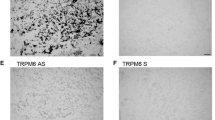
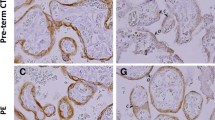
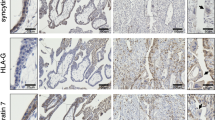
Abstract
During pregnancy, the calcium (Ca2+) transport machinery of the placenta is solely responsible for the nutrient supply to the developing fetus, where active Ca2+ transport occurs from the mother to the fetus. As part of a larger study to determine the role of Ca2+ in placental transport in vivo, we questioned whether calbindin-D9k (CaBP9k), which is mainly expressed in duodenum, uterus, and placenta of several mammals, is present in cytotrophoblast cells and syncytiotrophoblasts of human term placenta. We were interested in this protein because of its potential importance in serving as an indicator of Ca2+ availability and utilization in the placenta. Here, we demonstrated that CaBP9k transcript is present in both cell types, with a lower expression in cytotrophoblast cells as compared to syncytiotrophoblasts. Moreover, we showed by immunochemistry that CaBP9k protein was present in cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast placental tissue sections as well as in cultured cells. The occurrence of CaBP9k protein in trophoblast cells was further confirmed by Western blot analysis. Thus, these results indicate for the first time that CaBP9k is unequivocally expressed by trophoblast cells from human term placenta.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balmain N, Tisserand-Jochem E, Thomasset M, Cuisinier-Gleizes P, Mathieu H (1986) Vitamin-D-dependent calcium binding protein (CaBP9k) in rat growth cartilage. Histochemistry 84:161–168
Belkacemi L, Gariépy G, Mounier C, Simoneau L, Lafond L (2003) Expression of calbindin-D28k (CaBP28k) in trophoblast cells from human term placenta. Biol Rep 68:1943–1950
Brun P, Dupret JM, Perret C, Thomasset M, Mathieu H (1987) Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding proteins (CaBPs) in human fetuses: comparative distribution of 9k CaBP mRNA and 28k CaBP during development. Pediatr Res 21:362–367
Brunette MG (1988) Calcium transport through the placenta. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 66:1261–1219
Bruns MEH, Kleeman E, Mills SE, Bruns DE, Herr JC (1985) Immunological localization of vitamin-D dependent calcium binding protein in mouse placenta and yolk sac. Anat Rec 231:514–517
Bruns ME, Kleeman E, Bruns DE (1986) Vitamin D-dependent calcium binding protein in mouse yolk sac: biochemical and immunochemical properties and responses to 1, 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. J Biochem 261:7485–7490
Bruns ME, Overpeck JG, Smith GC, Hiysch GN, Mills GE, Bruns DE (1988) Vitamin D dependent CBP in rat uterus: differential effects of estrogen, tamoxifen, progesterone and pregnancy. Endocrinology 122:2371–2378
Bruns ME, Christakos S, Huang YC, Meyer MH, Meyer RA (1997) Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein in the kidney and intestine of X-linked hypophosphatemic mouse: changes with age and responses to 1, 25-dihydrocholecalciferol. Endocrinology 121:1–6
Campbell FM, Bush PG, Veerkamp JH, Dutta-Roy AK (1998) Detection and cellular localization of plasma membrane-associated and cytoplasmic fatty acid-binding proteins in human placenta. Placenta 19:409–415
Cao LP, Bolt MJG, Wei M, Sitrin MD, Li YC (2002) Regulation of calbindin-D9k expression by 1, 25-dihydrovitamin D3 and parathyroid hormone in mouse primary renal tubular cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 400:118–124
Care AD (1991) The placental transfer of calcium. J Dev Physiol 15:253–257
Christakos S, Gabrielides C, Rhoten WB (1989) Vitamin D-dependent calcium binding proteins: chemistry, distribution, functional considerations, and molecular biology. Endocr Rev 10:3–26
Comar CL (1956) Radiocalcium studies in pregnancy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 64:281–298
Davie M (1981) Calcium-ion-binding activity in human small-intestinal mucosal cytosol. Purification of two proteins and interrelationship of calcium-binding fractions. Biochem J 197:55–65
Dearden L, Ockleford C (1983) Structure of human trophoblasts: correlation with function. In: Loke YW, Whyte A (eds) Biology of trophoblast. Elsevier, New York, pp 69–110
Delorme AC, Danan JL, Mathieu H (1983) Biochemical evidence for the presence of two vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding proteins in mouse kidney. J Biol Chem 258:1878–1884
Dutta-Roy AK, Gopalswamy N, Trulzsch DV (1987) Prostaglandin E1 binds to Z protein of rat liver. Eur J Biochem 162:615–619
Fant M, Weisoly DL, Cocchia M, Huber R, Khan S, Lunt T, Schlessinger D (2002) PLAC1, a trophoblast-specific gene, is expressed throughout pregnancy in the human placenta and modulated by keratinocyte growth factor. Mol Reprod Dev 63:430–436
