Abstract.
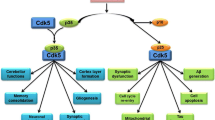
Many neurological disorders like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or stroke have in common a definite loss of CNS neurons due to apoptotic or necrotic neuronal cell death. Previous studies suggested that proapoptotic stimuli may trigger an abortive and, therefore, eventually fatal cell cycle reentry in postmitotic neurons. Neuroprotective effects of small molecule inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), which are key regulators of cell cycle progression, support the cell cycle theory of neuronal apoptosis. However, growing evidence suggests that deregulated CDK5, which is not involved in cell cycle control, rather than cell cycle relevant members of the CDK family, promotes neuronal cell death. Here we summarize the current knowledge about the involvement of CDK5 in neuronal cell death and discuss possible up- or downstream partners of CDK5. Moreover, we discuss potential therapeutic options that might arise from the identification of CDK5 as an important upstream element of neuronal cell death cascades.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlijanian MK, Barrezueta NX, Williams RD, Jakowski A, Kowsz KP, McCarthy S, Coskran T, Carlo A, Seymour PA, Burkhardt JE, Nelson RB, McNeish JD (2000) Hyperphosphorylated tau and neurofilament and cytoskeletal disruptions in mice overexpressing human p25, an activator of cdk5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:2910–2915
Alessandrini A, Namura S, Moskowitz MA, Bonventre JV (1999) MEK1 protein kinase inhibition protects against damage resulting from focal cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:12866–12869
Ankarcrona M, Dypbukt JM, Bonfoco E, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S, Lipton SA, Nicotera P (1995) Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron 15:961–973
Bian F, Nath R, Sobocinski G, Booher RN, Lipinski WJ, Callahan MJ, Pack A, Wang KK, Walker LC (2002) Axonopathy, tau abnormalities, and dyskinesia, but no neurofibrillary tangles in p25-transgenic mice. J Comp Neurol 446:257–266
Bibb JA, Chen J, Taylor JR, Svenningsson P, Nishi A, Snyder GL, Yan Z, Sagawa ZK, Ouimet CC, Nairn AC, Nestler EJ, Greengard P (2001) Effects of chronic exposure to cocaine are regulated by the neuronal protein Cdk5. Nature 410:376–380
Choi DW (1988) Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1:623–634
Evans DB, Rank KB, Bhattacharya K, Thomsen DR, Gurney ME, Sharma SK (2000) Tau phosphorylation at serine 396 and serine 404 by human recombinant tau protein kinase II inhibits tau's ability to promote microtubule assembly. J Biol Chem 275:24977–24983
Fischer A, Sananbenesi F, Schrick C, Spiess J, Radulovic J (2002) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is required for associative learning. J Neurosci 22:3700–3707
Floyd SR, Porro EB, Slepnev VI, Ochoa GC, Tsai LH, De Camilli P (2001) Amphiphysin 1 binds the cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) 5 regulatory subunit p35 and is phosphorylated by cdk5 and cdc2. J Biol Chem 276:8104–8110
Freeman RS, Estus S, Johnson EM Jr (1994) Analysis of cell cycle-related gene expression in postmitotic neurons: selective induction of cyclin D1 during programmed cell death. Neuron 12:343–355
Gunn-Moore FJ, Williams AG, Toms NJ, Tavare JM (1997) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and p70S6 kinase is not correlated with cerebellar granule cell survival. Biochem J 324:365–369
Ham J, Eilers A, Whitfield J, Neame SJ, Shah B (2000) c-Jun and the transcriptional control of neuronal apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 60:1015–1021
Harada T, Morooka T, Ogawa S, Nishida E (2001) ERK induces p35, a neuron-specific activator of Cdk5, through induction of Egr1. Nat Cell Biol 3:453–459
Heintz N (1993) Cell death and the cell cycle: a relationship between transformation and neurodegeneration? Trends Biochem Sci 18:157–159
Honma N, Hosono Y, Kishimoto T, Hisanaga S (1997) Phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein at apoptotic cell death in rat neuroblastoma B50 cells. Neurosci Lett 235:45–48
Julien JP, Mushynski WE (1998) Neurofilaments in health and disease. Prog Nucl Acid Res Mol Biol 61:1–23
Kato G, Maeda S (1999) Neuron-specific Cdk5 kinase is responsible for mitosis-independent phosphorylation of c-Src at Ser75 in human Y79 retinoblastoma cells. J Biochem (Tokyo) 126:957–961
