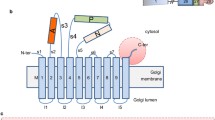
Abstract.
Slc30a4 is the fourth and last identified member of a mammalian proteins family presumably involved in the cellular transport of zinc, solute carrier family 30. The murine homologue of the human SLC30A4 gene has previously been investigated and found responsible for the lm, a phenotype due to zinc deficiency. According to the strong homology between mouse and human SLC30A4 coding sequences, and to the very similar clinical features encountered in the murine lm and in human acrodermatitis enteropathica, SLC30A4 has appeared to us to be a good candidate for acrodermatitis enteropathica. Here we detail the genomic structure of human SLC30A4 together with its localization on chromosome 15q15-q21. We also report the mutational analysis of human SLC30A4 in ten families with acrodermatitis enteropathica, which enabled us to exclude this gene from any involvement in the disorder of the patients examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Küry, S., Devilder, MC., Avet-Loiseau, H. et al. Expression pattern, genomic structure and evaluation of the human SLC30A4 gene as a candidate for acrodermatitis enteropathica. Hum Genet 109, 178–185 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390100539
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390100539