Abstract
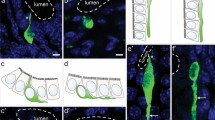
Bombesin receptor subtype-3 (BRS-3), a G-protein-coupled orphan receptor, shares 47% and 55% homology with other known mammalian bombesin receptors. Despite the molecular characterization of BRS-3, its function remains unclear as a consequence of its low affinity for bombesin and the absence of an identified natural ligand. Although the other mammalian bombesin receptors are widely distributed in the gut and central nervous system, expression of BRS-3 in the gastrointestinal tract has not been previously described. We report the expression of BRS-3 mRNA and protein in the tunica muscularis of the rat gastrointestinal tract. The mRNA expression pattern was studied by reverse transcription followed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. To identify the cellular sites of expression of BRS-3, we performed immunocytochemistry by using a N-terminus-specific affinity-purified antiserum. BRS-3 was found to be widely expressed in the rat gastrointestinal tract at both the mRNA and protein levels. BRS-3-like immunoreactivity (BRS-3-LI) was localized in neurons of the myenteric and submucosal ganglia, being primarily concentrated near the neuronal plasma membrane, and in fibers distributed in the longitudinal and circular muscle layers. In addition, BRS-3-LI was observed in the cell bodies and processes of c-kit+ interstitial cells of Cajal. These data have functional applications for the effects mediated by the activation of BRS-3 on gut motility through distinct neuronal and non-neuronal pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akeson M, Sainz E, Mantey SA, Jensen RT, Battey JF (1997) Identification of four amino acids in the gastrin-releasing peptide receptor that are required for high affinity agonist binding. J Biol Chem 272:17405–17409
Bunnett N (1994) Gastrin-releasing peptide. In: Walsh JH, Dockay GJ (eds) Gut peptides: biochemistry and physiology. Raven, New York, pp 423–445
Burns AJ, Herbert TM, Ward SM, Sanders KM (1997) Interstitial cells of Cajal in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract as revealed by c-Kit immunohistochemistry. Cell Tissue Res 290:11–20
Bustin SA (2002) Quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR): trends and problems. J Mol Endocrinol 29:23–39
Corjay MH, Dobrzanski DJ, Way JM, Viallet J, Shapira H, Worland P, Sausville EA, Battey JF (1991) Two distinct bombesin receptor subtypes are expressed and functional in human lung carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 266:18771–18779
DeMichele MA, Davis AL, Hunt JD, Landreneau RJ, Siegfried JM (1994) Expression of mRNA for three bombesin receptor subtypes in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 11:66–74
Erspamer V, Melchiorri P, Erspamer CF, Negri L (1978) Polypeptides of the amphibian skin active on the gut and their mammalian counterparts. Adv Exp Med Biol 106:51–64
Fathi Z, Corjay MH, Shapira H, Wada E, Benya R, Jensen R, Viallet J, Sausville EA, Battey JF (1993) BRS-3: a novel bombesin receptor subtype selectively expressed in testis and lung carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 268:5979–5984
Fischer JB, Schonbrunn A (1988) The bombesin receptor is coupled to a guanine nucleotide-binding protein which is insensitive to pertussis and cholera toxins. J Biol Chem 263:2808–2816
Furness JB, Costa M (1987) The enteric nervous system. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 26–54
Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D, Decallonne B, Bouillon R, Mathieu C (2001) An overview of real time quantitative PCR: applications to quantify cytokine gene expression 25:386–401
Glatzle J, Sternini C, Robin C, Zittel TT, Wong H, Reeve JR Jr, Raybould HE (2002) Expression of 5-HT3 receptors in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 123:217–226
Gorbulev V, Akhundova A, Buchner H, Fahrenholz F (1992) Molecular cloning of a new bombesin receptor subtype expressed in uterus during pregnancy. Eur J Biochem 208:405–410
Grider JR (2004) Gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP) is a modulatory neurotransmitter of the descending phase of the peristaltic reflex. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287:G1109–G1115
Horiguchi K, Komuro T (1998) Ultrastructural characterization of interstitial cells of Cajal in the rat small intestine using control and Ws/Ws mutant rats. Cell Tissue Res 293:277–284
Ishikawa K, Komuro T, Hirota S, Kitamura Y (1997) Ultrastructural identification of the c-kit-expressing interstitial cells in the rat stomach: a comparison of control and Ws/Ws mutant rats. Cell Tissue Res 289:137–143
Jennings CA, Harrison DC, Maycox PR, Crook B, Smart D, Hervieu GJ (2003) The distribution of the orphan bombesin receptor subtype-3 in the rat CNS. Neuroscience 120:309–324
Katsuno T, Pradhan TK, Ryan RR, Mantey SA, Hou W, Donohue PJ, Akeson MA, Spindel ER, Battey JF, Coy DH, Jensen RT (1999) Pharmacology and cell biology of the bombesin receptor subtype 4 (BB4-R). Biochemistry 38:7307–7320
Ladenheim EE, Moore KA, Salorio CF, Mantey SA, Taylor JE, Coy DH, Jensen RT, Moran TH (1997) Characterization of bombesin binding sites in the rat stomach. Eur J Pharmacol 319:245–251
Lavin ST, Southwell BR, Murphy R, Jenkinson KM, Furness JB (1998) Activation of neurokinin 1 receptors on interstitial cells of Cajal of the guinea-pig small intestine by substance P. Histochem Cell Biol 110:263–271
Lebacq-Verheyden AM, Trepel J, Sausville EA, Battey J (1990) Peptide growth factors and their receptors II. In: Sporn MB, Roberts AB, (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 71–124