Kermer P, Klöcker N, Bähr M (1999) Neuronal death after brain injury. Models, mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies in vivo. Cell Tissue Res 298:383–395
Kesavapany S, Lau KF, McLoughlin DM, Brownlees J, Ackerley S, Leigh PN, Shaw CE, Miller CC (2001) p35/cdk5 binds and phosphorylates beta-catenin and regulates beta-catenin/presenilin-1 interaction. Eur J Neurosci 13:241–247
Ko J, Humbert S, Bronson RT, Takahashi S, Kulkarni AB, Li E, Tsai LH (2001) p35 and p39 are essential for cyclin-dependent kinase 5 function during neurodevelopment. J Neurosci 21:6758–6771
Kuida K, Zheng TS, Na S, Kuan C, Yang D, Karasuyama H, Rakic P, Flavell RA (1996) Decreased apoptosis in the brain and premature lethality in CPP32-deficient mice. Nature 384:368–372
Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan CY, Gu Y, Taya C, Karasuyama H, Su MS, Rakic P, Flavell RA (1998) Reduced apoptosis and cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9. Cell 94:325–337
Kwon YT, Tsai LH, Crandall JE (1999) Callosal axon guidance defects in p35(−/−) mice. J Comp Neurol 415:218–229
Lazaro JB, Kitzmann M, Poul MA, Vandromme M, Lamb NJ, Fernandez A (1997) Cyclin dependent kinase 5, cdk5, is a positive regulator of myogenesis in mouse C2 cells. J Cell Sci 110:1251–1260
Leclerc S, Garnier M, Hoessel R, Marko D, Bibb JA, Snyder GL, Greengard P, Biernat J, Wu YZ, Mandelkow EM, Eisenbrand G, Meijer L (2001) Indirubins inhibit glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and CDK5/p25, two protein kinases involved in abnormal tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer's disease. A property common to most cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors? J Biol Chem 276:251–260
Lee MS, Kwon YT, Li M, Peng J, Friedlander RM, Tsai LH (2000) Neurotoxicity induces cleavage of p35 to p25 by calpain. Nature 405:360–364
Lefevre K, Clarke PG, Danthe EE, Castagne V (2002) Involvement of cyclin-dependent kinases in axotomy-induced retinal ganglion cell death. J Comp Neurol 447:72–81
Li BS, Sun MK, Zhang L, Takahashi S, Ma W, Vinade L, Kulkarni AB, Brady RO, Pant HC (2001) Regulation of NMDA receptors by cyclin-dependent kinase-5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:12742–12747
Li BS, Zhang L, Takahashi S, Ma W, Jaffe H, Kulkarni AB, Pant HC (2002) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 prevents neuronal apoptosis by negative regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3. EMBO J 21:324–333
Matsuura I, Wang JH (1996) Demonstration of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitory serine/threonine kinase in bovine thymus. J Biol Chem 271:5443–5450
Nguyen MD, Lariviere RC, Julien JP (2001) Deregulation of Cdk5 in a mouse model of ALS: toxicity alleviated by perikaryal neurofilament inclusions. Neuron 30:135–147
Nicotera P (2000) Caspase requirement for neuronal apoptosis and neurodegeneration. IUBMB Life 49:421–425
Nicotera P (2002) Apoptosis and age-related disorders: role of caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways. Toxicol Lett 127:189–195
Nicotera P, Leist M, Ferrando-May E (1999) Apoptosis and necrosis: different execution of the same death. Biochem Soc Symp 66:69–73
Niethammer M, Smith DS, Ayala R, Peng J, Ko J, Lee MS, Morabito M, Tsai LH (2000) NUDEL is a novel Cdk5 substrate that associates with LIS1 and cytoplasmic dynein. Neuron 28:697–711
Ohshima T, Ward JM, Huh CG, Longenecker G, Veeranna, Pant HC, Brady RO, Martin LJ, Kulkarni AB (1996) Targeted disruption of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 gene results in abnormal corticogenesis, neuronal pathology and perinatal death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:11173–11178
Ohshima T, Gilmore EC, Longenecker G, Jacobowitz DM, Brady RO, Herrup K, Kulkarni AB (1999) Migration defects of cdk5(−/−) neurons in the developing cerebellum is cell autonomous. J Neurosci 19:6017–6026
Osuga H, Osuga S, Wang F, Fetni R, Hogan MJ, Slack RS, Hakim AM, Ikeda JE, Park DS (2000) Cyclin-dependent kinases as a therapeutic target for stroke. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:10254–10259
Paglini G, Pigino G, Kunda P, Morfini G, Maccioni R, Quiroga S, Ferreira A, Caceres A (1998) Evidence for the participation of the neuron-specific CDK5 activator P35 during laminin-enhanced axonal growth. J Neurosci 18:9858–9869
