Abstract
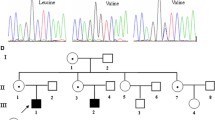
Alterations of the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) gene are responsible for X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA). Although mutations in various regions were reported mainly in the Caucasian population, correlation between the locations of mutation and the clinical phenotypes remains unclear. We report 12 abnormalities of the Btk gene found in 12 unrelated families out of 14 XLA families in Japan and their clinical features. We utilized Southern blotting and single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis. Gene rearrangement in the kinase domain was identified in two patients by Southern blotting. Seven point mutations, two small deletions, and one small insertion were detected by SSCP and sequencing. The SSCP analysis also provided information about the carriers in these families. We found some clinical heterogeneity in the affected family members with the same gene mutation. Moreover, there is considerable inconsistency between the locations of gene aberrations and the immunological phenotypes. Some patients with a nonsense mutation, which may result in the lack of kinase domain, have detectable B cells and immunoglobulins. These identified alterations will provide valuable clues to the Btk protein function and the pathogenesis of XLA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 May 1995 / Revised: 27 July 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, S., Iwata, T., Saito, M. et al. Mutations of the Btk gene in 12 unrelated families with X-linked agammaglobulinemia in Japan. Hum Genet 97, 424–430 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050066
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050066