Abstract
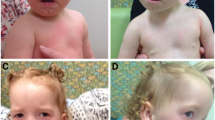
Patients with deletions in 22q13 are known to have phenotypic features that include normal or accelerated growth, large hands and feet, hypotonia, delayed psychomotor development and mild facial dysmorphism. To date, very few cases have been investigated by detailed molecular genetic analysis. We have analyzed three new patients with terminal deletions in 22q. We compared the cytogenetic observations with molecular data assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and an array of characterized bacterial artificial chromosome recombinants. The shortest region of deletion overlap is localized in 22q13.2–qter distal to the marker D22S94, but the telomeric repeat in the deleted chromosome appears to remain intact. When parental alleles were investigated in two of the three patients, the aberrant homolog was found to be of paternal origin in both cases. Although the deleted region still spans >20 cM, molecular analysis of additional patients and screening for new genes might help in elucidating candidate genes connected with the dysmorphisms defined by deletions of 22q13.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 August 1997 / Accepted: 27 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schröder, K., Schuffenhauer, S., Seidel, H. et al. Deletion mapping by FISH with BACs in patients with partial monosomy 22q13. Hum Genet 102, 557–561 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050739
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050739