Abstract
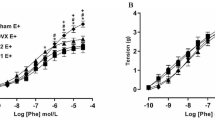
Endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells express both estrogen receptor (ER) α and β. Recent findings indicate that vascular ERβ and ERα may substitute for one another. Here, we investigate vascular morphology, contractility and protein expression in intact aorta from adult (4 months old) female mice lacking both ERα and ERβ (DERKO). The body weights were 17% higher (P<0.01) in DERKO than in wild-type mice. Vascular morphology, investigated in paraffin sections from aorta stained with hematoxylin-eosin or van Gieson, was identical in DERKO and wild-type mice. Endothelial cells were clearly visible in aorta of both DERKO and wild-type animals. Morphometric analysis of media thickness and wall to lumen ratio using a computerized image analyzing system demonstrated no differences between the two groups of mice. The vascular expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS, NOS III) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS, NOS II) was investigated using Western blotting. Aorta from both DERKO and wild-type mice expressed iNOS protein, but the iNOS expression was 3 times lower (P<0.05) in DERKO compared to wild-type mice. No difference in eNOS protein level between the two groups of animals was observed. Force responses to noradrenaline, determined either in the absence or in the presence of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor l-NAME and the cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor indomethacin, were unaffected by the lack of functional ERα/ERβ. In summary, combined lack of functional ERα and ERβ lowers the vascular expression of iNOS but has no effects on morphology, eNOS expression, and noradrenaline sensitivity in the intact aorta.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aavik E, Du Toit D, Myburgh E, Frösen J, Häyry P (2001) Estrogen receptor β dominates in baboon carotid after endothelial denudation injury. Mol Cell Endocrinol 182:91–98
Andersson C, Lydrup M-L, Fernö M, Idvall I, Gustafsson J-Å, Nilsson B-O (2001) Immunocytochemical demonstration of oestrogen receptor β in blood vessels of the female rat. J Endocrinol 169:241–247
Binko J, Majewski H (1998) 17β-estradiol reduces vasoconstriction in endothelium-denuded rat aortas through inducible NOS. Am J Physiol 274:H853–H859
Brouchet L, Krust A, Dupont S, Chambon P, Bayard F, Arnal JF (2001) Estradiol accelerates reendothelialization in mouse carotid artery through estrogen receptor-α but not estrogen receptor β. Circulation 103:423–428
Chen Z, Yuhanna IS, Galcheva-Gargova Z, Karas RH, Mendelsohn ME, Shaul PW (1999) Estrogen receptor α mediates the nongenomic activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by estrogen. J Clin Invest 103:401–406
Couse JF, Korach KS (1999) Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev 20:358–417
Critchley HO, Brenner RM, Henderson TA, Williams K, Nayak NR, Slayden OD, Millar MR, Saunders PT (2001) Estrogen receptor β, but not estrogen receptor α, is present in the vascular endothelium of the human and nonhuman primate endometrium. J Clin Endocr Metab 86:1370–1378
Darblade B, Pendaries C, Krust A, Dupont S, Fouque MJ, Rami J, Chambon P, Bayard F, Arnal JF (2002) Estradiol alters nitric oxide production in the mouse aorta through the alpha-, but not beta-, estrogen receptor. Circ Res 90:413–419
Freay AD, Curtis SW, Korach KS, Rubanyi GM (1997) Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by estrogen in depolarized rat and mouse aorta. Circ Res 81:242–248
Green S, Walter P, Kumar V, Krust A, Bornert J-M, Argos P, Chambon P (1986) Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature 320:134–139
Greene GL, Gilna P, Waterfield M, Baker A, Hort Y, Shine J (1986) Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science 231:1150–1154
Hodges YK, Tung L, Yan XD, Graham JD, Horwitz KB, Horwitz LD (2000) Estrogen receptors α and β: prevalence of estrogen receptor β mRNA in human vascular smooth muscle and transcriptional effects. Circulation 101:1792–1798
Iafrati MD, Karas RH, Aronovitz M, Kim S, Sullivan TR, Lubahn DB, O'Donnell TF, Korach KS, Mendelsohn ME (1997) Estrogen inhibits the vascular injury response in estrogen receptor α-deficient mice. Nat Med 3:545–548
Ihionkhan CE, Chambliss KL, Gibson LL, Hahner LD, Mendelsohn ME, Shaul PW (2002) Estrogen causes dynamic alterations in endothelial estrogen receptor expression. Circ Res 91:814–820
Karas RH, Hodgin JB, Kwoun M, Krege JH, Aronovitz M, Mackey W, Gustafsson J-Å, Korach KS, Smithies O, Mendelsohn ME (1999) Estrogen inhibits the vascular injury response in estrogen receptor β-deficient female mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:15133–15136
Karas RH, Schulten H, Pare G, Aronovitz MJ, Ohlsson C, Gustafsson J-Å, Mendelsohn ME (2001) Effects of estrogen on the vascular injury response in estrogen receptor α, β (Double) knockout mice. Circ Res 89:534–539
Kauser K, Sonnenberg D, Diel P, Rubanyi GM (1998) Effect of 17beta-oestradiol on cytokine-induced nitric oxide production in rat isolated aorta. Br J Pharmacol 123:1089–1096
Kuiper GGJM, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson J-Å (1996) Cloning of a novel estrogen receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:5925–5930
