Abstract
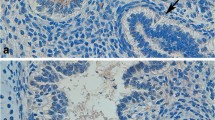
Alkaline phosphatase (AP) isozymes are surfactant-associated proteins (SPs). Since several different AP isozymes have been detected in the pneumocytes of lung cancer patients, we attempted to identify the relationship between pulmonary surfactant aggregate subtypes and AP isozymes. Pulmonary surfactant aggregates were isolated from carcinoma and non-carcinoma tissues of patients with non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Upon analysis, ultraheavy, heavy, and light surfactant aggregates were detected in the non-carcinoma tissues, but no ultraheavy surfactant aggregates were found in the carcinoma tissues. Surfactant-associated protein A (SP-A) was detected as two bands (a 27-kDa band and a 54-kDa band) in the ultraheavy, heavy, and light surfactant aggregates found in the non-carcinoma tissues. Although both SP-A bands were detected in the heavy and light surfactant aggregates from adenocarcinoma tissues, the 54-kDa band was not detected in squamous cell carcinoma tissues. Liver AP (LAP) was detected in the heavy and light surfactant aggregates from both non-carcinoma and squamous carcinoma tissues, but not in heavy surfactant aggregates from adenocarcinoma tissues. A larger amount of bone type AP (BAP) was found in light surfactant aggregate fractions from squamous cell carcinomas than those from adenocarcinoma tissues or non-carcinoma tissues from patients with either type of cancer. LAP, BAP, and SP-A were identified immunohistochemically in type II pneumocytes from non-carcinoma tissues and adenocarcinoma cells, but no distinct SP-A staining was observed in squamous cell carcinoma tissues. The present study has thus revealed several differences in pulmonary surfactant aggregates and AP isozymes between adenocarcinoma tissue and squamous cell carcinoma tissue.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg T, Leth-Larsen R, Holmskov U, Hojrup P (2000) Structural characterization of human proteinosis surfactant protein A. Biochim Biophys Acta 1543:159–173
Capelli A, Cerutti CG, Lusuardi M, Donner CF (1997) Identification of human pulmonary alkaline phosphatase isozymes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 155:1448–1452
Chung JH, Park MS, Kim YS, Chang J, Kim JH, Kim SH, Kim SK (2005) Usefulness of bone metabolic markers in the diagnosis of bone metastasis from lung cancer. Yonsei Med J 46:388–393
Cobben NA, Drent M, Lacobs JA, Schmitz MP, Mulder PG, Henderson RF, Wouters EF, Dieijen-Visser MP van (1999) Relationship between enzymatic markers of pulmonary cell damage and cellular profile: a study in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Exp Lung Res 25:99–111
Edelson JD, Shannon JM, Mason RJ (1988) Alkaline phosphatase: a marker of alveolar type II cell differentiation. Am Rev Respir Dis 138:1268–1275
Eliakim R, Goetz GS, Rubio S, Chailley-Heu B, Shao JS, Ducroc R, Alpers DH (1997) Isolation and characterization of surfactant-like particles in rat and human colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 272:425–434
Fehrenbach H (2001) Alveolar epithelial type II cell: defender of the alveolus revisited. Respir Res 2:33–46
Fehrenbach H, Kasper M, Tschernig T, Pan T, Schuh D, Shannon JM, Muller M, Mason RJ (1999) Keratinocyte growth factor-induced hyperplasia of rat alveolar type II cells in vivo is resolved by differentiation into type I cells and by apoptosis. Eur Respir J 14:534–544
Fishman WH (1990) Alkaline phosphatase isozymes: recent progress. Clin Biochem 23:99–104
Fujimori-Arai Y, Koyama I, Hirano K, Sakagishi Y, Komoda T (1991) Purification and partial characterization of intestinal-like alkaline phosphatase in rabbit kidney. Arch Biochem Biophys 284:320–325
Gazdar AF, Minna JD (1997) Cigarettes, sex, and lung adenocarcinoma. J Natl Cancer Int 89:1563–1565
Goldstein DJ, Rogers C, Harris H (1982) A search for trace expression of placental-like alkaline phosphatase in non-malignant human tissues: demonstration of its occurrence in lung, cervix, testis and thymus. Clin Chim Acta 125:63–75
Grigoriadis AE, Petkovich PM, Rosenthal EE, Heerche JN (1986) Modulation by retinoic acid of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 effects on alkaline phosphatase activity and parathyroid hormone responsiveness in an osteoblast-like osteosarcoma cell line. Endocrinology 119:932–939
Gross NJ, Narine KR (1989a) Surfactant subtype in mice: characterization and quantitation. J Appl Physiol 66:342–349
Gross NJ, Narine KR (1989b) Surfactant subtype in mice: metabolic relationships and conversion in vitro. J Appl Physiol 67:414–421
Haneji T, Kurihara N, Ikeda K, Kumegawa M (1983) 1 alpha, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and analogues of vitamin D3 induce alkaline phosphatase activity in osteoblastic cells derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J Biochem 94:1127–1132
Harada T, Koyama I, Shimoi A, Alpers DH, Komoda T (2002) Identification of pulmonary surfactant that bears intestinal-type and tissue-nonspecific-type alkaline phosphatase in endotoxin-induced rat bronchioalveolar fluid. Cell Tissue Res 307:69–77
Honda Y (1996) Clinical significance of serum surfactant proteins A and D in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi 34:181–185
Hoshino T, Kumasaka K, Kawano K, Koyama I, Arai-Fujimori Y, Yamagishi F, Sakagishi Y, Komoda T (1993) Abnormal alkaline phosphatase of hepatic type in cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with intracranial metastasis from lung cancer. J Clin Pathol 46:1059–1061