Feinman MA, Kliman HJ, Caltabiano S, Strauss JF III (1986) 8-Bromo-3’, 5’-adenosine monophosphate stimulates the endocrine activity of human cytotrophoblasts in culture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 63:1211–1217
Fleet JC, Wood RJ (1994) Identification of calbindin D-9k mRNA and its regulation by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in Caco-2 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 308:171–174
Frendo JL, Olivier D, Cheynet V, Blond JL, Bouton O, Vidaud M, Rabreau M, Evain-Brion D, Mallet F (2003) Direct Involvement of HERV-W Env glycoprotein in human trophoblast cell fusion and differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 23:3566–3574
Fukuoka H, Satoh K (1982) Characterization of the three Ca2+-binding proteins in the human placenta. Nippon Naibunpi Gakkai Zasshi 58:662–678
Given MH, Marcy IC (1933) The chemical composition of the human fetus. J Biol Chem 102:7–17
Glazier JD, Atkinson DE, Thornburg KL, Sharpe PT, Edwards D, Boyd RD, Sibley CP (1992) Gestational changes in Ca2+ transport across rat placenta and mRNA for calbindin9K and Ca(2+)-ATPase. Am J Physiol 263:R930–935
Glazier J, et al. (1994) 1st International Meeting of World Placenta Associations. Sydney, Australia, 24–28 October. Placenta 15:A1–75
Glazier J, et al. (2000) Society for Gynecologic Investigation, 47th annual meeting. Chicago, Illinois, USA. March 22–25. J Soc Gynecol Invest 7:43A–379A
Haigh T, Chen CP, Jones CJP, Aplin J (1999) Studies of mesenchymal cell from 1st trimester human placenta: expression of cytokeratin outside the trophoblast lineage. Placenta 20:615–626
Hamilton K, Tein M, Glazier J, Mawer EB, Berry JL, Balment RJ, Boyd RDH, Garland HO, Sibley CP (2000) Altered calbindin mRNA expression and calcium regulating hormones in rat diabetic pregnancy. J Endocrinol 164:67–76
Hellman P, Ridefelt P, Juhlin C, Akerstrom G, Rastad J, Gylfe E (1992) Parathyroid-like regulation of parathyroid-hormone-related protein release and cytoplasmic calcium in cytotrophoblast cells of human placenta. Arch Biochem Biophys 293:174–180
Hershberger ME, Tuan RS (1998) Placental 57-kDa Ca2+-binding protein: regulation of expression and function in trophoblast calcium transport. Dev Biol 199:80–92
Hill EP, Longo LD (1980) Dynamics of maternal-fetal nutrient transfer. Fed Proc Fedn Am Soc Exp Biol 39:239–244
Howard A, Legon S, Spurr NK, Walters JR (1992) Molecular cloning and chromosomal assignment of human calbindin-D9k. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 185:663–669
Husain SM, Birdsey TJ, Glazier JD, Mighal MZ, Garland HO, Sibley CP (1994) Effects of diabetes mellitus on maternofetal flux of calcium and magnesium and calbindin-D9k mRNA expression in rat placenta. Pediatr Res 35:376–381
Ibrahim MM, Thomas ML, Forte LR (1984) Maternal-fetal relationships in the parathyroid ectomized rat. Intestinal calcium transport, serum calcium, immunoreactive parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Biol Neonat 46:89–97
Jeung E-B, Krisinger J, Dann JL, Leung CK (1992) Molecular cloning of the full-length cDNA encoding the human calbindin-D9k. FEBS 307:224–228
Jeung E-B, Leung PC, Krisinger J (1994) The human calbindin-D9k gene. Complete structure and implications on steroid hormone regulation. J Mol Biol 235:1231–1238
Jeung E-B, Fan NC, Leung PC, Herr JC, Freemerman A, Krisinger J (1995) The baboon expresses the calbindin-D9k gene in intestine but not in uterus and placenta: implication for conservation of the gene in primates. Mol Reprod Dev 40:400–407
Kallfelz FA, Taylor AN, Wasserman RH (1967) Vitamin D-induced calcium binding factors in rat intestinal mucosa. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 125:54–58
Karl PI, Chusid J, Tagoe C, Fisher SE (1997) Ca2+ flux in human placental trophoblasts. Am J Physiol 272:C1776–1780
Kligman D, Hilt DC (1988) The S100 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci 13:437–443
Kliman HJ, Nestler JE, Sermasi E, Sanger JM, Strauss JF III (1986) Purification, characterization, and in vitro differentiation of cytotrophoblasts from human term placenta. Endocrinology 118:1567–1582
Kretsinger RH (1980) Structure and evolution of calcium-modulated proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 8:119–174
Krisinger J, Dann JL, Jeung EB, Leung PC (1992) Calbindin-D9k gene expression during pregnancy and lactation in the rat. Mol Cell Endocrinol 88:119–128
Krisinger J, Jeung E-B, Simmen RC, Leung PC (1995) Porcine calbindin-D9k gene: expression in endometrium, myometrium, and placenta in the absence of a functional estrogen response element in intron A. Biol Reprod 52:115–123