Kuiper GGJM, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Häggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson J-Å (1997) Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors α and β. Endocrinology 138:863–870
Liang M, Ekblad E, Gustafsson J-Å, Nilsson B-O (2001) Stimulation of vascular protein synthesis by activation of oestrogen receptor β. J Endocrinol 171:417–423
Mäkelä S, Savolainen H, Aavik E, Myllärniemi M, Strauss L, Taskinen E, Gustafsson J-Å, Häyry P (1999) Differentiation between vasculoprotective and uterotrophic effects of ligands with different binding affinities to estrogen receptors α and β. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7077–7082
Mendelsohn ME (2000) Nongenomic, estrogen receptor-mediated activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. How does it work? What does it mean? Circ Res 87:956–960
Mendelsohn ME, Karas RH (1999) The protective effects of estrogen on the cardiovascular system. N Engl J Med 340:1801–1811
Mershon JL, Scott Baker R, Clark KE (2002) Estrogen increases iNOS expression in the ovine coronary artery. Am J Physiol 283:H1169–H1180
Muramatsu M, Inoue S (2000) Estrogen receptors: how do they control reproductive and nonreproductive functions? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:1–10
Nilsson B-O, Ekblad E, Heine T, Gustafsson J-Å (2000) Increased magnitude of relaxation to oestrogen in aorta from oestrogen receptor β knock-out mice. J Endocrinol 166:R5–R9
Nilsson S, Mäkelä S, Treuter E, Tujague M, Thomsen J, Andersson G, Enmark E, Pettersson K, Warner M, Gustafsson J-Å (2001) Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol Rev 81:1535–1565
Ohlsson C, Hellberg N, Parini P, Vidal O, Bohlooly M, Ruding M, Lindberg MK, Warner M, Angelin B, Gustafsson J-Å (2000) Obesity and disturbed lipoprotein profile in estrogen receptor-α-deficient male mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 278:640–645
Pare G, Krust A, Karas RH, Dupont S, Aronovitz M, Chambon P, Mendelsohn ME (2002) Estrogen receptor-α mediates the protective effects of estrogen against vascular injury. Circ Res 90:1087–1092
Pendaries C, Darblade B, Rochaix P, Krust A, Chambon P, Korach KS, Bayard F, Arnal JF (2002) The AF-1 activation-function of ERα may be dispensable to mediate the effect of estradiol on endothelial NO production in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:2205–2210
Pettersson K, Gustafsson J-Å (2001) Role of estrogen receptor beta in estrogen action. Annu Rev Physiol 63:165–192
Pomerleau F, Fournier A, Cadieux A (1997) Mouse aorta: a preparation highly sensitive to the vasodilatory action of CGRP. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 30:343–351
Rubanyi GM, Freay AD, Kauser K, Sukovich D, Burton G, Lubahn DB, Couse JF, Curtis SW, Korach KS (1997) Vascular estrogen receptors and endothelium-derived nitric oxide production in the mouse aorta. Gender difference and effect of estrogen receptor gene disruption. J Clin Invest 99:2429–2437
Saji S, Jensen EV, Nilsson S, Rylander T, Warner M, Gustafsson J-Å (2000) Estrogen receptors α and β in the rodent mammary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:337–342
Simoncini T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Brazil DP, Ley K, Chin WW, Liao JK (2000) Interaction of oestrogen receptor with the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature 407:538–541
Simoncini T, Genazzani AR, Liao JK (2002) Nongenomic mechanisms of endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation by the selective estrogen receptor modulator raloxifene. Circulation 105:1368–1373
Stirone C, Duckles SP, Krause DN (2003) Multiple forms of estrogen receptor-α in cerebral blood vessels: regulation by estrogen. Am J Physiol 284:E184–E192
Vane JR, Botting RM (1996) Overview-mechanisms of action of anti-inflammatory drugs. In: Vane JR, Botting JH, Botting RM (eds) Improved non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs: COX-2 enzyme inhibitors, chap. 1. Kluwer Academic, London, pp 1–27
Zancan V, Santagati S, Bolego C, Vegeto E, Maggi A, Puglisi L (1999) 17β-estradiol decreases nitric oxide synthase II synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Endocrinology 140:2004–2009
Zhu Y, Bian Z, Lu P, Karas RH, Bao L, Cox D, Hodgin J, Shaul PW, Thorén P, Smithies O, Gustafsson J-Å, Mendelsohn ME (2002) Abnormal vascular function in mice deficient in estrogen receptor β. Science 295:505–508
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank Prof. Jan-Åke Gustafsson, Karolinska Institute, Huddinge University Hospital, Sweden, and Dr. Stefan Nilsson, KaroBio AB, Huddinge, Sweden, for kindly providing us with the DERKO and wild-type mice. We also gratefully thank Trine Fischer at Taconic M&B, Silkeborg, Denmark, for helping us with the genotyping of the mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the Swedish Medical Research Council (grant no. K99–0X-13017-01A), the Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation, KaroBio AB and the Åke Wiberg, Magnus Bergvall and Crafoord Foundations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, M., Ekblad, E., Lydrup, ML. et al. Combined lack of estrogen receptors α and β affects vascular iNOS protein expression. Cell Tissue Res 313, 63–70 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0731-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0731-3