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) The use of antiavidin antibody and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex in immunoperoxidase technics. Am J Clin Pathol 75:816–821
Ikegami M, Korfhagen TR, Whitsett JA, Bruno MD, Wert SE, Wada K, Jobe AH (1998) Characteristics of surfactant from SP-A-deficient mice. Am J Physiol 275:L247–L254
Jeng YJ, Watson CS, Thomas ML (1994) Identification of vitamin D-stimulated alkaline phosphatase in IEC-6 cells, a rat small intestine crypt cell line. Exp Cell Res 212:338–343
Korfhagen TR, Bruno MD, Ross GF, Huelsman KM, Ikegami M, Jobe AH, Wert SE, Stripp BR, Morris RE, Glasser SW, Bachurski CJ, Iwamoto HS, Whitsett JA (1996) Altered surfactant function and structure in SP-A gene targeted mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9594–9599
Komoda T, Koyama I, Nagata A, Sakagishi Y, DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K, Alpers DH (1986) Ontogenic and phylogenic studies of intestinal, hepatic, and placental alkaline phosphatases. Evidence that intestinal alkaline phosphatase is a late evolutionary development. Gastroenterology 91:277–286
Koyama I, Fujimori-Arai Y, Hirota N, Sakai T, Sakagishi Y, Komoda T (1991) Liver-like alkaline phosphatase in the tissue-unspecific type enzyme found in rabbit organs. Biochim Biophys Acta 1080:165–172
Krause MF, Wiemann T, Reisner A, Orlowska-Volk M, Kohler H, Ankermann T (2005) Surfactant reduces extravascular lung water and invasion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes into the lung in a piglet model of airway lavage. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 18:129–139
Kuroishi T, Hirose K, Tominaga S, Ogawa H, Tajima K (1992) Prediction of future cancer mortality in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol 22:365–369
Levi F, Lucchini F, Negri E, La Vecchia C (1999) World wide patterns of cancer mortality, 1990–1994. Eur J Cancer Prev 8:381–400
Madsen J, Tornoe I, Nielsen O, Koch C, Steinhilber W, Holmskov U (2003) Expression and localization of lung surfactant protein A in human tissues. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29:591–597
Meben C (1975) Fine structural localization of alkaline phosphatase in the granular pneumocytes of hamster lung. Histochemistry 43:367–372
Miura M, Matsuzaki H, Bailyes EM, Koyama I, Sakagishi Y, Sekine T, Komoda T (1989) Differences between human liver and bone-type alkaline phosphatases. Clin Chim Acta 180:177–187
Miura M, Sakagishi Y, Hata K, Komoda T (1994) Differences between the sugar moieties of liver- and bone-type alkaline phosphatase: a re-evaluation. Ann Clin Biochem 31:25–30
Miyanaga M, Sugimoto H, Komoda T, Nosjean O, Honma K, Nemoto K, Sato T (1996) A variant alkaline phosphatase detected in a patient with lung cancer. Enzyme Protein 49:313–320
Nosjean O, Koyama I, Goseki M, Roux B, Komoda T (1997) Human tissue non-specifoic alkaline phosphatases: sugar-moiety-induced enzymic and antigenic modulations and genetic aspects. Biochem J 321:297–303
Nouwen EJ, Pollet DK, Eerdekens MW, Hendrix PG, Briers TW, De Broe ME (1986) Immunohistochemical localization of placental alkaline phosphatase, carcinoembryonic antigen, and cancer antigen 125 in normal and neoplastic human lung. Cancer Res 46:866–876
Nouwen EJ, Buyssens N, De Broe ME (1990) Heat-stable alkaline phosphatase as marker for human and monkey type-I pneumocytes. Cell Tissue Res 260:321–335
Ochs M, Johnen G, Muller KM, Wahlers T, Hawgood S, Richter J, Brasch F (2002) Intracellular and intraalveolar localization of surfactant protein A (SP-A) in the parenchymal region of the human lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 26:91–98
Phelps DS, Umstead TM, Mejia M, Carrillo G, Pardo A, Selman M (2004) Increased surfactant protein-A levels in patients with newly diagnosed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 125:617–625
Travis WD, Luvin J, Ries L, Devesa S (1996) United States lung carcinoma incidence trends: declining for most histologic types among males, increasing among females. Cancer 15:2464–2470
Uhal BD (1997) Cell cycle kinetics in the alveolar epithelium. Am J Physiol 272:L1031–L1045
Veldhuizen RA, Nag K, Orgeig S, Possmayer F (1998) The role of lipids in pulmonary surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta 1408:90–108
Wali A, Dhall K, Sanyal SN, Juneja R, Majumdar S (1990) Sequential isolation and biochemical analysis of pulmonary surfactant from human lung homogenate. Biochem Int 20:869–877
Wright JR (1997) Immunomodulatory functions of surfactant. Physiol Rev 77:931–962
Wright JR, Clements JA (1987) Metabolism and turnover of lung surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:426–444
Yokomura K, Suda T, Sasaki S, Inui N, Chida K, Nakamura H (2003) Increased expression of the 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3)-1alpha-hydroxylase gene in alveolar macrophages of patients with lung cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5704–5709
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Kohei Yokoi and Dr. Yasuo Koyama for many insightful discussions during the course of this work. The authors also thank Masaru Tsumuraya and Etsuko Yaguchi for many helpful supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iino, N., Matsunaga, T., Harada, T. et al. Comparative characterization of pulmonary surfactant aggregates and alkaline phosphatase isozymes in human lung carcinoma tissue. Cell Tissue Res 328, 355–363 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0343-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0343-9