–159
Evans SM, Yan W, Murillo MP, Ponce J, Papalopulu N (1995) Tinman, a Drosophila homeobox gene required for heart and visceral mesoderm specification, may be represented by a family of genes in vertebrates: XNkx-2.3, a second vertebrate homologue of tinman. Development 121:3889–3899
Fu YX, Chaplin DD (1999) Development and maturation of secondary lymphoid tissues. Annu Rev Immunol 17:399–433
Fütterer A, Mink K, Luz A, Kosco-Vilbois MH, Pfeffer K (1998) The lymphotoxin beta receptor controls organogenesis and affinity maturation in peripheral lymphoid tissues. Immunity 9:59–70
Girkontaite I, Sakk V, Wagner M, Borggrafe T, Tedford K, Chun J, Fischer KD (2004) The sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) lysophospholipid receptor S1P3 regulates MAdCAM-1+ endothelial cells in splenic marginal sinus organization. J Exp Med 200:1491–1501
Gommerman JL, Browning JL (2003) Lymphotoxin/light, lymphoid microenvironments and autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol 3:642–655
Gonzalez M, Mackay F, Browning JL, Kosco-Vilbois MH, Noelle RJ (1998) The sequential role of lymphotoxin and B cells in the development of splenic follicles. J Exp Med 187:997–1007
Grayson MH, Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE, Holtzman MJ, Chaplin DD (2003) Intravital microscopy comparing T lymphocyte trafficking to the spleen and the mesenteric lymph node. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284:H2213–H2226
Kiel MJ, Yilmaz OH, Iwashita T, Yilmaz OH, Terhorst C, Morrison SJ (2005) SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell 121:1109–1121
Kraal G, Schornagel K, Streeter PR, Holzmann B, Butcher EC (1995) Expression of the mucosal vascular addressin, MAdCAM-1, on sinus-lining cells in the spleen. Am J Pathol 147:763–771
Mackay F, Majeau GR, Lawton P, Hochman PS, Browning JL (1997) Lymphotoxin but not tumor necrosis factor functions to maintain splenic architecture and humoral responsiveness in adult mice. Eur J Immunol 27:2033–2042
Mebius RE (2003) Organogenesis of lymphoid tissues. Nat Rev Immunol 3:292–303
Mebius RE, Nolte MA, Kraal G (2004) Development and function of the splenic marginal zone. Crit Rev Immunol 24:449–464
Pabst O, Herbrand H, Arnold HH (1998) Nkx2-9 is a novel homeobox transcription factor which demarcates ventral domains in the developing mouse CNS. Mech Dev 73:85–93
Pabst O, Forster R, Lipp M, Engel H, Arnold HH (2000) NKX2.3 is required for MAdCAM-1 expression and homing of lymphocytes in spleen and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. EMBO J 19:2015–2023
Poljak L, Carlson L, Cunningham K, Kosco-Vilbois MH, Siebenlist U (1999) Distinct activities of p52/NF-kappa B required for proper secondary lymphoid organ microarchitecture: functions enhanced by Bcl-3. J Immunol 163:6581–6588
Price M, Lazzaro D, Pohl T, Mattei MG, Ruther U, Olivo JC, Duboule D, Di Lauro R (1992) Regional expression of the homeobox gene Nkx-2.2 in the developing mammalian forebrain. Neuron 8:241–255
Qiu M, Shimamura K, Sussel L, Chen S, Rubinstein JL (1998) Control of anteroposterior and dorsoventral domains of Nkx-6.1 gene expression relative to other Nkx genes during vertebrate CNS development. Mech Dev 72:77–88
Rennert PD, Browning JL, Mebius R, Mackay F, Hochman PS (1996) Surface lymphotoxin alpha/beta complex is required for the development of peripheral lymphoid organs. J Exp Med 184:1999–2006
Schneider K, Potter KG, Ware CF (2004) Lymphotoxin and LIGHT signaling pathways and target genes. Immunol Rev 202:49–66
Steiniger B, Barth P (2000) Microanatomy and function of the spleen. Series: Advances in Anatomy, Embryology and Cell Biology, vol 151. Springer, Heidelberg
Steiniger B, Barth P, Hellinger A (2001) The perifollicular and marginal zones of the human splenic white pulp: do fibroblasts guide lymphocyte immigration? Am J Pathol 159:501–512
Sussel L, Kalamaras J, Hartigan-O’Connor DJ, Meneses JJ, Pedersen RA, Rubenstein JLR, German MS (1998) Mice lacking the homeodomain transcription factor Nkx2.2 have diabetes due to arrested differentiation of pancreatic beta cells. Development 125:2213–2221
Tanaka H, Habata Y, Saito S, Fukushima O, Miyasaka M (1996) Phenotypic characteristics and significance of reticular meshwork surrounding splenic white pulp of mice. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 45:407–416
Tarlinton D, Light A, Metcalf D, Harvey RP, Robb L (2003) Architectural defects in the spleens of Nkx2-3-deficient mice are intrinsic and associated with defects in both B cell maturation and T cell-dependent immune responses. J Immunol 170:4002–4010
Van Vliet E, Melis M, Ewijk W van (1984) Monoclonal antibodies to stromal cell types of the mouse thymus. Eur J Immunol 14:524–529
Wang CC, Biben C, Robb L, Nassir F, Barnett L, Davidson NO, Koentgen F, Tarlinton D, Harvey RP (2000a) Homeodomain factor Nkx2-3 controls regional expression of leukocyte homing coreceptor MAdCAM-1 in specialized endothelial cells of the viscera. Dev Biol 224:152–167
Wang SL, Kutche M, DiSciullo G, Schachner M, Bogen SA (2000b) Selective malformation of the splenic white pulp border in L1-deficient mice. J Immunol 165:2465–2473
Wang J, Foster A, Chin R, Yu P, Sun Y, Wang Y, Pfeffer K, Fu YX (2002) The complementation of lymphotoxin deficiency with LIGHT, a newly discovered TNF family member, for the restoration of secondary lymphoid structure and function. Eur J Immunol 32:1969–1979
Weih F, Caamano J (2003) Regulation of secondary lymphoid organ development by the nuclear factor-kappaB signal transduction pathway. Immunol Rev 195:91–105
Weih DS, Yilmaz ZB, Weih F (2001) Essential role of RelB in germinal center and marginal zone formation and proper expression of homing chemokines. J Immunol 167:1909–1919
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the expert contribution of Ms. Judit Melczer who maintained the hybridoma cells. The LTβR-Ig decoy receptor and the anti-LTβ hamster mAb were kindly provided by Dr. Jeffrey L. Browning (Biogen), and the ER-TR7 mAb was generously supplied by Dr. Willem van Ewijk (Leiden University Medial Center, The Netherlands).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by ETT grant no. 592/2003 from the Ministry of Health, Social and Family Affairs, Hungary (P.B.) and by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (F.W. and H.H.A.). P.B. is a recipient of the Széchenyi István Research Fellowship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balogh, P., Balázs, M., Czömpöly, T. et al. Distinct roles of lymphotoxin-β signaling and the homeodomain transcription factor Nkx2.3 in the ontogeny of endothelial compartments in spleen. Cell Tissue Res 328, 473–486 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0378-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0378-6