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Mantey SA, Weber HC, Sainz E, Akeson M, Ryan RR, Pradhan TK, Searles RP, Spindel ER, Battey JF, Coy DH, Jensen RT (1997) Discovery of a high affinity radioligand for the human orphan receptor, bombesin receptor subtype 3, which demonstrates that it has a unique pharmacology compared with other mammalian bombesin receptors. J Biol Chem 272:26062–26071
Mantey SA, Coy DH, Pradhan TK, Igarashi H, Rizo IM, Shen L, Hou W, Hocart SJ, Jensen RT (2001) Rational design of a peptide agonist that interacts selectively with the orphan receptor, bombesin receptor subtype 3. J Biol Chem 276:9219–9229
Milusheva EA, Kortezova NI, Mizhorkova ZN, Papasova M, Coy DH, Balint A, Vizi ES, Varga G (1998) Role of different bombesin receptor subtypes mediating contractile activity in cat upper gastrointestinal tract. Peptides 19:549–556
Moran TH, Moody TW, Hostetler AM, Robinson PH, Goldrich M, McHugh PR (1988) Distribution of bombesin binding sites in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Peptides 9:643–649
Nagalla SR, Barry BJ, Creswick KC, Eden P, Taylor JT, Spindel ER (1995) Cloning of a receptor for amphibian [Phe13]bombesin distinct from the receptor for gastrin-releasing peptide: identification of a fourth bombesin receptor subtype (BB4). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6205–6209
Ohki-Hamazaki H, Watase K, Yamamoto K, Ogura H, Yamano M, Yamada K, Maeno H, Imaki J, Kikuyama S, Wada E, Wada K (1997) Mice lacking bombesin receptor subtype-3 develop metabolic defects and obesity. Nature 390:165–169
Ohki-Hamazaki H, Sakai Y, Kamata K, Ogura H, Okuyama S, Watase K, Yamada K, Wada K (1999) Functional properties of two bombesin-like peptide receptors revealed by the analysis of mice lacking neuromedin B receptor. J Neurosci 19:948–954
Patterson LM, Zheng H, Ward SM, Berthoud HR (2001) Immunohistochemical identification of cholecystokinin A receptors on interstitial cells of Cajal, smooth muscle, and enteric neurons in rat pylorus. Cell Tissue Res 305:11–23
Pluja L, Alberti E, Fernandez E, Mikkelsen HB, Thuneberg L, Jimenez M (2001) Evidence supporting presence of two pacemakers in rat colon. Am J Physiol 281:G255–G266
Sanders KM (1996) A case for interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers and mediators of neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 111:492–515
Sanders KM, Koh SD, Ordog T, Ward SM (2004) Ionic conductances involved in generation and propagation of electrical slow waves in phasic gastrointestinal muscles. Neurogastroenterol Motil 1:100–105
Seybold VS, Parsons AM, Aanonsen LM, Brown DR (1990) Characterization and autoradiographic localization of gastrin releasing peptide receptors in the porcine gut. Peptides 11:779–787
Sternini C, Wong H, Wu SV, Giorgio R de, Yang M, Reeve J Jr, Brecha NC, Walsh JH (1997) Somatostatin 2A receptor is expressed by enteric neurons, and by interstitial cells of Cajal and enterochromaffin-like cells of the gastrointestinal tract. J Comp Neurol 386:396–408
Taché Y, Melchiorri P, Negri L (1988) Bombesin like peptides in health and disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 547:1–541
Ter Beek WP, Muller ES, Van Hogezand RA, Biemond I, Lamers CB (2004) Gastrin releasing peptide receptor expression is decreased in patients with Crohn’s disease but not in ulcerative colitis. J Clin Pathol 57:1047–1051
Tong Q, Kirchgessner AL (2003) Localization and function of metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 in the enteric nervous system. Am J Physiol 285:G992-G1003
Torihashi S, Ward SM, Nishikawa S, Nishi K, Kobayashi S, Sanders KM (1995) c-kit-dependent development of interstitial cells and electrical activity in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 280:97–111
Varga G, Liehr RM, Scarpignato C, Coy DH (1995) Distinct receptors mediate gastrin-releasing peptide and neuromedin beta-induced delay of gastric of liquids in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 286:109–112
Vigna SR, Mantyh CR, Giraud AS, Soll AH, Walsh JH, Mantyh PW (1987) Localization of specific binding sites for bombesin in the canine gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 93:1287–1295
Ward SM, Sanders KM, Hirst GD (2004) Role of interstitial cells of Cajal in neural control of gastrointestinal smooth muscles. Neurogastroenterol Motil 1:112–117
Yegen BC, Gurbuz V, Coskun T, Bozkurt A, Kurtel H, Alican I, Dockray GJ (1996) Inhibitory effects of gastrin releasing peptide on gastric emptying in rats. Regul Pept 61:175–180
Zafirov DH, Palmer JM, Nemeth PR, Wood JD (1985) Bombesin, gastrin releasing peptide and vasoactive intestinal peptide excite myenteric neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 115:103–107
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. C.A. Jennings (Psychiatry Centre of Excellence for Drug Discovery, GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, UK) for the generous gift of the BRS-3 antibody, and Dr. Béatrice Blot for assistance with Western immunoblot technique. Confocal microscopy was performed at the Institut Albert Bonniot of the University Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, France. Special thanks are also due to Alexei Grichine and Jacques Mazzega for help with confocal microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porcher, C., Juhem, A., Peinnequin, A. et al. Bombesin receptor subtype-3 is expressed by the enteric nervous system and by interstitial cells of Cajal in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 320, 21–31 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-1032-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-1032-1