Hamilton K, Tein M, Glazier J, Mawer EB, Berry JL, Balment RJ, Boyd RDH, Garland HO, Sibley CP (2000) Altered calbindin mRNA expression and calcium regulating hormones in rat diabetic pregnancy. J Endocrinol 164:67–76
L’Horset F, Blin C, Colnot S, Lambert M, Thomasset M, Perret C (1994) Calbindin D9k gene expression in the uterus. Endocrinology 134:11–18
Loke YW, Whyte A (1983) Biology of trophoblast. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 80–110
MacManus JP, Watson DC, Yaguci M (1986) The purification and complete acid sequence of 9000-Mr Ca2+-binding protein from rat placenta. Identity with the vitamin D-dependent intestinal Ca2+-binding protein. Biochem J 235:585–595
Mathieu CL, Mills SE, Burnett SH, Cloney DL, Bruns DE, Bruns ME (1989) The presence and estrogen control of immunoreactive calbindin-D9k in the fallopian tube of the rat. Endocrinology 125:2745–2750
Mattson MP, Rychlik B, Chu C, Christakos S (1991) Evidence for calbindin-D28k in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron 6:41–51
Moreau R, Hamel A, Daoud G, Simoneau L, Lafond J (2002) Expression of calcium channels along the differentiation of cultured trophoblast cells from human term placenta. Biol Reprod 67:1473–1479
Morgan G, Wooding FB, Care AD, Jones GV (1997) Genetic regulation of placental function: a quantitative in situ hybridization study of calcium binding protein (calbindin-D9k) and calcium ATPase mRNAs in sheep placenta. Placenta 18:211–218
Müller D, Hoenderop JGJ, Meij IC, van den Heuvel LPJ, Knoers NVAM, den Hollander AI, Eggert P, Garcia-Nieto V, Claveire-Martin F, Bindels RJM (2000) Molecular cloning, tissue distribution and chromosomal mapping of the human epithelial Ca2+ channel (ECAC1). Genomics 67:48–53
Nie G-Y, Li Y, Wang J, Minoura H, Findlay JK, Salamonsen LA (2000) Complex regulation of calcium binding protein D9k (calbindin-D9k) in the mouse uterus during early pregnancy and at the site of the embryo implantation. Biol Rep 62:27–36
Pitkin RM (1985) Calcium metabolism in pregnancy and the perinatal period. Am Obstet Gyn 151:99–109
Reisner PD, Christakos S, Vanaman TC (1992) In vitro enzyme activation with calbindin-D28k, the vitamin D-dependent 28 kDa calcium binding protein. FEBS Lett 297:127–131
Reiswig JD, Frazer GS, Inpanbutr N (1995) Calbindin-D9k expression in the pregnant cow uterus and placenta. Histochem Cell Biol 104:169–174
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor laboratory Press, USA, pp B13–B15
Shamley DR, Opperman LA, Buffenstein R, Ross FP (1992) Ontogeny of calbindin-D28k and calbindin-D9k in the mouse kidney, duodenum, cerebellum and placenta. Development 116:491–496
Tatsumi K, Higuchi T, Fujiwara H, Nayama T, Itoh K, Mori T, Fijii S, Fujita J (1999) Expression of calcium binding protein D-9k messenger RNA in the mouse uterine endometrium during implantation. Mol Hum Reprod 5:153–161
Trotter M, Hixon BB (1974) Sequential changes in weight, density, and percentage ash weight of human skeletons from an early fetal period through old age. Anat Rec 179:1–18
Truman P, Ford HC (1984) The brush border of the human term placenta. Biochem Biophys Acta 779:139–160
Warembourg M, Perret C, Thomasset M (1987) Analysis and in situ detection of cholecalcin messenger RNA (9000 Mr CaBP) in the uterus of the pregnant rat. Cell Tissue Res 247:51–57
Wasserman RH, Fullmer (1983) Calcium transport proteins, calcium absorption, and vitamin D. Annu Rev Physiol 45:375–390
Wasserman RH, Taylor AN (1966) Vitamin D3 induced calcium binding protein in chick intestinal mucosa. Science 152:791–793
Wood RJ, Tchack L, Taparia S (2001) 1, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 increases the expression of the CaT1 epithelial calcium channel in the Caco-2 human intestinal cell line. BMC Physiology 1:11
Wooding FBP, Morgan G, Jones GV, Care AD (1996) Calcium transport and the localization of calbindin-D9k in the ruminant placenta during the second half of pregnancy. Cell Tissue Res 285:477–489
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Mrs. Louise Lavigne and Mr. Victor Dumas for their skillful technical assistance. We are also grateful to Dr. Jean-Pierre Dion (UQAM, Montreal, PQ, Canada) for statistical data assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belkacemi, L., Gariépy, G., Mounier, C. et al. Calbindin-D9k (CaBP9k) localization and levels of expression in trophoblast cells from human term placenta. Cell Tissue Res 315, 107–117 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0811-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0811-4