Park DS, Farinelli SE, Greene LA (1996) Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases promote survival of post-mitotic neuronally differentiated PC12 cells and sympathetic neurons. J Biol Chem 271:8161–8169
Park DS, Levine B, Ferrari G, Greene LA (1997a) Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors and dominant negative cyclin dependent kinase 4 and 6 promote survival of NGF-deprived sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci 17:8975–8983
Park DS, Morris EJ, Greene LA, Geller HM (1997b) G1/S cell cycle blockers and inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases suppress camptothecin-induced neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 17:1256–1270
Park DS, Morris EJ, Stefanis L, Troy CM, Shelanski ML, Geller HM, Greene LA (1998) Multiple pathways of neuronal death induced by DNA-damaging agents, NGF deprivation, and oxidative stress. J Neurosci 18:830–840
Patrick GN, Zukerberg L, Nikolic M, de la Monte S, Dikkes P, Tsai LH (1999) Conversion of p35 to p25 deregulates Cdk5 activity and promotes neurodegeneration. Nature 402:615–622
Patzke H, Tsai LH (2002a) Calpain-mediated cleavage of the cyclin-dependent kinase-5 activator p39 to p29. J Biol Chem 277:8054–8060
Patzke H, Tsai LH (2002b) Cdk5 sinks into ALS. Trends Neurosci 25:8–10
Pritchard C, McMahon M (1997) Raf revealed in life-or-death decisions. Nat Genet 16:214–215
Qi Z, Huang QQ, Lee KY, Lew J, Wang JH (1995) Reconstitution of neuronal Cdc2-like kinase from bacteria-expressed Cdk5 and an active fragment of the brain-specific activator. Kinase activation in the absence of Cdk5 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 270:10847–10854
Rashid T, Banerjee M, Nikolic M (2001) Phosphorylation of Pak1 by the p35/Cdk5 kinase affects neuronal morphology. J Biol Chem 276:49043–49052
Saito K, Elce JS, Hamos JE, Nixon RA (1993) Widespread activation of calcium-activated neutral proteinase (calpain) in the brain in Alzheimer disease: a potential molecular basis for neuronal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:2628–2632
Sharma P, Veeranna, Sharma M, Amin ND, Sihag RK, Grant P, Ahn N, Kulkarni AB, Pant HC (2002) Phosphorylation of MEK1 by cdk5/p35 down-regulates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 277:528–534
Sun D, Leung CL, Liem RK (1996) Phosphorylation of the high molecular weight neurofilament protein (NF-H) by Cdk5 and p35. J Biol Chem 271:14245–14251
Tanaka T, Veeranna, Ohshima T, Rajan P, Amin ND, Cho A, Sreenath T, Pant HC, Brady RO, Kulkarni AB (2001) Neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity is critical for survival. J Neurosci 21:550–558
Tang D, Yeung J, Lee KY, Matsushita M, Matsui H, Tomizawa K, Hatase O, Wang JH (1995) An isoform of the neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) activator. J Biol Chem 270:26897–26903
Tsai LH, Delalle I, Caviness VS Jr, Chae T, Harlow E (1994) p35 is a neural-specific regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371:419–423
Van den Haute C, Spittaels K, Van Dorpe J, Lasrado R, Vandezande K, Laenen I, Geerts H, Van Leuven F (2001) Coexpression of human cdk5 and its activator p35 with human protein tau in neurons in brain of triple transgenic mice. Neurobiol Dis 8:32–44
White FJ, Cooper DC (2001) The vicious cyclin of addiction. Nat Med 7:416–417
Xiong Y, Zhang H, Beach D (1992) D type cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Cell 71:505–514
Zheng M, Leung CL, Liem RK (1998) Region-specific expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5) and its activators, p35 and p39, in the developing and adult rat central nervous system. J Neurobiol 35:141–159
Zheng TS, Hunot S, Kuida K, Flavell RA (1999) Caspase knockouts: matters of life and death. Cell Death Differ 6:1043–1053
Zukerberg LR, Patrick GN, Nikolic M, Humbert S, Wu CL, Lanier LM, Gertler FB, Vidal M, Van Etten RA, Tsai LH (2000) Cables links Cdk5 and c-Abl and facilitates Cdk5 tyrosine phosphorylation, kinase upregulation, and neurite outgrowth. Neuron 26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weishaupt, J.H., Neusch, C. & Bähr, M. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) and neuronal cell death. Cell Tissue Res 312, 1–8 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0703-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0703-7