Abstract.
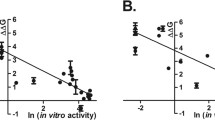
In order to better understand the disease-causing role of missense mutations found in the CYP21 gene from patients affected with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency, we built two three-dimensional (3D) models of human P450c21 using all known 3D structures of P450s. For each residue affected by a missense mutation, its location in the 3D structure and the putative changes in terms of biochemical properties brought about by the mutation were analyzed. Most of the severe alleles were found to affect residues located in functionally important regions of the molecule such as substrate recognition sites (SRS) or the heme region, whereas moderate mutations were mostly found in less crucial regions of the molecule. Thus, there is a good correlation between the 3D structure study and clinical data and mutagenesis experiments previously reported. In one case, however, the observed clinical severity of the mutation (E380D) did not match its expected severity deduced from the model, pointing to a potential functionally important region of the molecule. Our 3D human models provide a basic model for further studies of mutations responsible for 21-hydroxylase, and for identification of important residues involved in the specific activity of the enzyme.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mornet, E., Gibrat, JF. A 3D model of human P450c21: study of the putative effects of steroid 21-hydroxylase gene mutations. Hum Genet 106, 330–339 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000262
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000262